| 1 |
赵瑞雪, 李甜, 关陟昊, 等. 知识服务与新质生产力: 双向赋能机制与实践路径[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(2): 4-14.
|
|
ZHAO R X, LI T, GUAN Z H, et al. Bidirectional empowerment between knowledge service and new quality productive forces theoretical interpretation and practical path[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2024, 36(2): 4-14.
|
| 2 |
张晓林. AI赋能的P4ST决策智能分析: 寻找知识服务的新质生产力[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2024, 8(3): 1-9.
|
|
ZHANG X L. AI-empowered policy for science & technology decision intelligence - Developing new quality productive forces for knowledge services[J]. Data analysis and knowledge discovery, 2024, 8(3): 1-9.
|
| 3 |
张智雄. 构建支持智能化科研(AI4S)的科技文献知识底座[C]. 上海: 第七届未来智慧图书馆发展论坛暨第二十届数智图书馆前沿问题高级研讨会, 2024.
|
| 4 |
赵瑞雪. AI4S时代知识服务的变革与应对[C]. 乌鲁木齐: 中国图书馆学会专业图书馆分会2024年会, 2024.
|
| 5 |
钱力, 刘志博, 胡懋地, 等. AI就绪的科技情报数据资源建设模式研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(3): 32-45.
|
|
QIAN L, LIU Z B, HU M D, et al. Construction model of AI-ready for scientific and technological intelligence data resources[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2024, 36(3): 32-45.
|
| 6 |
范可昕, 鲜国建, 赵瑞雪, 等. 面向农作物种质资源智能化管控与应用的本体构建[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(3): 92-107.
|
|
FAN K X, XIAN G J, ZHAO R X, et al. Ontology construction for intelligent control and application of crop germplasm resources[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2024, 36(3): 92-107.
|
| 7 |
白如江, 陈启明, 张玉洁, 等. 基于ChatGPT+Prompt的专利技术功效实体自动生成研究[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2024, 8(4): 14-25.
|
|
BAI R J, CHEN Q M, ZHANG Y J, et al. Generating effectiveness entities of patent technology based on ChatGPT+Prompt[J]. Data analysis and knowledge discovery, 2024, 8(4): 14-25.
|
| 8 |
时宗彬, 朱丽雅, 乐小虬. 基于本地大语言模型和提示工程的材料信息抽取方法研究[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2024, 8(7): 23-31.
|
|
SHI Z B, ZHU L Y, LE X Q. Material information extraction based on local large language model and prompt engineering[J]. Data analysis and knowledge discovery, 2024, 8(7): 23-31.
|
| 9 |
袁虎声, 唐嘉乐, 赵洗尘, 等. ChatLib: 重构智慧图书馆知识服务平台[J]. 大学图书馆学报, 2024, 42(2): 72-80.
|
|
YUAN H S, TANG J L, ZHAO X C, et al. ChatLib: Revolutionizing the knowledge service platform of smart library[J]. Journal of academic libraries, 2024, 42(2): 72-80.
|
| 10 |
PRANAB S, AYUSH K S, SRIPARNA S, et al. A systematic survey of prompt engineering in large language models: techniques and applications[J/OL]. arXiv:2402.07927, 2024.
|
| 11 |
ZHANG H P, YU P S, ZHANG J. A systematic survey of text summarization: From statistical methods to large language models[J/OL]. arXiv:2406.11289, 2024.
|
| 12 |
ZHANG B, Extract SOH H., define, canonicalize: An LLM-based framework for knowledge graph construction[J/OL]. arXiv:2404.03868, 2024.
|
| 13 |
WANG Y, GUO Q, YAO W, et al. AutoSurvey: Large language models can automatically write surveys[J/OL]. arXiv:2406.10252, 2024.
|
| 14 |
ZHOU Y, LIU H, SRIVASTAV T, et al. Hypothesis generation with large language models[J/OL]. arXiv: 2404.04326v1, 2024.
|
| 15 |
HUANG X, LIU W, CHEN X, et al. Understanding the planning of LLM agents: A survey[J/OL]. arXiv: 2402.02716, 2024.
|
| 16 |
ZHOU R, CHEN L, YU K. Is LLM a reliable reviewer? A comprehensive evaluation of LLM on automatic paper reviewing tasks[C]. Turin, Italy: LREC-COLING 2024, 2024.
|
| 17 |
WANG Y, YANG C, LAN S, et al. Towards industrial foundation models: Framework, key issues and potential applications[C]. Tianjin: Proceedings of the 2024 27th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, 2024.
|
| 18 |
COSMAS A, CRUZ G, CUBELA S, et al. Digital twins and generative AI: A powerful pairing[EB/OL]. [2024-04-11].
