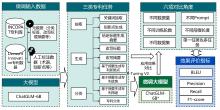
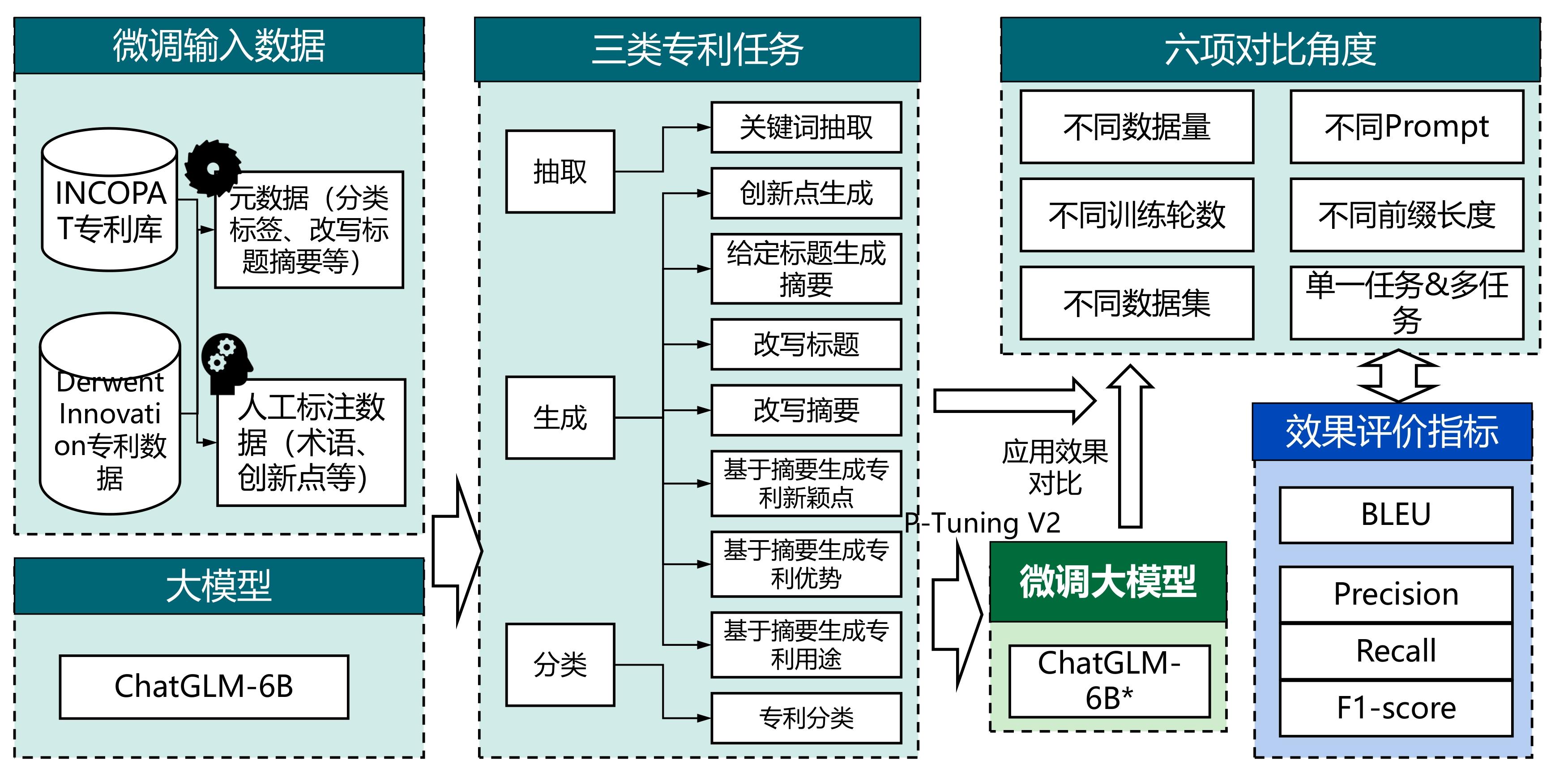
