| [1] |
HEAD B W. Reconsidering evidence-based policy: Key issues and challenges[J]. Policy and society, 2010, 29(2): 77-94.
|
| [2] |
杨开峰, 魏夏楠. 政府循证决策: 美国联邦政府的实践及启示[J]. 经济社会体制比较, 2021(3): 139-149.
|
|
YANG K F, WEI X N. Evidence-based policy making in government: The practice and implications of the U.S. federal government[J]. Comparative economic & social systems, 2021(3): 139-149.
|
| [3] |
武楷彪, 王溯, 朱相丽, 等. 日本支撑循证决策的科技情报数据资源建设与应用[J]. 图书情报工作, 2021, 65(22): 126-133.
|
|
WU K B, WANG S, ZHU X L, et al. Construction and application of S & T intelligence data resources supporting evidence-based policymaking in Japan[J]. Library and information service, 2021, 65(22): 126-133.
|
| [4] |
李晓轩, 杨可佳, 杨柳春. 基于证据的政策制定: 英国的实践与启示[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2013, 28(6): 740-749.
|
|
LI X X, YANG K J, YANG L C. Evidence-based policy making: The practice and enlightenment from the UK[J]. Bulletin of Chinese academy of sciences, 2013, 28(6): 740-749.
|
| [5] |
何莹, 孙巍, 马晓敏. 科技循证政策制定实践路径探索[J]. 图书情报工作, 2025, 69(2): 121-129.
|
|
HE Y, SUN W, MA X M. Exploring practical path of evidence-based policy making in science and technology[J]. Library and information service, 2025, 69(2): 121-129.
|
| [6] |
STRYDOM W F, FUNKE N, NIENABER S, et al. Evidence-based policymaking: A review[J]. South African journal of science, 2010, 106(5/6): 17-24.
|
| [7] |
张继亮. 循证政策: 政策证据的类型、整合与嵌入[J]. 社会科学, 2019(11): 39-47.
|
|
ZHANG J L. Evidence-based policy: The types, integration and embeddedness of policy evidence[J]. Journal of social sciences, 2019(11): 39-47.
|
| [8] |
姚清晨, 张颖. 基于循证理念的公共政策制定研究[J]. 四川行政学院学报, 2018(4): 27-32.
|
|
YAO Q C, ZHANG Y. Research on public policy making based on evidence-based concept[J]. Journal of Sichuan administration college, 2018(4): 27-32.
|
| [9] |
杨代福, 程曦. 基于证据的政策制定: 理论逻辑与制度框架[J]. 渭南师范学院学报, 2021, 36(1): 51-59.
|
|
YANG D F, CHENG X. Evidence-based policy making: Theoretical logic and institutional framework[J]. Journal of Weinan normal university, 2021, 36(1): 51-59.
|
| [10] |
DAVIES P. What is evidence-based education?[J]. British journal of educational studies, 1999, 47(2): 108-121.
|
| [11] |
LEVIN A. The cochrane collaboration[J]. Annals of internal medicine, 2001, 135(4): 309-312.
|
| [12] |
SCHUERMAN J, SOYDAN H, MACDONALD G, et al. The Campbell collaboration[J]. Research on social work practice, 2002, 12(2): 309-317.
|
| [13] |
郁俊莉, 姚清晨. 从数据到证据: 大数据时代政府循证决策机制构建研究[J]. 中国行政管理, 2020(4): 81-87.
|
|
YU J L, YAO Q C. From data to evidence: Research on the construction of evidence-based policy-making mechanism in the era of big data[J]. Chinese public administration, 2020(4): 81-87.
|
| [14] |
MOHER D, OLKIN I. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. A concern for standards[J]. JAMA, 1995, 274(24): 1962-1964.
|
| [15] |
CARTWRIGHT N, HARDIE J. Evidence-based policy: A practical guide to doing it better[M]. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2012.
|
| [16] |
PAWSON R. Evidence-based policy: The promise of "realist synthesis"[J]. Evaluation, 2002, 8(3): 340-358.
|
| [17] |
BACHE I. Evidence, Policy and wellbeing[M]. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, 2020.
|
| [18] |
田晨, 晏毅龙, 王勇, 等. 证据智能合成与分级: AutoMeta平台开发与验证[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2024, 24(4): 459-465.
|
|
TIAN C, YAN Y L, WANG Y, et al. Evidence intelligent synthesis and grading: Development and validation of AutoMeta[J]. Chinese journal of evidence-based medicine, 2024, 24(4): 459-465.
|
| [19] |
AFZAL M, HUSSAIN M, HAYNES R B, et al. Context-aware grading of quality evidences for evidence-based decision-making[J]. Health informatics journal, 2019, 25(2): 429-445.
