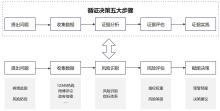
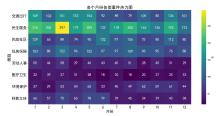
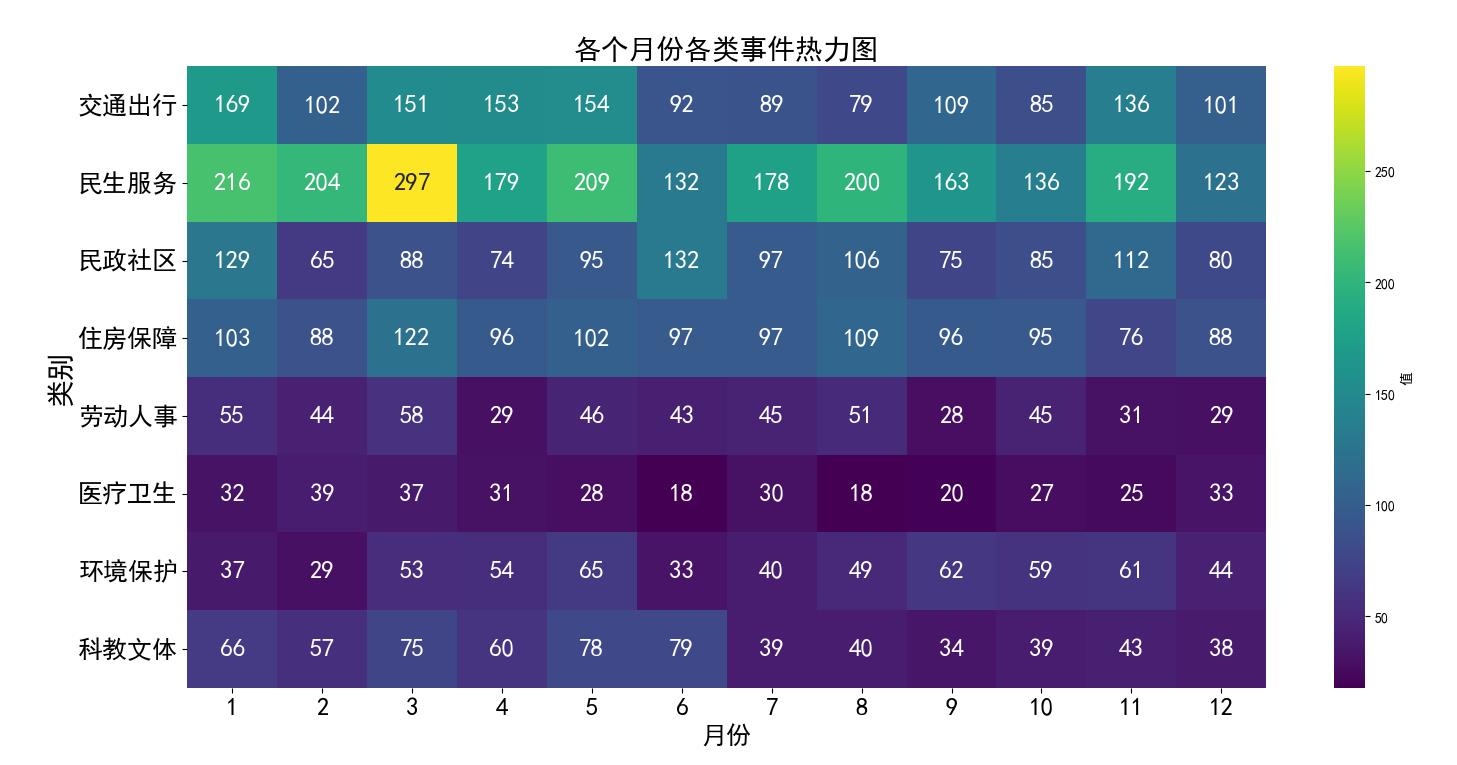
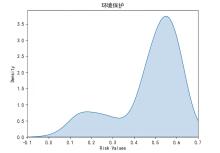
