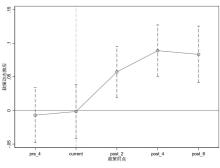
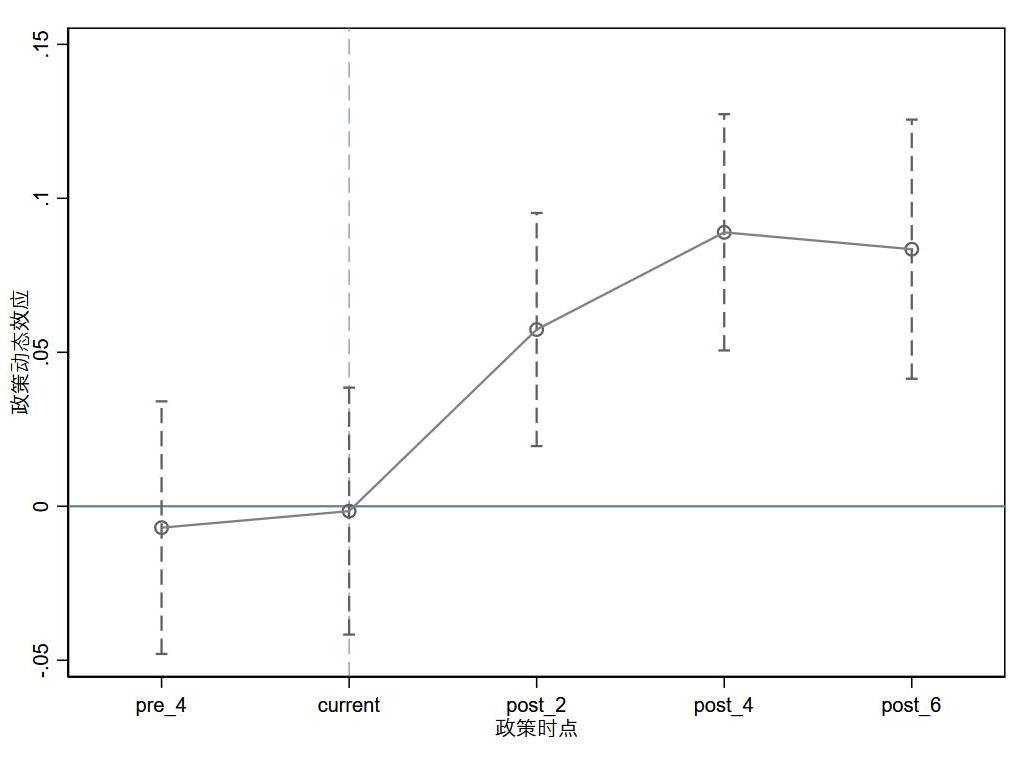
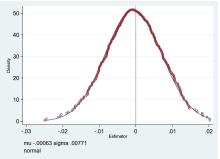
| [1] |
中国网信办. 2024年数字乡村发展工作要点[EB/OL]. [2024-05-15]. .
|
| [2] |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中共中央国务院关于学习运用“千村示范、万村整治”工程经验有力有效推进乡村全面振兴的意见[EB/OL]. [2024-02-03]. .
|
| [3] |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中共中央国务院关于进一步深化农村改革扎实推进乡村全面振兴的意见[EB/OL]. [2024-02-23]. .
|
| [4] |
陈昕, 胡友, 祁春节. 互联网使用对农户家庭支出的影响研究: 兼顾生产和消费两个维度[J]. 调研世界, 2022(5): 72-80.
|
|
CHEN X, HU Y, QI C J. Research on the influence of Internet use on rural household expenditure: Based on productive investment and daily consumption[J]. The world of survey and research, 2022(5): 72-80.
|
| [5] |
KONGAUT C, BOHLIN E. Investigating mobile broadband adoption and usage: A case of smartphones in Sweden[J]. Telematics and informatics, 2016, 33(3): 742-752.
|
| [6] |
JI L, WHITACRE B. Estimating willingness-to-pay for broadband attributes among low-income consumers: Results from two FCC lifeline pilot projects[J]. Telecommunications policy, 2017, 41(9): 769-780.
|
| [7] |
刘顿. 数字经济时代美好生活消费的功能价值及实践向度[J]. 社会科学家, 2022(2): 79-87.
|
|
LIU D. Functional value and practical dimension of good life consumption in digital economy era[J]. Social scientist, 2022(2): 79-87.
|
| [8] |
李国健. 数字化时代下的新消费主义批判: 存在形态、生成机制及应对策略[J]. 中南大学学报(社会科学版), 2024, 30(4): 158-165.
|
|
LI G J. Critique of new consumerism in the digital era: Existence forms, generation mechanisms, and response strategies[J]. Journal of central south university (social sciences), 2024, 30(4): 158-165.