|
| [20] |
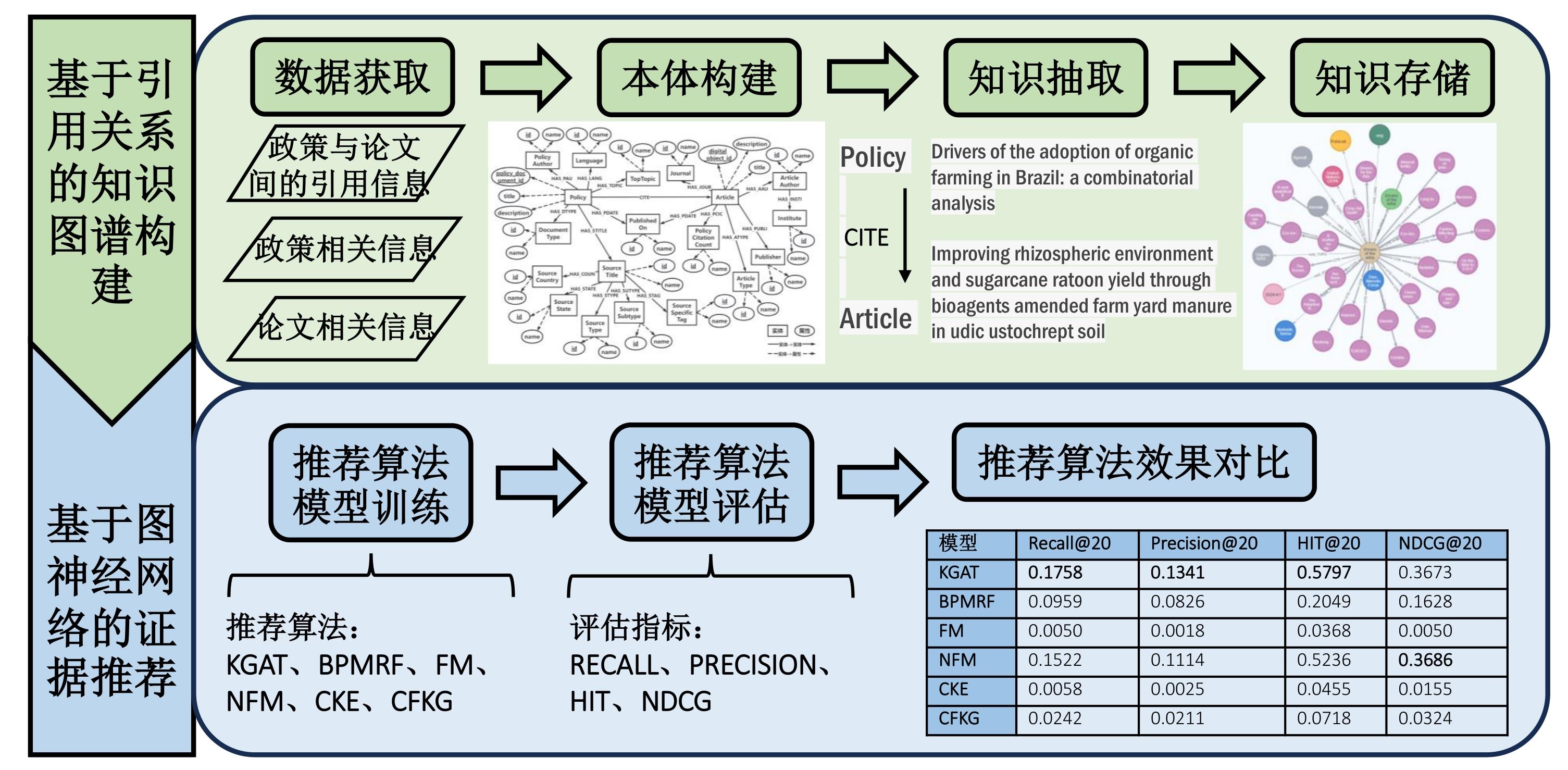
任超, 杨孟辉, 杨冠灿, 等. 基于知识图谱的循证政策中科学证据推荐研究: 以新冠肺炎疫情防控政策为例[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(2): 108-118.
|
|
REN C, YANG M H, YANG G C, et al. A research on the recommendation of scientific evidence in evidence-based policy based on knowledge graph: An example of the policies fighting on COVID-19[J]. Library and information service, 2023, 67(2): 108-118.
|
| [21] |
WANG X, HE X, CAO Y, et al. KGAT: Knowledge graph attention network for recommendation[C]// In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2019: 950-958.
|
| [22] |
RENDLE S, GANTNER Z, FREUDENTHALER C, et al. Fast context-aware recommendations with factorization machines[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Beijing, China: ACM, 2011: 635-644.
|
| [23] |
HE X N, CHUA T S. Neural factorization machines for sparse predictive analytics[C]//Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Shinjuku Tokyo Japan: ACM, 2017: 355-364.
|
| [24] |
ZHANG F Z, YUAN N J, LIAN D F, et al. Collaborative knowledge base embedding for recommender systems[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.San Francisco, California, USA: ACM, 2016: 353-362.
|
| [25] |
AI Q Y, AZIZI V, CHEN X, et al. Learning heterogeneous knowledge base embeddings for explainable recommendation[J]. Algorithms, 2018, 11(9): 137.
|

 ), 李周晶1,2, 马晓敏1,2
), 李周晶1,2, 马晓敏1,2
 ), LI Zhoujing1,2, MA Xiaomin1,2
), LI Zhoujing1,2, MA Xiaomin1,2