农业图书情报学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 82-95.doi: 10.13998/j.cnki.issn1002-1248.24-0444
基于SEM和fsQCA的虚拟兴趣社区用户信息采纳的影响因素研究
- 1. 中国农业大学 图书馆,北京 100083
2. 天津师范大学 管理学院,天津 300382
-
收稿日期:2024-07-07出版日期:2024-08-05发布日期:2024-12-13 -
通讯作者:周群 -
作者简介:韩龙(2000- ),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为信息行为
郭晋成(2002- ),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为信息行为
鲁羿廷(2000- ),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为信息计量与评价
-
基金资助:中央高校基本科研业务费“‘双一流’涉农高校期刊学术影响力综合评价研究”(2024TC004)
Factors Influencing User Information Adoption in Virtual Communities of Interest: A Study Based on SEM and fsQCA
Long HAN1, Jincheng GUO1, Yiting LU2, Qun ZHOU1( )
)
- 1. Library, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193
2. School of Management, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin 300382
-
Received:2024-07-07Online:2024-08-05Published:2024-12-13 -
Contact:Qun ZHOU
摘要:
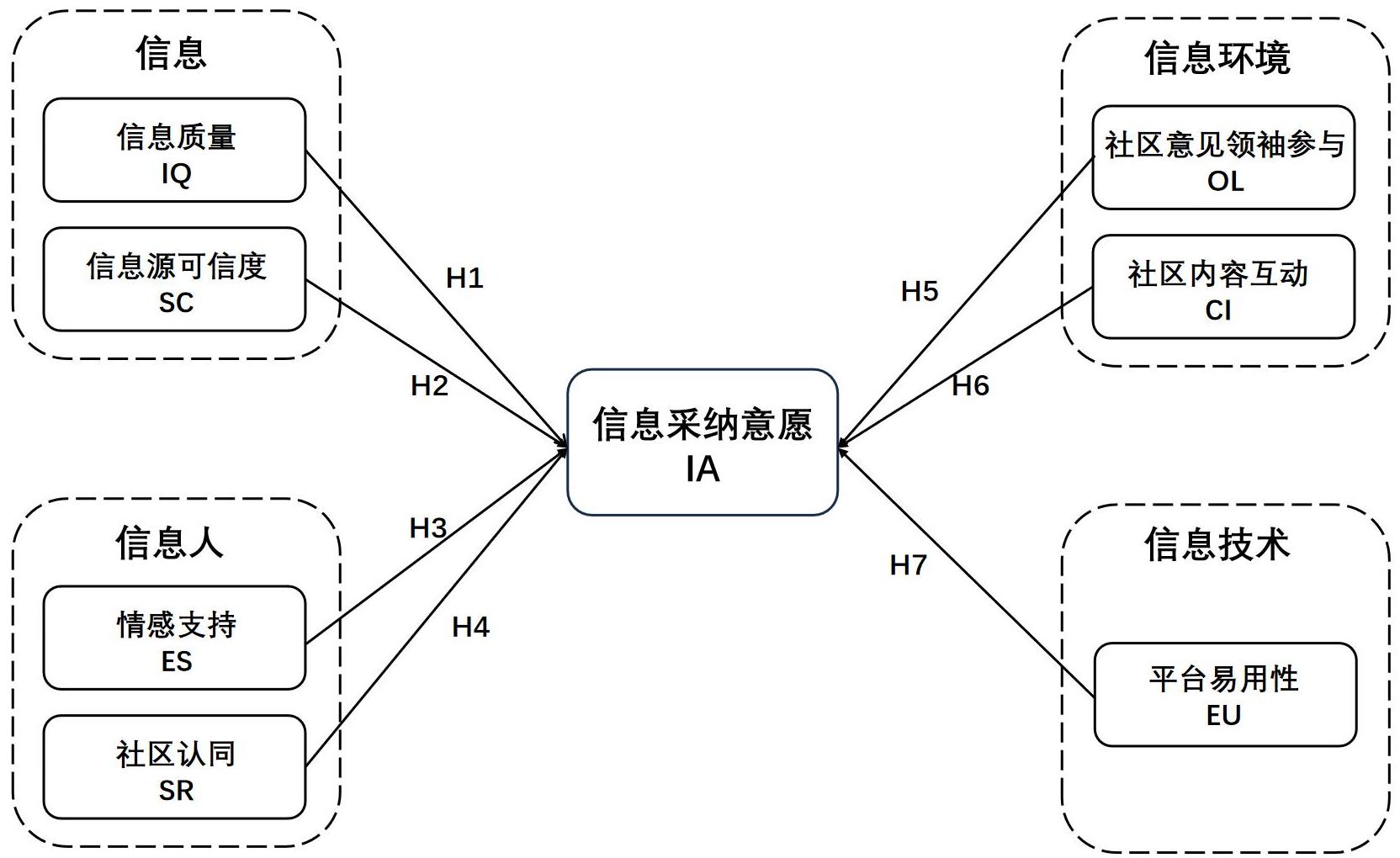
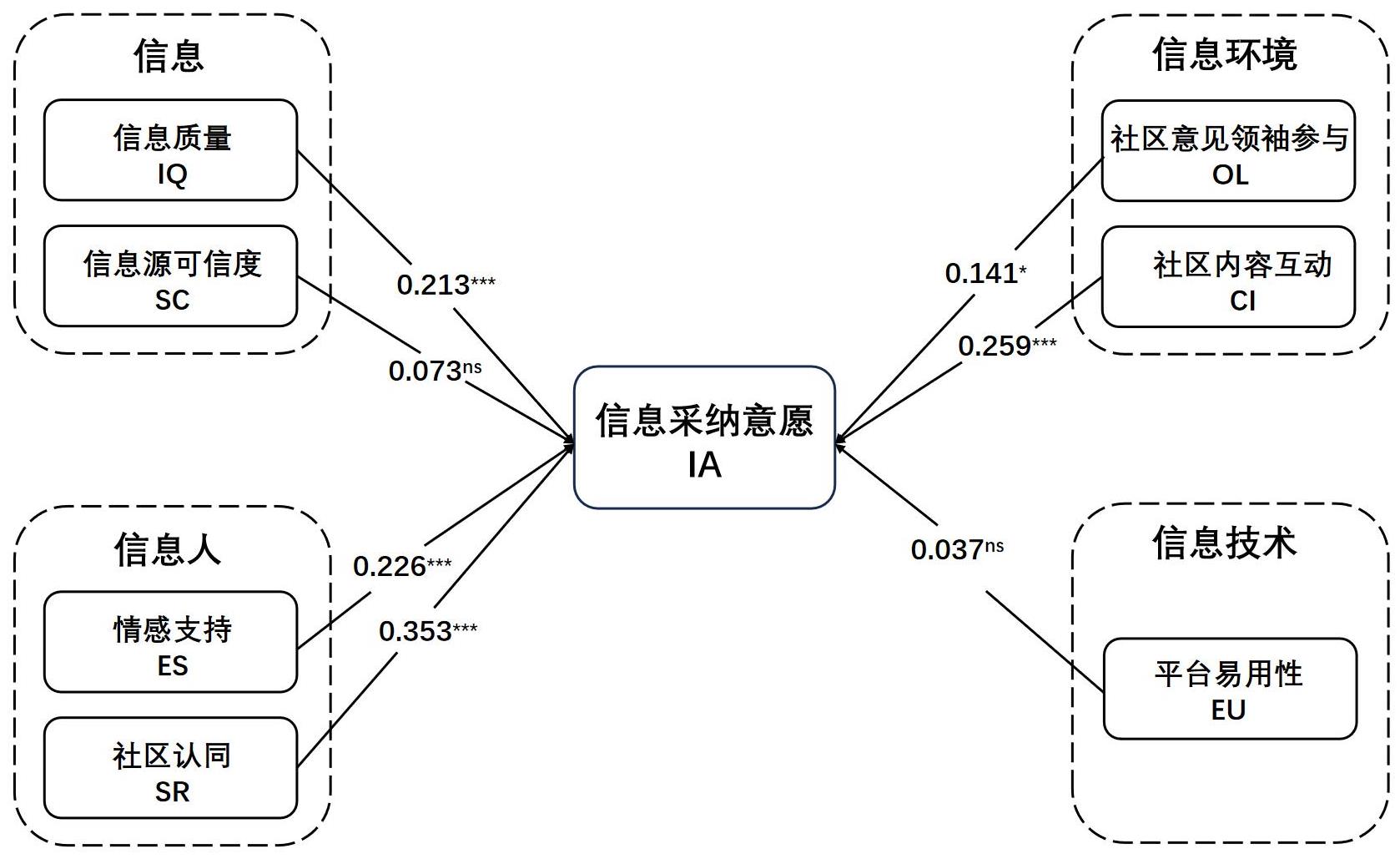
[目的/意义] 虚拟兴趣社区资源聚合、深度交流、互动性强等特点使其成为用户利用信息决策的重要信息来源,探究虚拟兴趣社区用户信息采纳的影响因素及其作用机理,有助于满足用户信息需求,优化社区管理与服务。 [方法/过程] 以信息生态理论为分析框架,构建虚拟兴趣社区用户信息采纳的影响因素研究模型,利用结构方程模型(SEM)和模糊集定性比较分析(fsQCA)方法对影响路径和前因构型进行实证分析。 [结果/结论] SEM结果表明,信息质量、情感支持、社区认同、社区意见领袖参与、社区内容互动对用户信息采纳意愿有显著正向影响;信息源可信度和平台易用性对用户信息采纳意愿无显著影响。fsQCA分析发现,用户信息采纳意愿的前因构型有两种模式,信任驱动型与体验促进型,共6条组态路径,结果与SEM分析存在差异,显示其能够揭示复杂的决策环境中多因素相互作用的价值。