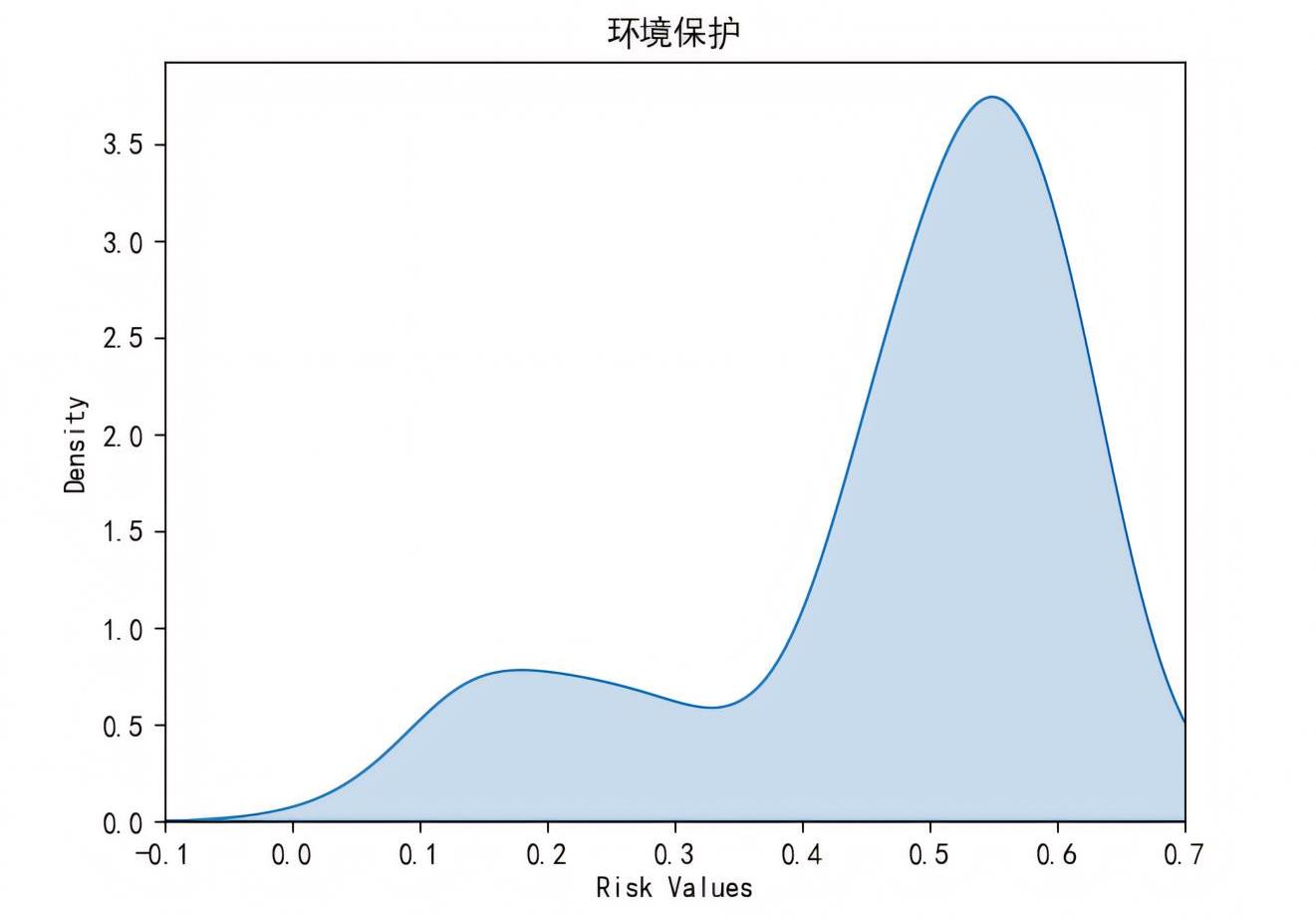
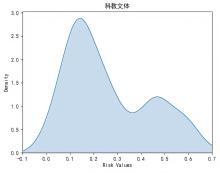
| 1 |
中国政府网. 国务院关于加强数字政府建设的指导意见[EB/OL]. [2024-03-15]. .
