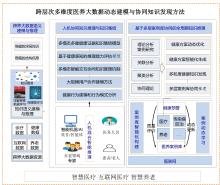
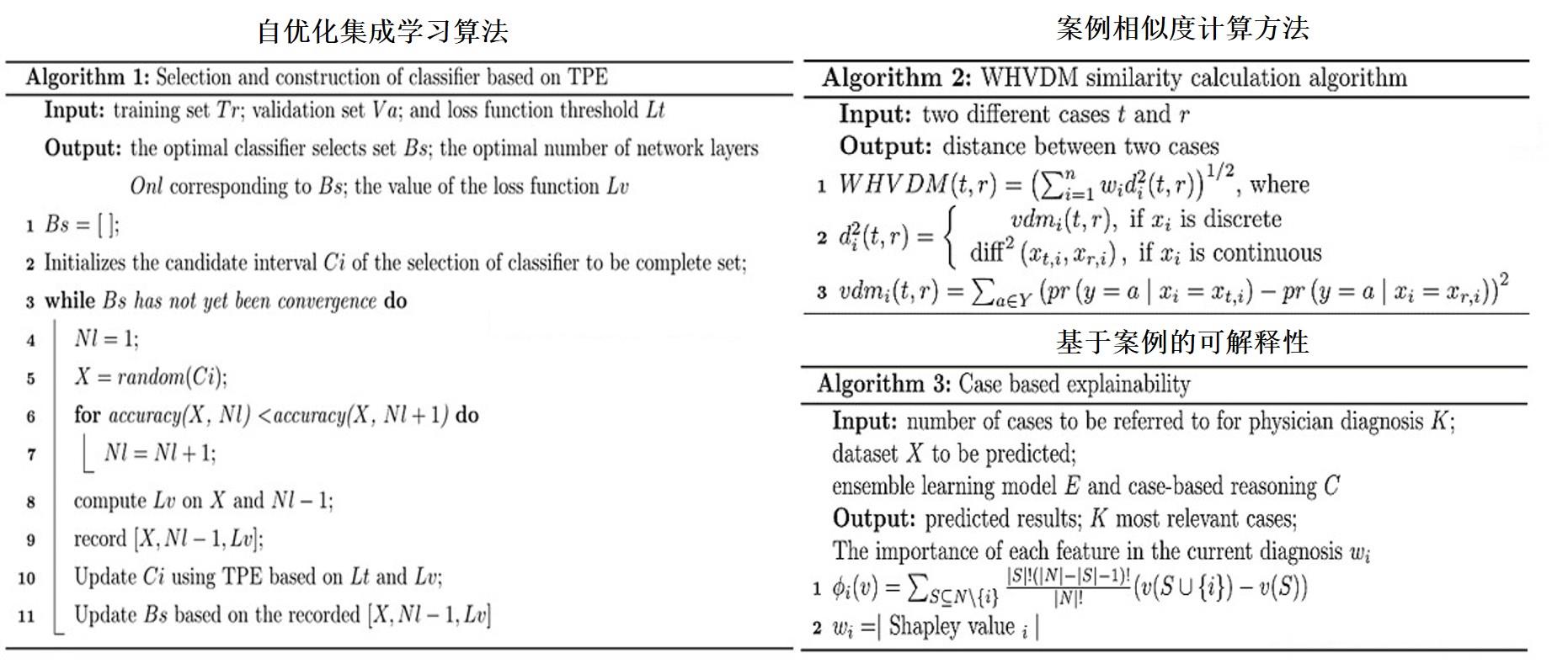
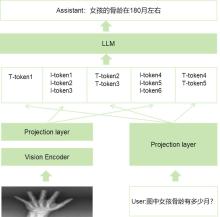
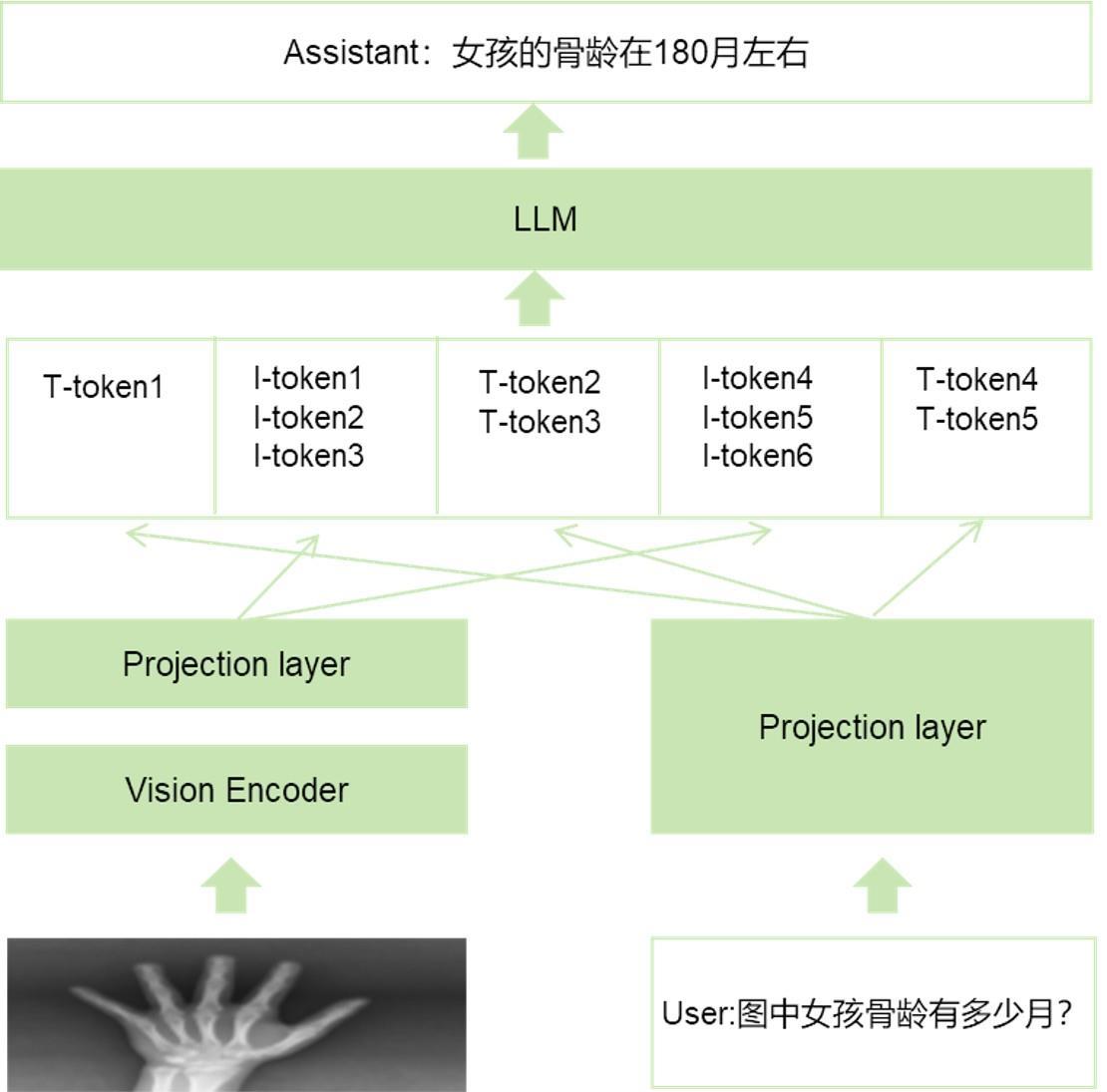
| 1 |
陈国青, 吴刚, 顾远东, 等. 管理决策情境下大数据驱动的研究和应用挑战: 范式转变与研究方向[J]. 管理科学学报, 2018, 21(7): 1-10.
|
|
CHEN G Q, WU G, GU Y D, et al. The challenges for big data driven research and applications in the context of managerial decision-making: Paradigm shift and research directions[J]. Journal of management sciences in China, 2018, 21(7): 1-10.
|
| 2 |
杨善林, 丁帅, 顾东晓, 等. 医联网: 新时代医疗健康模式变革与创新发展[J]. 管理科学学报, 2021, 24(10): 1-11.
|
|
YANG S L, DING S, GU D X, et al. Internet of healthcare systems(IHS): Revolution and innovations of healthcare management in the new era[J]. Journal of management sciences in China, 2021, 24(10): 1-11.
|
| 3 |
ESPOSITO C, DE SANTIS A, TORTORA G, et al. Blockchain: A Panacea for healthcare cloud-based data security and privacy [J]. IEEE cloud computing, 2018, 5(1): 31-37.