中图分类号: G252
引用本文
韩龙, 郭晋成, 鲁羿廷, 周群. 基于SEM和fsQCA的虚拟兴趣社区用户信息采纳的影响因素研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(8): 82-95.
Long HAN, Jincheng GUO, Yiting LU, Qun ZHOU. Factors Influencing User Information Adoption in Virtual Communities of Interest: A Study Based on SEM and fsQCA[J]. Journal of Library and Information Science in Agriculture, 2024, 36(8): 82-95.
表1
量表测量题项及来源"
| 变量 | 题项 | 题项内容 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 信息质量 | IQ1 | 我认为我在虚拟兴趣社区中获取的信息是准确的 | LIAO等[ |
| IQ2 | 我认为我在虚拟兴趣社区中获取的信息是全面的 | ||
| IQ3 | 我认为我在虚拟兴趣社区中获取的信息是及时更新的 | ||
| IQ4 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区的信息表达方式清晰易懂 | ||
| IQ5 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区的信息能够满足我的需求 | ||
| 信息源可信度 | SC1 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区中信息的来源是值得信赖的 | HUO等[ |
| SC2 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区中信息发布者的专业知识对我有帮助 | ||
| SC3 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区中的信息发布者是值得信赖的专家 | ||
| SC4 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区的信息来源是权威的 | ||
| 情感支持 | ES1 | 我觉得虚拟兴趣社区中的其他用户对我的问题给予了同理心和支持 | CHIU等[ |
| ES2 | 我觉得虚拟兴趣社区中的用户互动让我感受到情感上的支持或鼓励 | ||
