| [1] |
詹希旎, 李白杨. 生成式人工智能(GAI)背景下的数智可供性与认知带宽调节研究[J]. 图书与情报, 2024(1): 110-120.
|
|
ZHAN X N, LI B Y. Research on data intelligence affordance and cognitive bandwidth adjustment in the context of generative artificial intelligence(GAI)[J]. Library & information, 2024(1): 110-120.
|
| [2] |
李思睿, 侯婧羽. ChatGPT用户使用行为的影响因素研究[J]. 传播创新研究, 2025(1): 118-137, 231.
|
|
LI S R, HOU J Y. Research on the influencing factors of ChatGPT user behavior[J]. Communication innovation research, 2025(1): 118-137, 231.
|
| [3] |
罗国锋, 刘清生. ChatGPT赋能高校信息素养教育应用场景与实践研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(4): 91-101.
|
|
LUO G F, LIU Q S. Application scene and practice of ChatGPT empowering information literacy education[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2024, 36(4): 91-101.
|
| [4] |
吴佳桧, 傅海伦. 成就目标定向与学业成绩关系的元分析: 自我效能感、学习投入的中介作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(7): 1104-1131.
|
|
WU J H, FU H L. A meta-analysis of the relationship between achievement goal orientation and academic achievement: The mediating role of self-efficacy and student engagement[J]. Advances in psychological science, 2024, 32(7): 1104-1131.
|
| [5] |
范哲. 基于用户画像的数字原住民社会化媒体采纳意愿的阶段性分析[J]. 现代情报, 2017, 37(6): 99-106.
|
|
FAN Z. The stage analysis about digital natives' adoption intentions of social media based on person[J]. Journal of modern information, 2017, 37(6): 99-106.
|
| [6] |
SAHNA SREEN A H, MAJID M H M. Leveraging ChatGPT for personalized learning: A systematic review in educational settings[J]. Amandemen: Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Studies, 2024, 2(1): 63-78.
|
| [7] |
侯浩翔, 管培俊. 生成式人工智能时代的高校整体性治理[J]. 江苏高教, 2025(6): 1-10.
|
|
HOU H X, GUAN P J. Overall governance of universities in the era of generative artificial intelligence[J]. Jiangsu higher education, 2025(6): 1-10.
|
| [8] |
GAŠEVIĆ D, SIEMENS G, SADIQ S. Empowering learners for the age of artificial intelligence[J]. Computers and education: Artificial intelligence, 2023, 4: 100130.
|
| [9] |
陈昂轩, 贾积有. 可解释性人工智能有助于提升自适应学习的学习效果吗?: 基于29项实验与准实验的元分析[J]. 现代教育技术, 2024, 34(10): 92-102.
|
|
CHEN A X, JIA J Y. Does the explainable artificial intelligence help enhance the learning outcomes of adaptive learning? : Meta-analysis based on 29 experiments and quasi-experiments[J]. Modern educational technology, 2024, 34(10): 92-102.
|
| [10] |
SPARKS J R, KATZ I R, BEILE P M. Assessing digital information literacy in higher education: A review of existing frameworks and assessments with recommendations for next-generation assessment[J]. ETS research report series, 2016, 2016(2): 1-33.
|
| [11] |
WISMATH S L, ORR D. Collaborative learning in problem solving: A case study in metacognitive learning[J]. The Canadian journal for the scholarship of teaching and learning, 2015, 6(3): 10.