|
| 2 |
张莉曼, 吴鹏, 尹熙成, 等. 政民互动数据中公众诉求的故事化描述: 集成、重构与叙事[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2023, 46(4): 141-149.
|
|
ZHANG L M, WU P, YIN X Z, et al. Storytelling description of public appeal in government-to-citizen interaction data: Integration, reconstruction and narration[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2023, 46(4): 141-149.
|
| 3 |
马亮, 郑跃平, 张采薇. 政务热线大数据赋能城市治理创新: 价值、现状与问题[J]. 图书情报知识, 2021, 38(2): 4-12, 24.
|
|
MA L, ZHENG Y P, ZHANG C W. The big data empowering effect of government hotlines on city governance innovation: Value, status and issues[J]. Documentation, information & knowledge, 2021, 38(2): 4-12, 24.
|
| 4 |
张莉曼, 张向先, 孙绍丹. 分布式认知视角下政民互动数据的交互叙事研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(9): 53-62.
|
|
ZHANG L M, ZHANG X X, SUN S D. Research on interactive narrative of government-citizen interaction data from the perspective of distributed cognition[J]. Library and information service, 2023, 67(9): 53-62.
|
| 5 |
周霞, 王萍, 陈为东, 等. 政府开放数据用户认知图式联结模型——数据故事视角[J]. 情报资料工作, 2021, 42(4): 64-71.
|
|
ZHOU X, WANG P, CHEN W D, et al. Government open data user cognitive schematic connection model: From the perspective of data story[J]. Information and documentation services, 2021, 42(4): 64-71.
|
| 6 |
曹艳辉. “适度压力型”政民互动: 基于中部省级网络问政平台的数据分析[J]. 新闻与传播评论, 2023, 76(2): 70-81.
|
|
CAO Y H. Political interaction with "appropriate pressure": Large sample data analysis based on the central provincial online political platform[J]. Journalism & communication review, 2023, 76(2): 70-81.
|
| 7 |
贾改革. 政民互动中社会诉求主题挖掘和情感分析——基于人民网领导留言板的数据分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2023.
|
|
JIA G G. Social appeal theme mining and emotional analysis in the interaction between government and people - Based on the data analysis of people's daily online leadership message board[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2023.
|
| 8 |
HUBERT R B, ESTEVEZ E, MAGUITMAN A, et al. Analyzing and visualizing government-citizen interactions on twitter to support public policy-making[J]. Digital government: Research and practice, 2020, 1(2): 1-20.
|
| 9 |
BELKAHLA DRISS O, MELLOULI S, TRABELSI Z. From citizens to government policy-makers: Social media data analysis[J]. Government information quarterly, 2019, 36(3): 560-570.
|
| 10 |
孙倬, 赵红, 王宗水. 网络舆情研究进展及其主题关联关系路径分析[J]. 图书情报工作, 2021, 65(7): 143-154.
|
|
SUN Z, ZHAO H, WANG Z S. Analysis on the association and evolution path of Internet public opinion[J]. Library and information service, 2021, 65(7): 143-154.
|
| 11 |
杨柳, 罗文倩, 邓春林, 等. 基于灰色关联分析的舆情分级与预警模型研究[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(8): 28-34.
|
|
YANG L, LUO W Q, DENG C L, et al. Classification and early warning model of public opinion based on grey correlation analysis[J]. Information science, 2020, 38(8): 28-34.
|
| 12 |
武慧娟, 张海涛, 王尽晖, 等. 基于熵权法的网络舆情预警模糊综合评价模型研究[J]. 情报科学, 2018, 36(7): 58-61.
|
|
WU H J, ZHANG H T, WANG J H, et al. Research on the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model of online public opinion pre-warning based on entropy weight method[J]. Information science, 2018, 36(7): 58-61.