|
| 4 |
PETERSON K, DEEDUVANU R, KANJAMALA P, et al. A blockchain-based approach to health information exchange networks[J]. NIST workshop blockchain healthcare, 2016, 1: 1-10.
|
| 5 |
HE J X, BAXTER S L, XU J, et al. The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine[J]. Nature medicine, 2019, 25(1): 30-36.
|
| 6 |
FERREIRA J F, CASTELO-BRANCO M, DIAS J. A hierarchical bayesian framework for multi modal active perception[J]. Adaptive behavior, 20(3): 172-90.
|
| 7 |
PARK C H, JEON M, HOWARD A M. Robotic framework with multi-modal perception for physio-musical interactive therapy for children with autism[C]//2015 Joint IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning and Epigenetic Robotics (ICDL-EpiRob). August 13-16, 2015, Providence, RI, USA. IEEE, 2015: 150-151.
|
| 8 |
马茜, 谷峪, 张天成, 等. 一种基于数据质量的异构多源多模态感知数据获取方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2013, 36(10): 2120-2131.
|
|
MA Q, GU Y, ZHANG T C, et al. A heterogeneous multi-source multi-mode sensory data acquisition method based on data quality[J]. Chinese journal of computers, 2013, 36(10): 2120-2131.
|
| 9 |
杨善林, 丁帅, 顾东晓, 等. 医疗健康大数据驱动的知识发现与知识服务方法[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38(1): 219-229.
|
|
YANG S L, DING S, GU D X, et al. Healthcare big data driven knowledge discovery and knowledge service approach[J]. Journal of management world, 2022, 38(1): 219-229.
|
| 10 |
王雪鹏, 刘康, 何世柱, 等. 基于网络语义标签的多源知识库实体对齐算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40(3): 701-711.
|
|
WANG X P, LIU K, HE S Z, et al. Multi-source knowledge bases entity alignment by leveraging semantic tags[J]. Chinese journal of computers, 2017, 40(3): 701-711.
|
| 11 |
AJAMI H, MCHEICK H. Ontology-based model to support ubiquitous healthcare systems for COPD patients[J]. Electronics, 2018, 7(12): 371.
|
| 12 |
SHI L X, LI S J, YANG X R, et al. Semantic health knowledge graph: Semantic integration of heterogeneous medical knowledge and services[J]. BioMed research international, 2017, 2017(1): 2858423.
|
| 13 |
YOU Q, FANG S, CHEN J Y. Gene terrain: Visual exploration of differential gene expression profiles organized in native biomolecular interaction networks[J]. Information visualization, 2010, 9(1): 1-12.
|
| 14 |
PAPAGEORGIOU E I. A Fuzzy Inference Map approach to cope with uncertainty in modeling medical knowledge and making decisions[J]. Intelligent decision technologies, 2011, 5(3): 219-235.
|
| 15 |
ABIDI S R. Ontology-based knowledge modeling to provide decision support for comorbid diseases[M]//Knowledge Representation for Health-Care. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011: 27-39.
|
| 16 |
韦昌法, 晏峻峰. 从知识表示与推理方法探讨中医数字辨证发展[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(10): 4471-4473.
|
|
WEI C F, YAN J F. Study on Chinese medicine digital syndrome differentiation with its knowledge representation and reasoning methods[J]. China journal of traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacy, 2019, 34(10): 4471-4473.
|
| 17 |
UNIVERSITY F S, LIN Y-K, CHEN H, et al. Healthcare predictive analytics for risk profiling in chronic care: A Bayesian multitask learning approach[J]. MIS quarterly, 2017, 41(2): 473-495.
|
| 18 |
GULSHAN V, PENG L, CORAM M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs[J]. JAMA, 2016, 316(22): 2402-2410.
|
| 19 |
ESTEVA A, KUPREL B, NOVOA R A, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks[J]. Nature, 2017, 542(7639): 115-118.
|
| 20 |
BLOBEL B, LOPEZ D M, GONZALEZ C. Patient privacy and security concerns on big data for personalized medicine[J]. Health and technology, 2016, 6(1): 75-81.
|
| 21 |
SON J, FLATLEY BRENNAN P, ZHOU S Y. A data analytics framework for smart asthma management based on remote health information systems with bluetooth-enabled personal inhalers[J]. MIS quarterly, 2020, 44(1): 285-303.