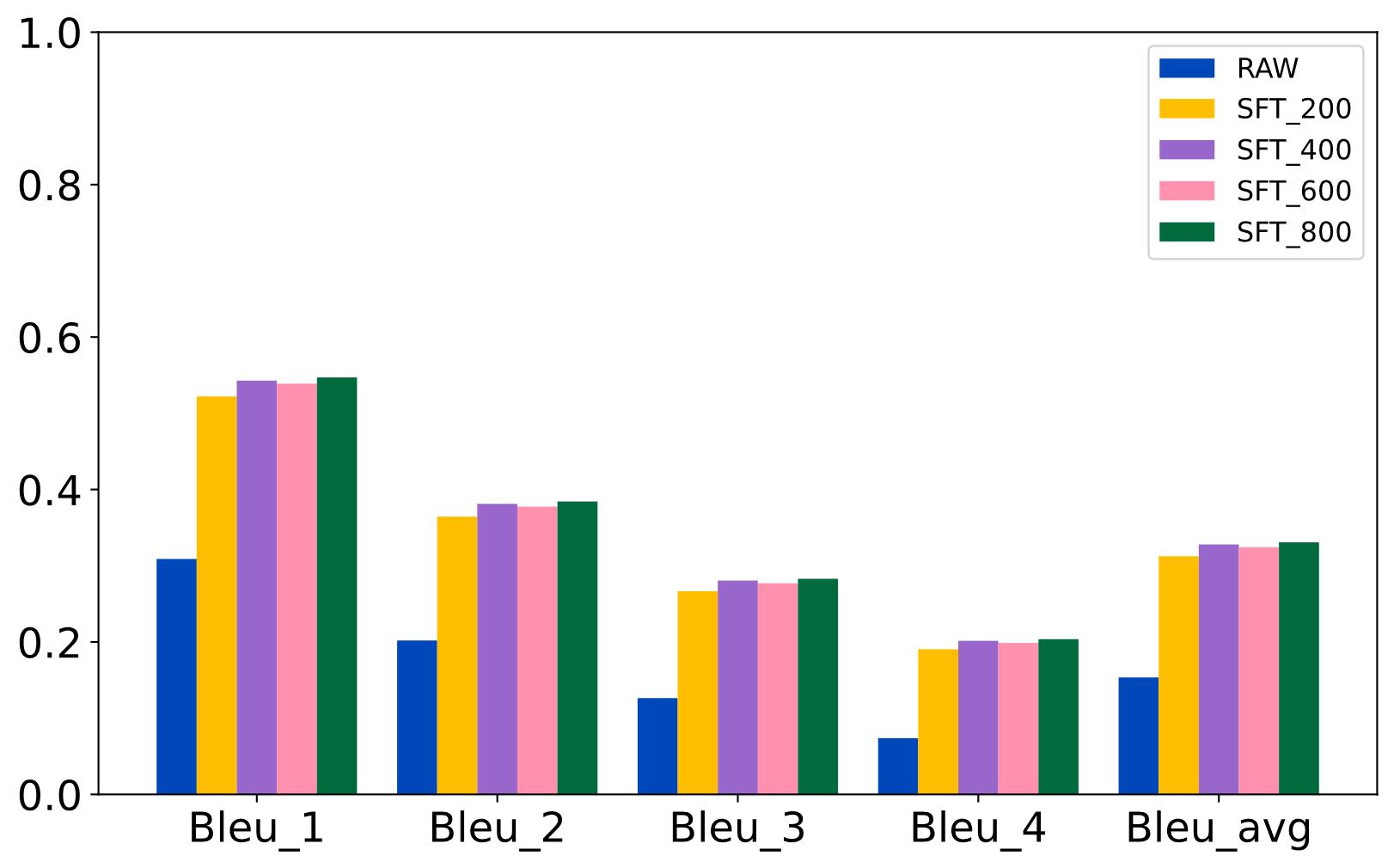
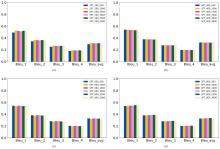