|
| [12] |
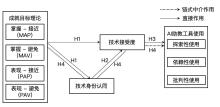
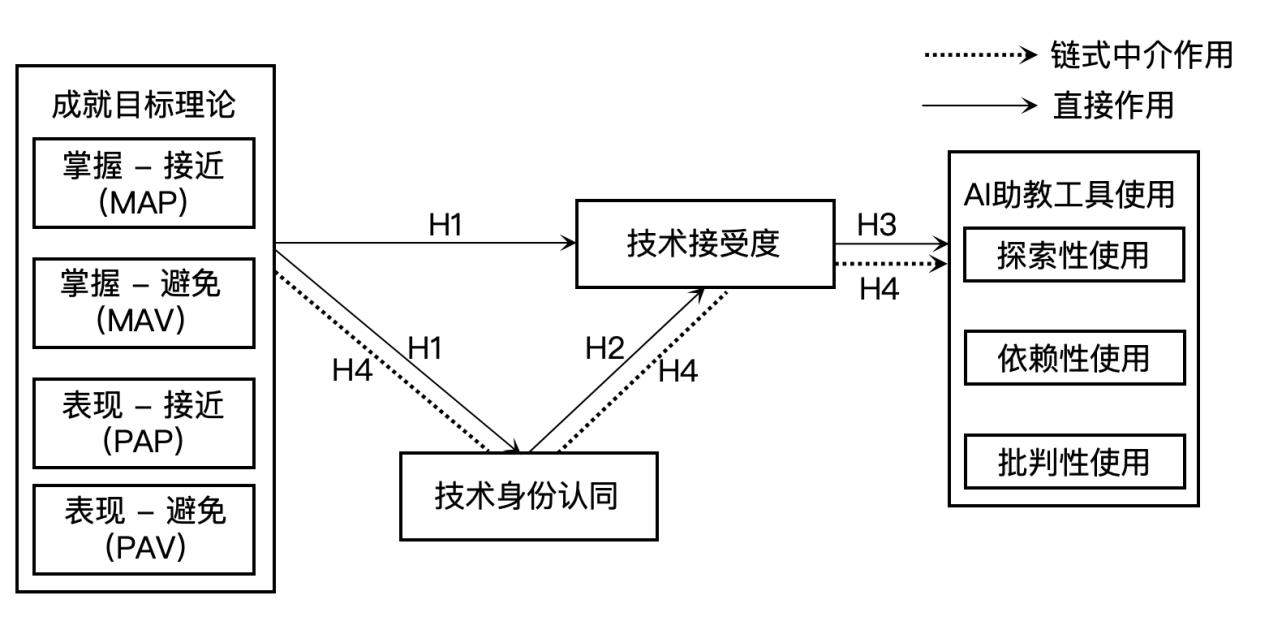
ELLIOT A J, MCGREGOR H A. A 2 × 2 achievement goal framework[J]. Journal of personality and social psychology, 2001, 80(3): 501-519.
|
| [13] |
SHARMA K, GIANNAKOS M, DILLENBOURG P. Eye-tracking and artificial intelligence to enhance motivation and learning[J]. Smart learning environments, 2020, 7(1): 13.
|
| [14] |
DAVIS F D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology[J]. MIS quarterly, 1989, 13(3): 319.
|
| [15] |
黄成立. 大学生AIGC利用现状与高校图书馆服务的实证分析[J]. 情报探索, 2025(2): 119-126.
|
|
HUANG C L. Empirical analysis of college students' utilization of AIGC and university library services[J]. Information research, 2025(2): 119-126.
|
| [16] |
郭亚军, 刘振阳, 郭一若, 等. AIGC大学生用户信息需求研究: 以ChatGPT为例[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(8): 34-44.
|
|
GUO Y J, LIU Z Y, GUO Y R, et al. Study on the information needs of college students using AIGC: Taking ChatGPT as an example[J]. Information science, 2024, 42(8): 34-44.
|
| [17] |
徐顺, 田潇湘. 基于TAM的在线学习平台用户使用意愿影响因素研究[J]. 中国教育信息化, 2020, 26(8): 78-85.
|
|
XU S, TIAN X X. Research on influencing factors of users' intention to use online learning platform based on TAM[J]. The Chinese journal of ICT in education, 2020, 26(8): 78-85.
|
| [18] |
张敏, 祝安, 张芳. 在线教育平台用户持续使用行为研究的影响因素[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2020, 40(5): 82-91.
|
|
ZHANG M, ZHU A, ZHANG F. Research on influencing factors of online education platform users' continuous use behavior[J]. Library tribune, 2020, 40(5): 82-91.
|
| [19] |
吴冰, 王毓芳. 移动健身APP持续使用的影响因素研究[J]. 软科学, 2019, 33(10): 87-92.
|
|
WU B, WANG Y F. Research on the influencing factors of continuous use of mobile fitness APP[J]. Soft science, 2019, 33(10): 87-92.
|
| [20] |
常桂林, 毕强, 费陆陆. 微信平台(公众号)用户持续使用意愿分析: 基于期望确认模型与媒介系统依赖理论[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2017(22): 85-92.
|
|
CHANG G L, BI Q, FEI L L. An analysis of users' continuance intention to use WeChat public platform: Based on the expectation confirmation model and media system dependency theory[J]. Research on library science, 2017(22): 85-92.
|
| [21] |
ALI I, WARRAICH N F, BUTT K. Acceptance and use of artificial intelligence and AI-based applications in education: A meta-analysis and future direction[J]. Information development, 2025, 41(3): 859-874.