|
| 22 |
MU B, WANG P Q, YUAN S J. A requirement evolution system for medical service composition[C]//2013 IEEE 4th International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science. May 23-25, 2013, Beijing, China. IEEE, 2013: 330-333.
|
| 23 |
LAHTI L. Supporting online health queries by modeling patterns of creation, modification and retrieval of medical knowledge[C]. Vancouver, BC, Canada: In Proceedings of EdMedia 2016 - World Conference on Educational Media and Technology, 2016: 711-718.
|
| 24 |
赵栋祥. 在线健康社区信息服务质量优化研究: 基于演化博弈的分析[J]. 情报科学, 2018, 36(8): 149-154.
|
|
ZHAO D X. Research on online health community information service quality optimization: Based on evolutionary game theory[J]. Information science, 2018, 36(8): 149-154.
|
| 25 |
徐宗本, 冯芷艳, 郭迅华, 等. 大数据驱动的管理与决策前沿课题[J]. 管理世界, 2014, 30(11): 158-163.
|
|
XU Z B, FENG Z Y, GUO X H, et al. Frontier topics of management and decision-making driven by big data[J]. Management world, 2014, 30(11): 158-163.
|
| 26 |
CONSTANTINOU A C, FENTON N, MARSH W, et al. From complex questionnaire and interviewing data to intelligent Bayesian network models for medical decision support[J]. Artificial intelligence in medicine, 2016, 67: 75-93.
|
| 27 |
GOLDSTEIN B A, NAVAR A M, PENCINA M J, et al. Opportunities and challenges in developing risk prediction models with electronic health records data: A systematic review[J]. Journal of the American medical informatics association, 2017, 24(1): 198-208.
|
| 28 |
ESCOBAR G J, BAKER J M, KIPNIS P, et al. Prediction of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection using comprehensive electronic medical records in an integrated healthcare delivery system[J]. Infection control and hospital epidemiology, 2017, 38(10): 1196-1203.
|
| 29 |
STANTCHEV V, PRIETO-GONZÁLEZ L, TAMM G. Cloud computing service for knowledge assessment and studies recommendation in crowdsourcing and collaborative learning environments based on social network analysis[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2015, 51: 762-770.
|
| 30 |
RHO M J, KIM H S, YOON K H, et al. Compliance patterns and utilization of e-health for glucose monitoring: Standalone Internet gateway and tablet device[J]. Telemedicine journal and e-health, 2017, 23(4): 298-304.
|
| 31 |
BURANARACH M, SUPNITHI T, CHALORTHAM N, et al. A semantic web framework to support knowledge management in chronic disease healthcare[M]//Metadata and Semantic Research. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009: 164-170.
|
| 32 |
马费成, 周利琴. 面向智慧健康的知识管理与服务[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2018, 44(5): 4-19.
|
|
MA F C, ZHOU L Q. Knowledge management and services for smart health[J]. Journal of library science in China, 2018, 44(5): 4-19.
|
| 33 |
GREENHALGH T, JACKSON C, SHAW S, et al. Achieving research impact through co-creation in community-based health services: Literature review and case study[J]. The milbank quarterly, 2016, 94(2): 392-429.
|
| 34 |
GU D X, ZHAO W, XIE Y, et al. A personalized medical decision support system based on explainable machine learning algorithms and ECC features: Data from the real world[J]. Diagnostics, 2021, 11(9): 1677.