| ES3 | 我认为在虚拟兴趣社区中,用户之间的互动帮助我减轻了信息获取时的压力或疑虑 | ||
| ES4 | 我觉得在虚拟兴趣社区中的交流让我产生了积极的情感体验,增加了对信息的信任 | ||
| 社区认同 | SR1 | 我觉得自己与虚拟兴趣社区中的其他用户有共同的兴趣或目标 | FANG等[ |
| SR2 | 我觉得虚拟兴趣社区的价值观与我的想法相符 | ||
| SR3 | 我愿意在虚拟兴趣社区中更多地参与和分享信息 | ||
| SR4 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区对我的观点表示了尊重和重视 | ||
| 社区意见领袖参与 | OL1 | 我认为虚拟兴趣社区中的意见领袖对我有影响 | 蒋惠芳[ |
| OL2 | 我信任虚拟兴趣社区中具有较高影响力的用户提供的信息 | ||
| OL3 | 我经常关注虚拟兴趣社区中意见领袖发布的内容 | ||
| 社区内容互动 | CI1 | 我经常参与虚拟兴趣社区的讨论和互动 | 范晓屏等[ |
| CI2 | 我觉得虚拟兴趣社区的讨论帮助我更好地理解信息 | ||
| CI3 | 我认为通过与其他用户的互动,我对信息的信任度增强了 | ||
| 平台易用性 | EU1 | 我觉得虚拟兴趣社区平台的界面设计简单明了,易于操作 | ZLATOLAS等[ |
| EU2 | 我能够在虚拟兴趣社区平台上快速找到自己所需的信息 | ||
| EU3 | 我觉得在虚拟兴趣社区平台上的操作过程流畅,没有不必要的障碍 | ||
| 信息采纳意愿 | IA1 | 我愿意依据虚拟兴趣社区中获取的信息做出决策或采取行动 | SUSSMAN[ |
| IA2 | 我经常参考虚拟兴趣社区中的信息来解决实际问题 | ||
| IA3 | 我觉得虚拟兴趣社区中的信息对我来说有足够的可信度,因此愿意采纳 | ||
| IA4 | 我会向他人推荐虚拟兴趣社区中的有用信息或内容 |
表4
区分效度检验结果"
| 变量 | AVE | MD | EU | CI | OL | IC | SC | IQ | IA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | 0.621 | 0.788 | |||||||
| EU | 0.635 | 0.383 | 0.797 | ||||||
| CI | 0.602 | 0.422 | 0.351 | 0.776 | |||||
| OL | 0.612 | 0.463 | 0.452 | 0.412 | 0.782 | ||||
| ES | 0.579 | 0.309 | 0.359 | 0.359 | 0.386 | 0.761 | |||
| SC | 0.519 | 0.433 | 0.453 | 0.492 | 0.475 | 0.372 | 0.720 | ||