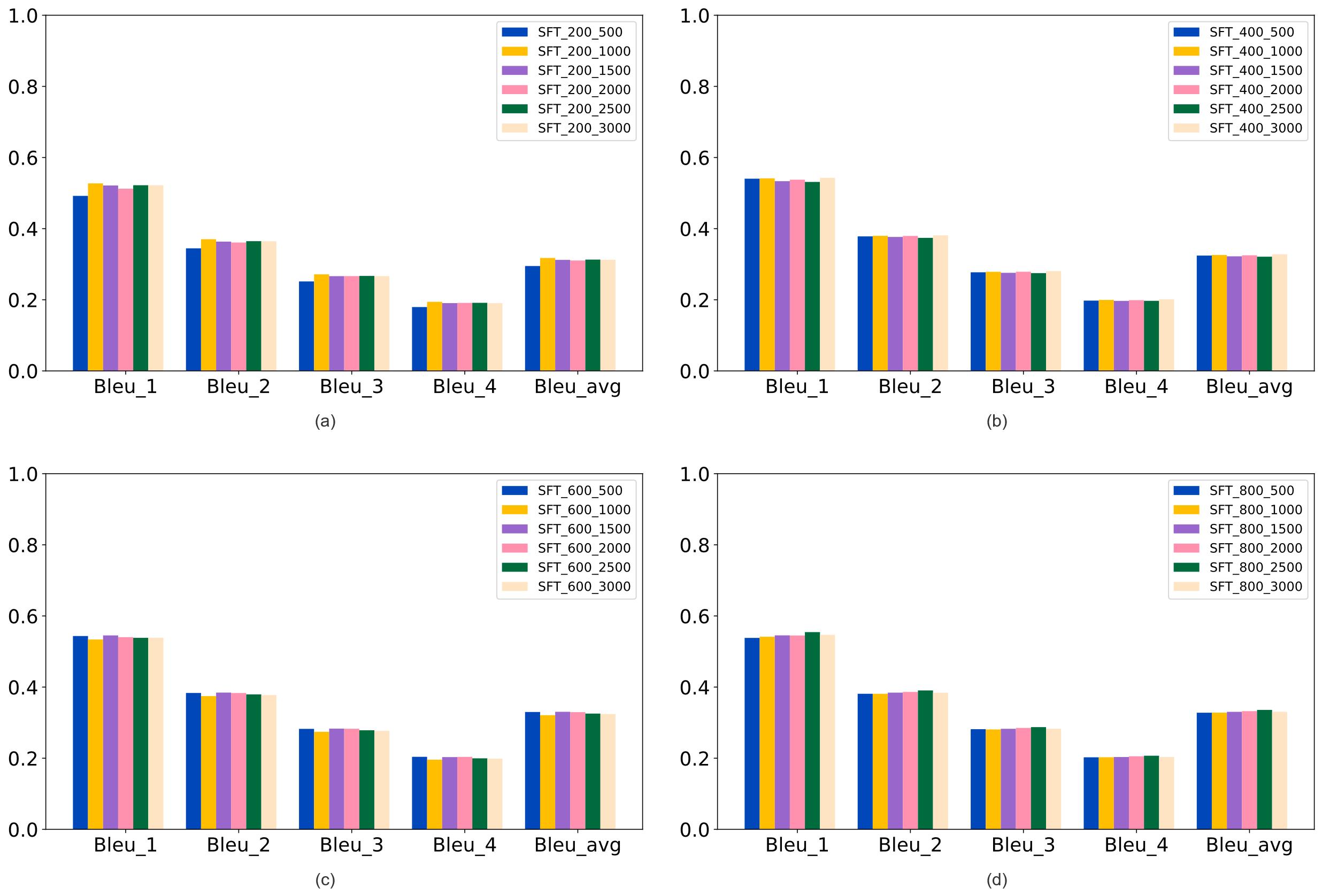