|
| 19 |
JAUHIANNEN J. The metaverse: Innovations and generative AI[J]. International journal of innovation studies, 2024, 8(3): 262-272.
|
| 20 |
HIRABAYASHI S, JAIN R, JURKOVIC N, et al. Harvard undergraduate survey on generative AI[J/OL]. arXiv:2406.00833, 2024.
|
| 21 |
上海科技大学图书信息中心. 重点关注-AI在高校教学中的部分应用场景[R]. 一流高校改革发展动态快报, 2024-08.
|
| 22 |
YEE L, CHUI M, ROBERTS R. Why agents are the next frontier of generative AI[EB/OL]. [2024-07-24].
|
| 23 |
XI Z, CHEN W, GUO X, et al. The rise and potential of large language model based agents: A survey[J/OL]. arXiv: 2309.07864, 2023.
|
| 24 |
LU C, LU C, LANGE R T, et al. The AI scientist: Towards fully automated open-ended scientific discovery[J/OL]. arXiv: 2408.06292, 2024.
|
| 25 |
GUO T, CHEN X, WANG Y, et al. Large language model based multi-agents: A survey of progress and challenges[J/OL]. arXiv: 2402.01680, 2024.
|
| 26 |
REN S, CUI Z, SONG R, et al. Emergence of social norms in generative agent societies: Principles and architecture[J/OL]. arXiv: 2403.08251, 2024.
|
| 27 |
DUÉÑEZ-GUZMÁN E A, SADEDIN S, WANG J X, et al. A social path to human-like artificial intelligence[J]. Nature machine intelligence, 2023(5): 1181-1188.
|
| 28 |
LIN S, HUA W, LI L, et al. Battle agent: Multi-modal dynamic emulation on historical battles to complement historical analysis[J/OL]. arXiv: 2404.15532, 2024.
|
| 29 |
AI agent builders: A comparative analysis[EB/OL]. [2024-08-19].
|
| 30 |
20个国内AI Agent构建平台盘点[EB/OL]. [2024-08-14].
|
| 31 |
SAMIR J, JOHN S. 2024 state of edge AI report: Exploring the dynamic world of edge AI applications across industries[R/OL]. [2024-07-01].
|
| 32 |
LIU Y, CHEN W, BAI Y, et al. Aligning cyber space with physical world: A comprehensive survey on embodied AI[J/OL]. arXiv: 2407.06886, 2024.
|
| 33 |
祁晓亮. 时间、信息与人工智能: 从信息动力学角度看大模型的未来[J]. 物理, 2024(6): 357-367.
|
| 34 |
李国杰. 智能化科研(AI4R): 第五科研范式[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2024, 39(1): 1-9.
|
|
LI G J. AI4R: The fifth scientific research paradigm[J]. Bulletin of Chinese academy of sciences, 2024, 39(1): 1-9.
|
| 35 |
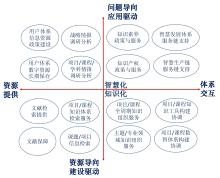
尹西明, 苏雅欣, 陈劲, 等. 场景驱动的创新: 内涵特征、理论逻辑与实践进路[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2022, 39(15): 1-10.
|
|
YIN X M, SU Y X, CHEN J, et al. Context-driven innovation: Connotation, theoretical logic and practical approach[J]. Science & technology progress and policy, 2022, 39(15): 1-10.
|
| 36 |
张晓林, 梁娜. 知识的智慧化、智慧的场景化、智能的泛在化——探索智慧知识服务的逻辑框架[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2023, 49(3): 4-18.
|
|
ZHANG X L, LIANG N. Knowledge is towards being wisdom, wisdom needs to be scenario-based, and intelligence can be ubiquitously embedded - Exploration of the logical framework of intelligent knowledge services[J]. Journal of library science in China, 2023, 49(3): 4-18.
|
| 37 |
李政道图书馆, 不只是图书馆[EB/OL]. [2024-09-03].
|
| 38 |
让阅读变得好玩, 上海图书馆变身“超好玩图书馆”[EB/OL]. [2024-08-19].