|
| [9] |
曾亿武, 孙文策, 李丽莉, 等. 数字鸿沟新坐标: 智慧城市建设对城乡收入差距的影响[J]. 中国农村观察, 2022(3): 165-184.
|
|
ZENG Y W, SUN W C, LI L L, et al. A new coordinate of digital divide: The impact of smart city construction on urban-rural income gap[J]. China rural survey, 2022(3): 165-184.
|
| [10] |
何宜庆, 熊子怡, 张科, 等. 数字经济发展、非农就业与农民增收[J]. 统计与决策, 2023, 39(16): 111-115.
|
|
HE Y Q, XIONG Z Y, ZHANG K, et al. Development of digital economy, non-agricultural employment and increasing farmers' income[J]. Statistics & decision, 2023, 39(16): 111-115.
|
| [11] |
魏下海, 韦庆芳. 通往农村共富之路: 网络基础设施建设与相对贫困缓解[J]. 统计研究, 2023, 40(6): 134-144.
|
|
WEI X H, WEI Q F. The road to common prosperity in rural areas: Network infrastructure construction and the alleviation of relative poverty[J]. Statistical research, 2023, 40(6): 134-144.
|
| [12] |
KATZ R, CALLORDA F. Accelerating the development of Latin American digital ecosystem and implications for broadband policy[J]. Telecommunications policy, 2018, 42(9): 661-681.
|
| [13] |
STOCKER V, WHALLEY J. Speed isn't everything: A multi-criteria analysis of the broadband consumer experience in the UK[J]. Telecommunications policy, 2018, 42(1): 1-14.
|
| [14] |
刘涛, 伍骏骞. 数字金融与农户消费: 基于中国家庭金融调查数据的经验分析[J]. 农业技术经济, 2023(2): 111-128.
|
|
LIU T, WU J Q. Digital finance and farmers’ consumption: An empirical analysis based on the data of China household finance survey[J]. Journal of agrotechnical economics, 2023(2): 111-128.
|
| [15] |
范丹, 李琴. 金融素养对农户消费结构的影响: 基于第三方支付的中介机制分析[J]. 农村金融研究, 2023(3): 36-46.
|
|
FAN D, LI Q. The impact of financial literacy on the consumption structure of rural households: The analysis of intermediary mechanism based on third-party payment[J]. Rural finance research, 2023(3): 36-46.
|
| [16] |
彭千芮, 黄序阳. 社会保障安全网何以提升家庭消费?[J]. 消费经济, 2024, 40(4): 61-72.
|
|
PENG Q R, HUANG X Y. How does the social security safety net enhance household consumption?[J]. Consumer economics, 2024, 40(4): 61-72.
|
| [17] |
万建香, 汪亮. 数字乡村发展对农村家庭消费升级的影响[J]. 消费经济, 2024, 40(4): 87-102.
|
|
WAN J X, WANG L. The impact of digital village development on rural households' consumption upgrading[J]. Consumer economics, 2024, 40(4): 87-102.
|
| [18] |
董翀. 数字金融使用与农户消费升级[J]. 农村金融研究, 2023(3): 26-35.
|
|
DONG C. Digital finance using and farmers' consumption upgrading[J]. Rural finance research, 2023(3): 26-35.
|
| [19] |
马彪, 张琛, 郭军, 等. 电子商务会促进农户家庭的消费吗? : 基于“电子商务进农村综合示范”项目的准自然实验研究[J]. 经济学(季刊), 2023, 23(5): 1846-1864.
|
|
MA B, ZHANG C, GUO J, et al. Does E-commerce increase the consumption of rural households? : A quasi-experiment of "national rural E-commerce comprehensive demonstration policy"[J]. China economic quarterly, 2023, 23(5): 1846-1864.
|
| [20] |
刘导波, 张思麒. 数字经济赋能居民消费: 理论机制与微观证据[J]. 消费经济, 2022, 38(1): 72-82.
|
|
LIU D B, ZHANG S Q. The digital economy promotes the consumption of residents: Theoretical mechanism and micro evidence[J]. Consumer economics, 2022, 38(1): 72-82.
|
| [21] |
张诚, 翁希演. 电子商务进农村综合示范政策实施缩小了农户消费差距吗[J]. 中国农村观察, 2024(2): 46-68.
|
|
ZHANG C, WENG X Y. Does the national rural E-commerce comprehensive demonstration policy narrow the consumption gap among rural households[J]. China rural survey, 2024(2): 46-68.
|
| [22] |
李军, 李敬. 数字赋能与老年消费: 基于“宽带中国”战略的准自然实验[J]. 湘潭大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2021, 45(2): 83-90.