| IQ | 0.566 | 0.493 | 0.472 | 0.400 | 0.358 | 0.306 | 0.517 | 0.752 | |
| IA | 0.683 | 0.687 | 0.491 | 0.617 | 0.570 | 0.529 | 0.571 | 0.601 | 0.826 |
表6
前因变量必要性分析结果"
| 变量 | 一致性 | 覆盖度 |
|---|---|---|
| IQfz | 0.738 2 | 0.855 9 |
| ~IQfz | 0.621 7 | 0.614 5 |
| SCfz | 0.846 8 | 0.860 6 |
| ~SCfz | 0.530 8 | 0.596 2 |
| ESfz | 0.775 9 | 0.855 2 |
| ~ESfz | 0.607 6 | 0.628 3 |
| SRfz | 0.779 8 | 0.875 6 |
| ~SRfz | 0.607 1 | 0.617 2 |
| OLfz | 0.853 7 | 0.835 0 |
| ~OLfz | 0.531 2 | 0.626 3 |
| CIfz | 0.807 1 | 0.849 7 |
| ~CIfz | 0.561 8 | 0.607 8 |
| EUfz | 0.823 1 | 0.835 8 |
| ~EUfz | 0.542 8 | 0.610 3 |
表7
虚拟兴趣社区用户与信息采纳意愿的前因构型"
| 前因条件 | 模式一 | 模式二 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | |
| 信息质量(IQ) | 〇 | ⊗ | 〇 | 〇 | ⊗ | |
| 信息源可信度(SC) | ● | ● | ● | 〇 | 〇 | |
| 情感支持(ES) | ● | 〇 | ● | ● | ● | |
| 社区认同(SR) | ⊗ | 〇 | ⊗ | |||
| 社区意见领袖参与(OL) | ● | ● | ● | ● | 〇 | |
| 社区内容互动(CI) | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| 平台易用性(EU) | 〇 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 一致性 | 0.963 | 0.958 | 0.967 | 0.958 | 0.956 | 0.965 |
| 覆盖率 | 0.461 | 0.487 | 0.366 | 0.454 | 0.452 | 0.357 |
| 净覆盖率 | 0.041 | 0.025 | 0.041 | 0.058 | 0.033 | 0.021 |
| 总体一致性 | 0.946 | |||||
| 总体覆盖率 | 0.693 | |||||
| 1 |
中国互联网络信息中心. 第53次中国互联网络发展状况统计报告[R]. 北京: 中国互联网络信息中心, 2021.