|
| 39 |
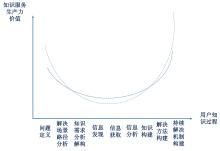
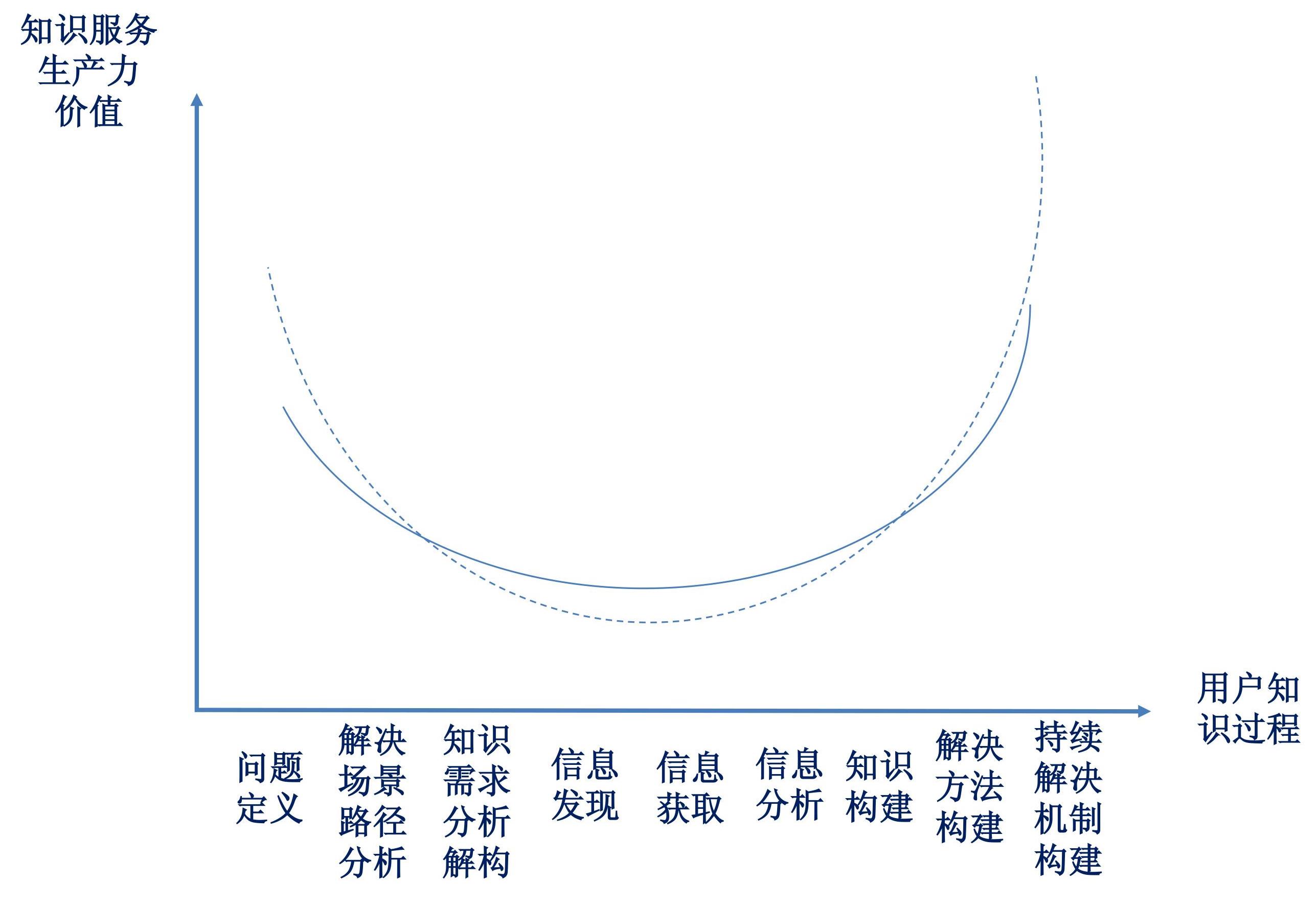
微笑曲线. 百度百科[EB/OL]. [2024-05-19]. 微笑曲线/10847621.
|
| 40 |
黄奇帆. 新质生产力的逻辑内涵与实施路径——在中共广东省委党校春季主体班上的讲话[EB/OL]. [2024-04-26].
|
| 41 |
AI in the service industry: Transforming customer experience & operational efficiency[EB/OL]. [2024-01-16].
|
| 42 |
CASWELL D. AI and journalism: What's next? [EB/OL]. [2023-09-19].
|
| 43 |
Gartner says AI ambition and AI-ready scenarios must be a top priority for CIOs for next 12-24 months[EB/OL]. [2023-11-06].
|
| 44 |
吴文, 王怡颖. 加快形成与新质生产力相适应的新型生产关系[N]. 北京日报, 2024.4.1.
|
| 45 |
张晓林. Library-Inside: AI赋能图书馆新质生产力的一种基础模型[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2024, 50(3): 4-16.
|
|
ZHANG X L. Library-inside: A foundation model for AI-empowered new quality productive forces for library services[J]. Journal of library science in China, 2024, 50(3): 4-16.
|
| 46 |
张晓林. Inside-Out & Outside-In: 图书馆服务社会高质量发展的组合模型[J/OL]. 图书馆杂志, 2024: 1-9.
|
|
ZHANG X L. Inside-Out & Outside-In: A combinatorial model for libraries' support of the high-quality development of the society[J/OL]. Library journal, 2024: 1-9.