|
| 35 |
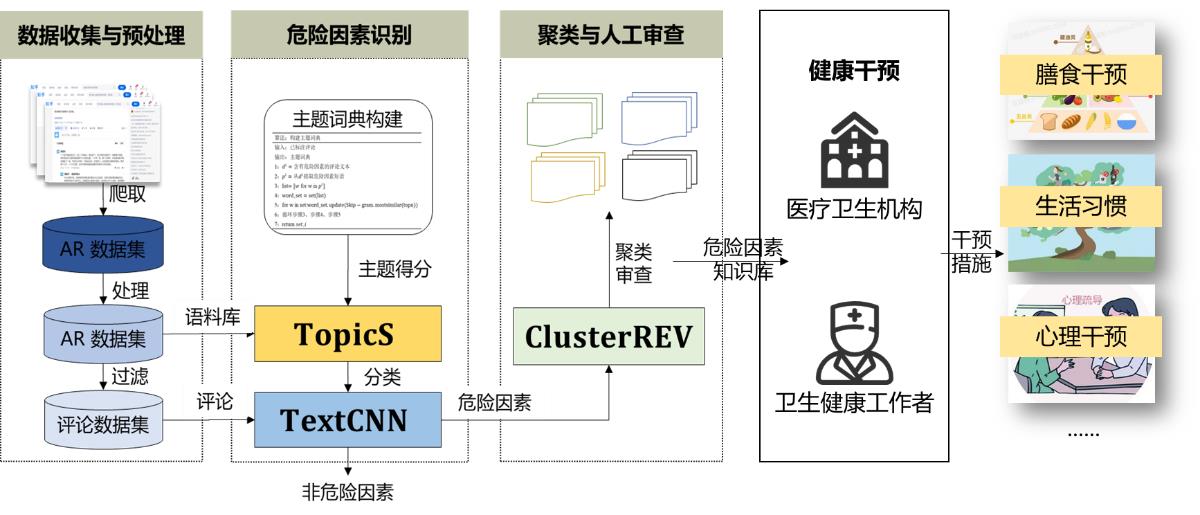
GU D X, WANG Q, CHAI Y D, et al. Identifying the risk factors of allergic rhinitis based on Zhihu comment data using a topic-enhanced word-embedding model: Mixed method study and cluster analysis[J]. Journal of medical Internet research, 2024, 26: e48324.
|
| 36 |
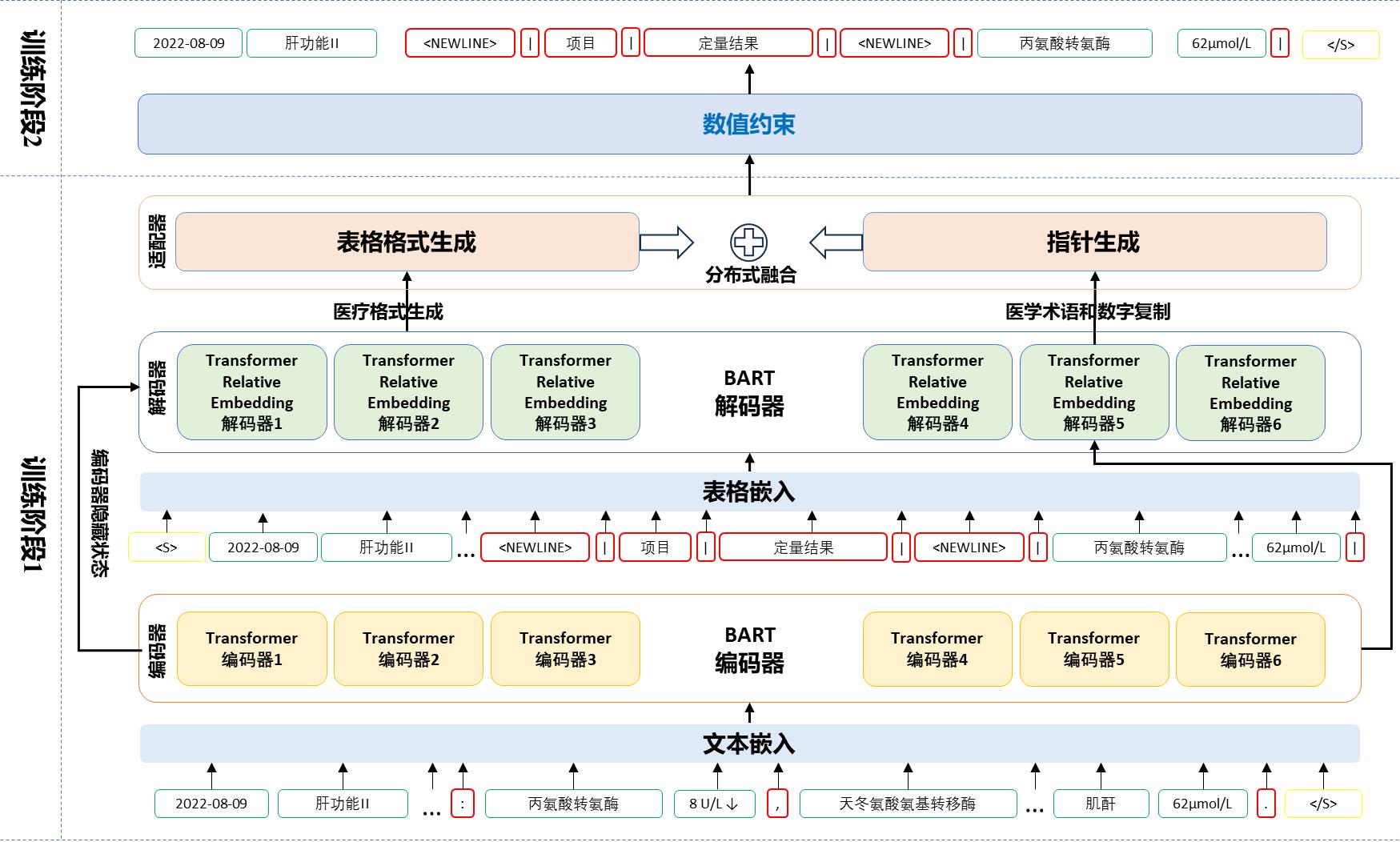
ZHAO W, GU D X, YANG X J, et al. MedT2T: An adaptive pointer constrain generating method for a new medical text-to-table task[J]. Future generation computer systems, 2024, 161: 586-600.