|
|
China Internet Network Information Center. The 53rd Statistical Report on China's Internet Development[R]. Beijing: China Internet Network Information Center, 2021.
|
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
孟笛. 虚拟社区国际研究综述——基于SSCI、A&HCI高被引文献的分析[J]. 图书情报工作, 2015, 59(18): 127-133.
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
刘颖捷. 娱乐类网络社区的用户粘性研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2017.
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
卢倩. 虚拟兴趣社区激励用户参与的策略及机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2021.
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
赵小建. 基于MOA理论模型的兴趣型虚拟社区知识共享行为研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021.
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
张瑞, 涂凯, 黄炜. 中美网络兴趣型社区粉丝行为对比研究——基于扎根理论探索分析[J]. 现代情报, 2023, 43(8): 54-65.
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
宋雪雁, 王萍. 信息采纳行为概念及影响因素研究[J]. 情报科学, 2010, 28(5): 760-762, 767.
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
陶晓波, 徐鹏宇, 樊潮, 等. 创新社区中新产品开发人员信息采纳行为的影响机理研究[J]. 管理评论, 2020, 32(10): 135-146.
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
郭爱芳, 陈佳凤, 郭静, 等. 虚拟创新社区用户相关特征对其创意采纳的影响——以戴尔“头脑风暴” 社区为例[J]. 中国科技论坛, 2018(8): 140-146.
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
洪闯, 李贺, 毛太田. 开放式创新社区用户知识贡献的采纳机理研究[J]. 现代情报, 2020, 40(5): 33-40.
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
王楠, 陈详详, 祁运丽, 等. 基于详尽可能性模型的用户创新社区创意采纳影响因素研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2020, 28(3): 213-222.
|
|
|
|
| 17 |
李娟娟, 郭顺利. 认知视域下社会化问答社区用户知识采纳行为的影响因素——基于扎根理论的探索性分析[J]. 情报科学, 2022, 40(2): 91-98.
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
付少雄, 陈晓宇, 邓胜利. 社会化问答社区用户信息行为的转化研究——从信息采纳到持续性信息搜寻的理论模型构建[J]. 图书情报知识, 2017, 34(4): 80-88.
|
|
|
|
| 19 |
费豪泽, 周斌, 刘鹏, 等. 社会化问答中回答者在线互动行为对信息采纳影响的实证分析[J]. 数字图书馆论坛, 2019(10): 45-54.
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
唐旭丽, 张斌, 张岩. 在线健康社区用户的信息采纳意愿研究——基于健康素养和信任的视角[J]. 信息资源管理学报, 2018, 8(3): 102-112.
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
涂瑞德, 操慧子, 明均仁. 虚拟学术社区用户采纳意愿的影响因素[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2020, 40(2): 10-16.
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
娄策群, 周承聪. 信息生态链: 概念、本质和类型[J]. 图书情报工作, 2007, 51(9): 29-32.
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
冯献, 李瑾, 崔凯, 等. 基于信息生态视角的乡村居民公共数字文化服务采纳意愿影响因素分析[J]. 图书馆建设, 2022(4): 139-146.
|
|
|
|
| 31 |
刘春明, 郝庆升, 周杨, 等. 电商平台中绿色农产品消费者信息采纳行为及影响因素研究——基于信息生态视角[J]. 情报科学, 2019, 37(7): 151-157.
|
|
|
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
徐嘉徽, 李全喜, 张健. 共享服务平台信息质量对消费者信息采纳行为的影响分析与提升对策研究[J]. 情报科学, 2019, 37(5): 148-154.