|
| 47 |
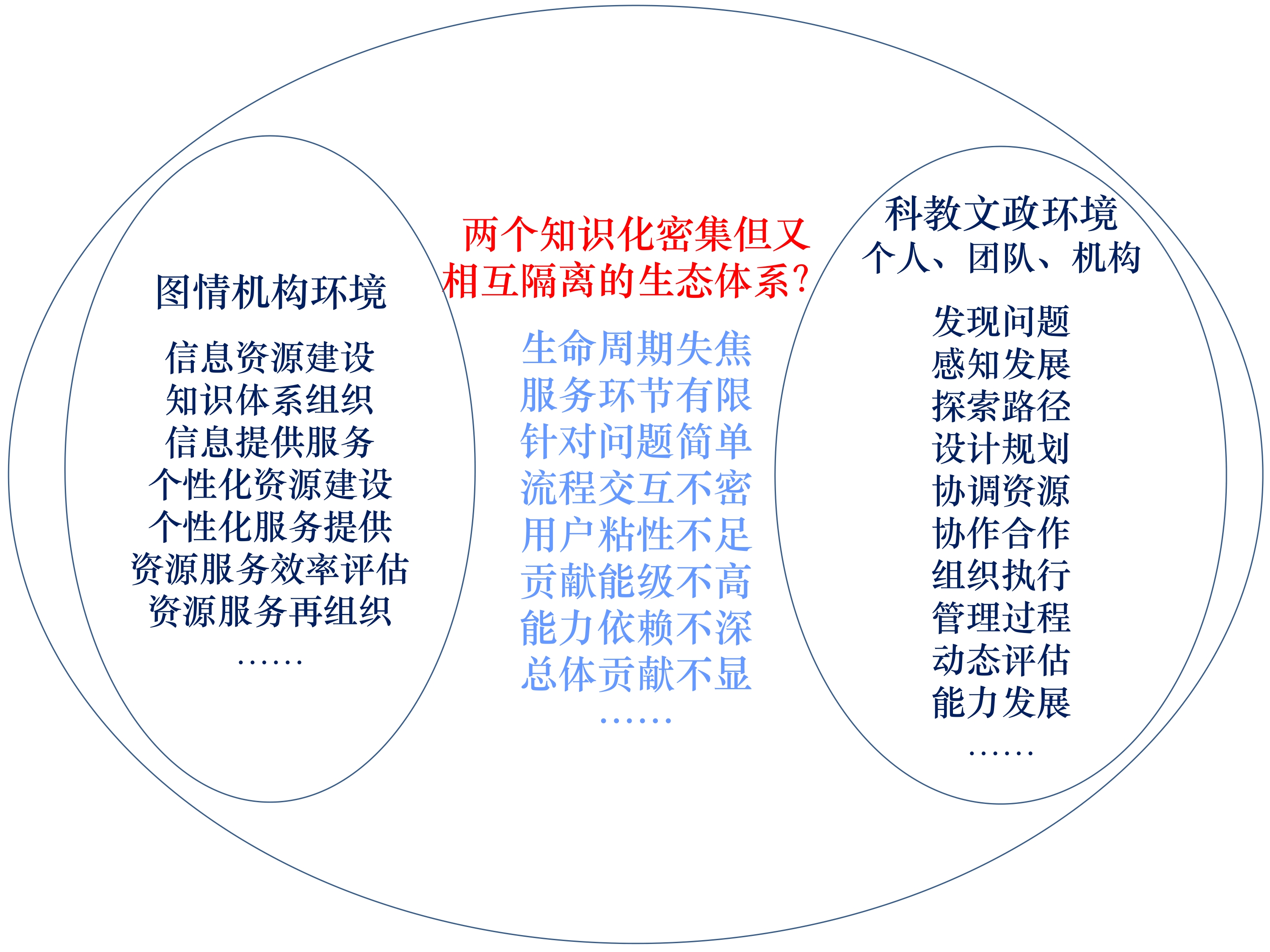
ABBATE T, CODINI A, AQUILANI B, et al. From knowledge ecosystems to capabilities ecosystems[J]. Journal of the knowledge economy, 2022(13): 290-304.
|
| 48 |
陈超. 全面阅读推广服务体系中图书馆的新认识与新担当[Z]. 宜昌: 2024中国图书馆年会, 2024.
|
| 49 |
意)罗伯托·维甘提. 第三种创新: 设计驱动式创新如何缔造新的竞争法则[M]. 戴莎, 译. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2014.
|
|
ROBERTO V. Design-driven innovation: Changing the rules of competition by radically innovating what things mean[M]. Beijing: China Renmin University Press, 2014.
|
| 50 |
刘涛. 美国敏捷作战运用概念内涵及运用浅析[EB/OL]. [2024-05-08].
|