|
| 13 |
彭程, 祁凯, 黎冰雪. 基于SIR-EGM模型的复杂网络舆情传播与预警机制研究[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(3): 145-153.
|
|
PENG C, QI K, LI B X. Communication and early warning mechanism of public opinion in complex networks based on SIR-EGM model[J]. Information science, 2020, 38(3): 145-153.
|
| 14 |
李知谕, 杨柳, 邓春林. 基于弹幕与评论情感倾向的食品安全舆情预警研究[J]. 科技情报研究, 2022, 4(3): 33-45.
|
|
LI Z Y, YANG L, DENG C L. Public opinion early warning on food security based on sentiment of video bullet screen and comments[J]. Scientific information research, 2022, 4(3): 33-45.
|
| 15 |
GROUP E B M W. Evidence-based medicine. A new approach to teaching the practice of medicine[J]. JAMA, 1992, 268(17): 2420-2425.
|
| 16 |
刘瑞, 马海群. 基于循证决策的开放数据政策制定体系构建[J]. 现代情报, 2020, 40(8): 129-133.
|
|
LIU R, MA H Q. Construction of open data policy making system based on evidence-based decision making[J]. Journal of modern information, 2020, 40(8): 129-133.
|
| 17 |
马小亮, 樊春良. 基于证据的政策: 思想起源、发展和启示[J]. 科学学研究, 2015, 33(3): 353-362.
|
|
MA X L, FAN C L. The origin and development of "evidence-based policy"[J]. Studies in science of science, 2015, 33(3): 353-362.
|
| 18 |
NAM T, PARDO T A. Understanding municipal service integration: An exploratory study of 311 contact centers[J]. Journal of urban technology, 2014, 21(1): 57-78.
|
| 19 |
DAVIES P. What is evidence-based education?[J]. British journal of educational studies, 1999, 47(2): 108-121.
|
| 20 |
ROUSSEAU D M. Making evidence-based organizational decisions in an uncertain world[J]. Organizational dynamics, 2018, 47(3): 135-146.
|
| 21 |
魏景容. 大数据时代循证决策研究: 一个分析框架[J]. 中国科技论坛, 2020(7): 24-32.
|
|
WEI J R. Research on evidence-based decision making in the era of big data: An analytical framework[J]. Forum on science and technology in China, 2020(7): 24-32.
|
| 22 |
叶艳, 吴鹏. 循证决策视角下的患者健康咨询主题分析[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2022, 45(2): 198-203, 190.
|
|
YE Y, WU P. Topic analysis of patients' health consultation based on evidence-based decision-making theory[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2022, 45(2): 198-203, 190.
|
| 23 |
何玉仙. 大数据时代政府循证决策模式探究[J]. 信息系统工程, 2023(8): 120-123.
|
|
HE Y X. Research on evidence-based decision-making model of government in the era of big data[J]. China CIO news, 2023(8): 120-123.
|
| 24 |
CHEVALIER J A, MAYZLIN D. The effect of word of mouth on sales: Online book reviews[J]. Journal of marketing research, 2006, 43(3): 345-354.
|
| 25 |
范逢春. 国家治理现代化场域中的社会治理话语体系重构——基于话语分析的基本框架[J]. 行政论坛, 2018, 24(6): 109-115.
|
|
FAN F C. Reconstruction of social governance discourse system in the field of modernizing the state governance: Based on general framework of discourse analysis[J]. Administrative tribune, 2018, 24(6): 109-115.
|
| 26 |
王瑶. 网络问政平台中公众诉求表达对政府回应的影响研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2024.
|
|
WANG Y. Research on the influence of public appeal expression on the government response in the online politics platform[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2024.
|
| 27 |
赵国洪, 刘伟章. 我国政府网站政民互动模型及实证分析[J]. 情报杂志, 2012, 31(2): 195-202.
|
|
ZHAO G H, LIU W Z. Construction and empirical analysis of interactivity model for government websites in China[J]. Journal of intelligence, 2012, 31(2): 195-202.