|
| 37 |
SU K X, WU J, GU D X, et al. An adaptive deep ensemble learning method for dynamic evolving diagnostic task scenarios[J]. Diagnostics, 2021, 11(12): 2288.
|
| 38 |
GU D X, SU K X, ZHAO H M. A case-based ensemble learning system for explainable breast cancer recurrence prediction[J]. Artificial intelligence in medicine, 2020, 107: 101858.
|
| 39 |
顾东晓, 黄智勇, 朱凯旋, 等. 医疗健康大模型知识体系构建、服务应用与风险协同治理[J/OL]. 情报科学, 2025: 1-29.
|
|
GU D X, HUANG Z Y, ZHU K X, et al. Medical health large language models construction of knowledge system, service applications, and synergetic governance of risk management[J/OL]. Information science, 2025: 1-29.
|
| 40 |
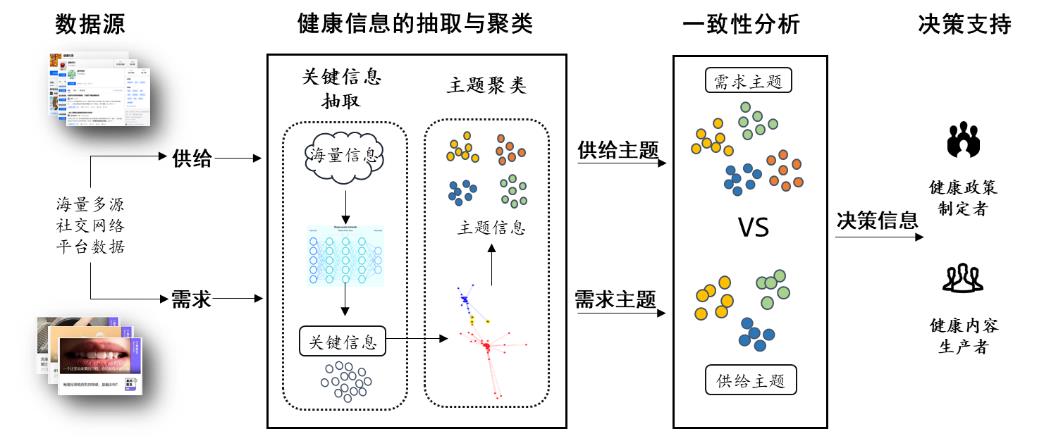
GU D X, LIU H, ZHAO H M, et al. A deep learning and clustering-based topic consistency modeling framework for matching health information supply and demand[J]. Journal of the association for information science and technology, 2024, 75(2): 152-166.
|
| 41 |
顾东晓, 张铭钰, 杨雪洁, 等. 整体治理观: “四力耦合”的智慧健康养老理论构建: 来自合肥的实践[J]. 公共管理学报, 2025, 22(1): 151-163, 176.
|
|
GU D X, ZHANG M Y, YANG X J, et al. Holistic governance view: The construction of "four forces integration" smart health elderly care theory: Insights from Hefei's practice[J]. Journal of public management, 2025, 22(1): 151-163, 176.
|

 )
)
 )
)