|
|
LI J, LI J. Digital empowerment and elderly consumption: A quasi-natural experiment based on "broadband China" strategy[J]. Journal of Xiangtan University (philosophy and social sciences), 2021, 45(2): 83-90.
|
| [23] |
尹志超, 吴子硕, 严雨. 数字经济能激发农村家庭消费活力吗?[J]. 经济管理, 2023, 45(12): 5-25.
|
|
YIN Z C, WU Z S, YAN Y. Can digital economy stimulate rural household consumption vitality?[J]. Business and management journal, 2023, 45(12): 5-25.
|
| [24] |
陈华帅, 马伟, 毛璐璐. 网络基础设施建设与家庭旅游消费: 来自“宽带中国”试点的证据[J]. 消费经济, 2024, 40(3): 88-100.
|
|
CHEN H S, MA W, MAO L L. Network infrastructure construction and family tourism consumption: Evidence from the "broadband China" pilot[J]. Consumer economics, 2024, 40(3): 88-100.
|
| [25] |
张杰, 魏振琪. 数字经济能否驱动家庭消费低碳转型? : 基于中国家庭追踪调查的经验证据[J]. 现代财经(天津财经大学学报), 2023, 43(9): 3-19.
|
|
ZHANG J, WEI Z Q. Can the digital economy drive the low-carbon transformation of household consumption? Empirical evidence based on CFPS[J]. Modern finance and economics-Journal of Tianjin University of finance and economics, 2023, 43(9): 3-19.
|
| [26] |
曾世宏, 吴金龙. 数字鸿沟如何影响居民消费结构: 基于可行能力视角的CFPS微观证据[J]. 延边大学学报(社会科学版), 2024, 57(3): 59-72, 141-142.
|
|
ZENG S H, WU J L. Digital divide's impacts on residents' consumption structure: Based on micro evidence of CFPS from the feasible capability perspective[J]. Journal of Yanbian University (social sciences), 2024, 57(3): 59-72, 141-142.
|
| [27] |
王彦芳, 王恺涛, 陈则霖, 等. 数字鸿沟对家庭消费相对剥夺的加剧效应研究[J]. 西部论坛, 2023, 33(5): 36-51.
|
|
WANG Y F, WANG K T, CHEN Z L, et al. The aggravating effect of digital divide on relative deprivation of household consumption[J]. West forum, 2023, 33(5): 36-51.
|
| [28] |
杨碧云, 王艺璇, 易行健, 等. “数字鸿沟”是否抑制了居民消费?: 来自中国家庭金融调查的微观证据[J]. 南开经济研究, 2023(3): 95-112.
|
|
YANG B Y, WANG Y X, YI X J, et al. Whether or not the "digital divide" has inhibited household consumption-micro evidence from the China household finance survey[J]. Nankai economic studies, 2023(3): 95-112.
|
| [29] |
黄漫宇, 窦雪萌. 城乡数字鸿沟会阻碍农村居民消费结构升级吗? : 基于中国家庭追踪调查(CFPS)数据的分析[J]. 经济问题探索, 2022(9): 47-64.
|
|
HUANG M Y, DOU X M. Will the urban-rural digital divide hinder the upgrading of rural residents' consumption structure: Analysis based on China family panel studies(CFPS)data[J]. Inquiry into economic issues, 2022(9): 47-64.
|
| [30] |
王修华, 赵亚雄. 数字金融发展是否存在马太效应? : 贫困户与非贫困户的经验比较[J]. 金融研究, 2020(7): 114-133.
|
|
WANG X H, ZHAO Y X. Does the Matthew effect exist in digital finance development? empirical evidence from poor and non-poor households[J]. Journal of financial research, 2020(7): 114-133.
|
| [31] |
CITONI B, FIORANELLI F, IMRAN M A, et al. Internet of things and LoRaWAN-enabled future smart farming[J]. IEEE Internet of things magazine, 2019, 2(4): 14-19.
|
| [32] |
王胜, 余娜, 付锐. 数字乡村建设: 作用机理、现实挑战与实施策略[J]. 改革, 2021(4): 45-59.
|
|
WANG S, YU N, FU R. Digital rural construction: Action mechanism, realistic challenge and implementation strategy[J]. Reform, 2021(4): 45-59.
|
| [33] |
张蔚文, 李学文. 城乡一体化路径的理论探析: 从商品实体交易时代到电子商务时代[J]. 中共浙江省委党校学报, 2016, 32(4): 90-98.
|
|
ZHANG W /Y)W, LI X W. Theoretical analysis on the path of urban-rural integration-from the era of commodity entity transaction to the era of e-commerce[J]. Journal of Zhejiang party school of CPC, 2016, 32(4): 90-98.