|
| 28 |
詹承豫. 中国城市风险沟通决策的影响因素研究[J]. 治理研究, 2019, 35(5): 13-21.
|
|
ZHAN C Y. Research on the influencing factors of communication and decision about urban risk[J]. Governance studies, 2019, 35(5): 13-21.
|
| 29 |
邱文. 公众诉求事件关键数据的空间智能提取与分析[J]. 城市勘测, 2020(2): 27-30.
|
|
QIU W. Spatial intelligence extraction and analysis of key data of public appeal events[J]. Urban geotechnical investigation & surveying, 2020(2): 27-30.
|
| 30 |
张楠迪扬, 郑旭扬, 赵乾翔. 政府回应性: 作为日常治理的“全回应”模式——基于LDA主题建模的地方政务服务“接诉即办”实证分析[J]. 中国行政管理, 2023(3): 68-78.
|
|
ZHANG N, ZHENG X Y, ZHAO Q X. Government responsiveness: An all-response' pattern of daily governance - An empirical study of local government hotline appeals using latent dirichlet allocation(LDA)[J]. Chinese public administration, 2023(3): 68-78.
|
| 31 |
王东琪. 网络问政的舆情挖掘及引导研究——以河北省“领导留言板”为例[D]. 石家庄: 河北经贸大学, 2023.
|
|
WANG D Q. Research on public opinion mining and guidance of online politics - A case study of "leader message board" in Hebei Province[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Economics and Business, 2023.
|
| 32 |
梅潇, 查先进, 严亚兰. 智能推荐环境下移动社交媒体用户隐私风险感知影响机理研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(1): 57-64.
|
|
MEI X, ZHA X J, YAN Y L. Influencing mechanism of privacy risk perception in the context of mobile social media intelligent recommendation[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2024, 47(1): 57-64.
|
| 33 |
SAZZED S. BengSentiLex and BengSwearLex: Creating lexicons for sentiment analysis and profanity detection in low-resource Bengali language[J]. PeerJ computer science, 2021, 7: e681
|
| 34 |
曾子明, 孙守强, 李青青. 基于融合策略的突发公共卫生事件网络舆情多模态负面情感识别[J]. 情报学报, 2023, 42(5): 611-622.
|
|
ZENG Z M, SUN S Q, LI Q Q. Multimodal negative sentiment recognition in online public opinion during public health emergencies based on fusion strategy[J]. Journal of the China society for scientific and technical information, 2023, 42(5): 611-622.
|
| 35 |
臧雷振, 王栋, 仉佳璐. 社会科学研究中的敏感议题: 特征判断与应对方法[J]. 学习与探索, 2023(4): 36-42, 186.
|
|
ZANG L Z, WANG D, ZHANG J L. Sensitive issues in social science research: Judging features and handling methods[J]. Study & exploration, 2023(4): 36-42, 186.
|
| 36 |
王磊, 高茂庭. 基于CRITIC权与灰色关联的隐写分析算法综合评估[J]. 计算机工程, 2017, 43(4): 154-159.
|
|
WANG L, GAO M T. Comprehensive evaluation of steganography analysis algorithm based on CRITIC weight and grey relation[J]. Computer engineering, 2017, 43(4): 154-159.
|
| 37 |
夏立新, 杨元, 周鼎. “双一流”建设视阈下我国高校文献资源保障水平评价指标体系构建研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2022, 66(7): 57-65.
|
|
XIA L X, YANG Y, ZHOU D. Research on the construction of the evaluation index system of the document resource guarantee level in Chinese universities in "double first-class" construction view[J]. Library and information service, 2022, 66(7): 57-65.
|
| 38 |
苏州市行政审批局. “苏州12345”2023年度工作情况发布[EB/OL]. [2024-05-12]. .
|
| 39 |
苏州市人民政府. 2024年政府工作报告[EB/OL]. [2024-05-12]. .
|

 ), 孙辛欣2
), 孙辛欣2
 ), SUN Xinxin2
), SUN Xinxin2