|
|
|
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
周密, 罗露阳, 刘伟. 在线知识问答社区中答案的内容特征和社区地位对答案采纳的影响机制研究[J]. 图书馆研究与工作, 2023(8): 45-54.
|
|
|
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
李宗伟, 张艳辉, 夏伟伟. 卖家反馈能否引发高质量的在线评论信息?——基于淘宝网的实证分析[J]. 中国管理科学, 2021, 29(5): 221-230.
|
|
|
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
张秋霞. 信息生态视角下消费者选择跨境电商平台的影响因素研究[D]. 太原: 山西财经大学, 2020.
|
|
|
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
|
| 48 |
蒋惠芳. 社交电商意见领袖对消费者在线购买行为意向的影响研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2022.
|
|
|
|
| 49 |
吴娇娇. 社交平台中用户生成内容对消费者购买意愿的影响研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.
|
|
|
|
| 50 |
范晓屏, 马庆国. 基于虚拟社区的网络互动对网络购买意向的影响研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版)预印本, 2009(1): 94-102.
|
|
|
|
| 51 |
|
| 52 |
郭瑞. 娱乐类移动短视频平台用户使用行为影响因素研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2018.
|
|
|
|
| 53 |
|
| 54 |
谭春辉, 王晓宇, 刁斐, 等. 基于fsQCA方法的社会化问答社区用户持续使用意愿影响机理研究[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2023(1): 74-86.
|
|
|
|
| 55 |
莫敏, 匡宇扬, 朱庆华, 等. 在线问诊信息用户采纳意愿的影响因素研究[J]. 现代情报, 2022, 42(6): 57-68.
|
|
|
| [1] | 万小蝶, 夏一雪. 网络圈群中风险感知对群体极化的影响研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(9): 66-79. |
| [2] | 吴祎玮, 文庭孝. 公众网络健康信息搜寻对线下就医行为的影响因素研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(8): 30-42. |
| [3] | 惠晓萌, 陈宇晴, 惠良虹. 大学生数字原住民特征对数字公民素养的影响研究——基于结构方程模型和fsQCA的分析[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(3): 37-51. |
| [4] | 李力, 韩平, 张弘, 张伟娟. 启发-系统式线索对移动短视频用户健康信息采纳的影响研究——基于SEM和QCA的混合方法[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(1): 73-86. |
| [5] | 邢飞, 刘彩华, 柴雪飞, 彭国超. 基于社交平台的老年用户健康信息采纳行为影响因素研究——以微信为例[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2022, 34(7): 53-64. |
| [6] | 郭维嘉. 图书馆人工智能准备度影响因素研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2022, 34(5): 47-56. |
| [7] | 陈璟浩, 罗淇. 突发公共卫生事件中老年人防疫信息技术采纳意愿影响因素研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2022, 34(4): 30-40. |
| [8] | 李嘉雯, 秦琴, 柯青. 虚拟问答社区用户知识隐藏行为影响因素实证研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2022, 34(2): 48-62. |
| [9] | 乐承毅,李佩佩,陈水琳. 用户感知视角下的高校移动数字图书馆用户满意度分析[J]. 农业图书情报, 2019, 31(2): 20-29. |
| [10] | 吴绮云. 信息生态理论视域下数字图书馆馆藏资源优化配置研究[J]. 农业图书情报学刊, 2018, 30(9): 38-41. |
| [11] | 孙研子. 用户体验视角下高校图书馆图书借阅满意度研究——以长治学院为例[J]. 农业图书情报学刊, 2018, 30(7): 84-90. |
| [12] | 赵丽梅, 陶易. 在线评论有用性影响因素的实证研究[J]. 农业图书情报学刊, 2018, 30(7): 14-17. |
| [13] | 刘丽萍. 基于信息生态理论的图书馆联盟协同创新服务模式研究[J]. 农业图书情报学刊, 2017, 29(8): 201-204. |
| [14] | 李明真, 王真. 基于个人信息世界理论的数字图书馆信息采纳模型构建[J]. 农业图书情报学刊, 2016, 28(11): 9-12. |
|
||