|
| [34] |
张勋, 万广华, 张佳佳, 等. 数字经济、普惠金融与包容性增长[J]. 经济研究, 2019, 54(8): 71-86.
|
|
ZHANG X, WAN G H, ZHANG J J, et al. Digital economy, financial inclusion, and inclusive growth[J]. Economic research journal, 2019, 54(8): 71-86.
|
| [35] |
程名望, 张家平. 新时代背景下互联网发展与城乡居民消费差距[J]. 数量经济技术经济研究, 2019, 36(7): 22-41.
|
|
CHENG M W, ZHANG J P. Internet development and consumption gap between urban and rural residents in the New Era of China[J]. The journal of quantitative & technical economics, 2019, 36(7): 22-41.
|
| [36] |
杨柳, 万江红. “廉价的高品位”: 农户清洁能源消费中的家庭禀赋与接近效应[J]. 华中农业大学学报(社会科学版), 2022(2): 131-145.
|
|
YANG L, WAN J H. "Cheap high-quality consumption": Household endowment and proximity effect on farmers' clean energy consumption[J]. Journal of Huazhong agricultural university (social sciences edition), 2022(2): 131-145.
|
| [37] |
夏玉莲, 张园. 家庭禀赋对农民家庭收入的影响分析: 基于1188户农户的实证分析[J]. 农林经济管理学报, 2018, 17(4): 427-433.
|
|
XIA Y L, ZHANG Y. Influence of family endowment on farming households' income: An empirical analysis based on 1188 households[J]. Journal of agro-forestry economics and management, 2018, 17(4): 427-433.
|
| [38] |
王子豪, 贾铖, 赵伟. 乡村数字基础设施与共同富裕: 基于“宽带乡村”试点工程和电信普遍服务试点项目的证据[J]. 世界农业, 2025(1): 103-115.
|
|
WANG Z H, JIA C, ZHAO W. Rural digital infrastructure and common prosperity: Evidence based on the pilot project of "broadband countryside" and the pilot project of universal telecommunication service[J]. World agriculture, 2025(1): 103-115.
|
| [39] |
刘国强, 韩振, 李金锴. 信贷获取对农村居民家庭消费结构升级的微观效应研究: 基于CFPS的实证分析[J]. 经济社会体制比较, 2024(5): 78-90.
|
|
LIU G Q, HAN Z, LI J K. Examining the micro effects of credit access on the upgrading of rural household consumption structures: An empirical analysis using CFPS data[J]. Comparative economic & social systems, 2024(5): 78-90.
|
| [40] |
尹志超, 吴子硕. 电商下乡能缩小农村家庭消费不平等吗: 基于“电子商务进农村综合示范”政策的准自然实验[J]. 中国农村经济, 2024(3): 61-85.
|
|
YIN Z C, WU Z S. Can E-commerce going to the countryside reduce rural household consumption inequality? A quasi-natural experiment based on the "comprehensive demonstration of E-commerce going to rural areas" policy[J]. Chinese rural economy, 2024(3): 61-85.
|
| [41] |
贺达, 顾江. 互联网对农村居民消费水平和结构的影响: 基于CFPS数据的PSM实证研究[J]. 农村经济, 2018(10): 51-57.
|
|
HE D, GU J. The influence of Internet on the consumption level and structure of rural residents: An empirical study of PSM based on CFPS data[J]. Rural economy, 2018(10): 51-57.
|
| [42] |
赖娟, 罗继美, 唐凡, 等. “保险+期货”试点能否促进农业产业规模化: 基于全国146个县域经济数据的证据[J]. 金融与经济, 2024(7): 73-84, 94.
|
|
LAI J, LUO J M, TANG F, et al. Whether the "insurance + futures"pilot can promote the scale of the agricultural industry: Evidence based on economic data from 146 counties across the country[J]. Finance and economy, 2024(7): 73-84, 94.
|
| [43] |
牛子恒, 崔宝玉. 网络基础设施建设与大气污染治理: 来自“宽带中国”战略的准自然实验[J]. 经济学报, 2021, 8(4): 153-180.
|
|
NIU Z H, CUI B Y. Network infrastructure construction and air pollution control: A quasi-natural experiment from the "Broadband China"[J]. China journal of economics, 2021, 8(4): 153-180.
|
| [44] |
王琴, 丁可可, 雷俐, 等. 数字基础设施、要素配置效率与城乡融合发展[J/OL]. 调研世界, 2024: 1-11. .
|
|
WANG Q, DING K K, LEI L, et al. Digital infrastructure, factor allocation efficiency and urban-rural integration development[J/OL]. The world of survey and research, 2024: 1-11. .
|
| [45] |
WELCH F. Education in production[J]. Journal of political economy, 1970, 78(1): 35-59.
|