|
| [22] |
HWANG Y, YI M Y. Predicting the use of web-based information systems: Intrinsic motivation and self-efficacy[J]. AMCIS 2002 Proceedings, 2002: 149.
|
| [23] |
CARTER M, GROVER V, et al. Me, myself, and I(T): Conceptualizing information technology identity and its implications[J]. MIS quarterly, 2015, 39(4): 931-957.
|
| [24] |
CARTER M, PETTER S, GROVER V, et al. Information technology identity: A key determinant of IT feature and exploratory usage[J]. MIS quarterly, 2020, 44(3): 983-1021.
|
| [25] |
OGBANUFE O, GERHART N. The mediating influence of smartwatch identity on deep use and innovative individual performance[J]. Information systems journal, 2020, 30(6): 977-1009.
|
| [26] |
CHEN K, Alan Hoi Shou Chan. Gerontechnology acceptance by elderly Hong Kong Chinese: A senior technology acceptance model (STAM) [J]. Ergonomics, 2014, 57(5): 635-652.
|
| [27] |
SUNDAR S S, BELLUR S, OH J, et al. Theoretical importance of contingency in human-computer interaction[J]. Communication research, 2016, 43(5): 595-625.
|
| [28] |
GUALTIERI L, RAUCH E, VIDONI R. Emerging research fields in safety and ergonomics in industrial collaborative robotics: A systematic literature review[J]. Robotics and computer-integrated manufacturing, 2021, 67: 101998.
|
| [29] |
DECI E L, RYAN R M. The "what" and "why" of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior[J]. Psychological inquiry, 2000, 11(4): 227-268.
|
| [30] |
GILLIER T, PIAT G. Exploring over: The presumed identity of emerging technology[J]. Creativity and innovation management, 2011, 20(4): 238-252.
|
| [31] |
VENKATESH, THONG, XU. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology[J]. MIS quarterly, 2012, 36(1): 157.
|
| [32] |
PINTRICH P R. Multiple goals, multiple pathways: The role of goal orientation in learning and achievement[J]. Journal of educational psychology, 2000, 92(3): 544-555.
|
| [33] |
VENKATESH V, DAVIS F D. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies[J]. Management science, 2000, 46(2): 186-204.
|
| [34] |
BLISS J, OGBORN J. Tools for exploratory learning: A research programme[J]. Journal of computer assisted learning, 1989, 5(1): 37-50.
|
| [35] |
HUANG C-W, COLEMAN M, GACHAGO D, et al. Using ChatGPT to encourage critical AI literacy skills and for assessment in higher education[M]//ICT Education. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2023: 105-118.
|
| [36] |
PRATIWI H, RIWANDA A, HASRUDDIN H, et al. Transforming learning or creating dependency teachers perspectives and barriers to AI integration in education[J]. Journal of pedagogical research, 2025: 2.
|
| [37] |
HAIR J F, RISHER J J, SARSTEDT M, et al. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM[J]. European business review, 2019, 31(1): 2-24.
|
| [38] |
NUNNALLY J C. Psychometric theory: 25 years ago and now[J]. Educational researcher, 1975, 4(10): 7-21.
|
| [39] |
FORNELL C, LARCKER D F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error[J]. Journal of marketing research, 1981, 18(1): 39.
|
| [40] |
PREACHER K J, HAYES A F. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models[J]. Behavior research methods, 2008, 40(3): 879-891.
|
| [41] |
刘琼, 刘星, 刘桂锋. “人工智能+高等教育”应用场景下的AI素养框架研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(8): 43-55.
|
|
LIU Q, LIU X, LIU G F. Framework of AI literacy for multi-role capabilities in future education: Based on typical cases of "AI+Higher education" application scenarios[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2024, 36(8): 43-55.
|
| [42] |
李白杨, 唐昆. AIGC背景下全民数字素养教育的内涵变革与应对策略[J]. 图书与情报, 2024(3): 32-39.
|
|
LI B Y, TANG K. Connotation change and countermeasures of digital literacy education for all in the context of AIGC[J]. Library & information, 2024(3): 32-39.
|
| [43] |
赵一鸣, 郑乔治, 沈校亮. 虚拟数字人对用户在线学习效果的影响研究[J]. 现代情报, 2025, 45(1): 81-96.
|
|
ZHAO Y M, ZHENG Q Z, SHEN X L. Research on the influence of virtual digital human on users' online learning performance[J]. Journal of modern information, 2025, 45(1): 81-96.
|