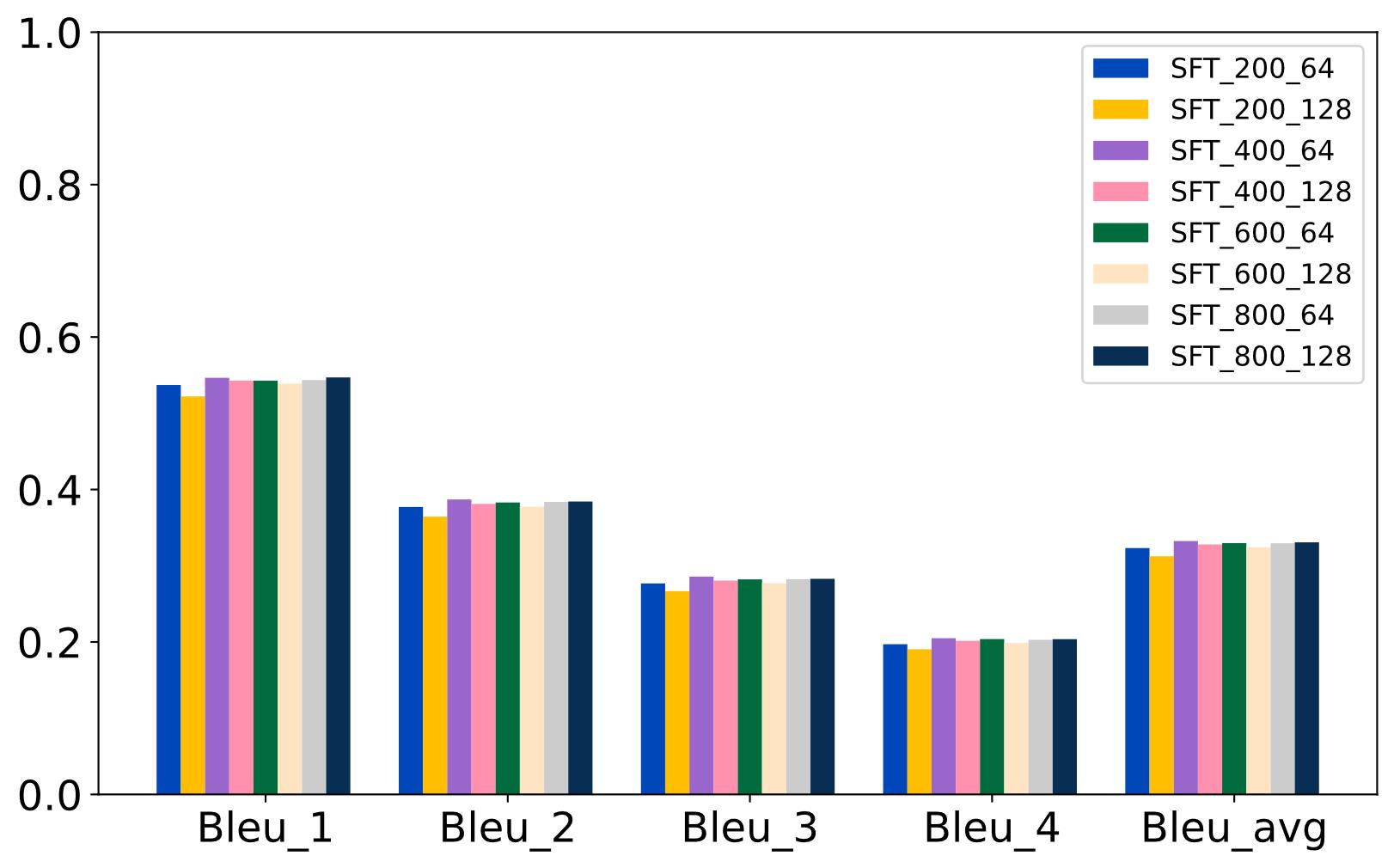
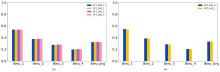
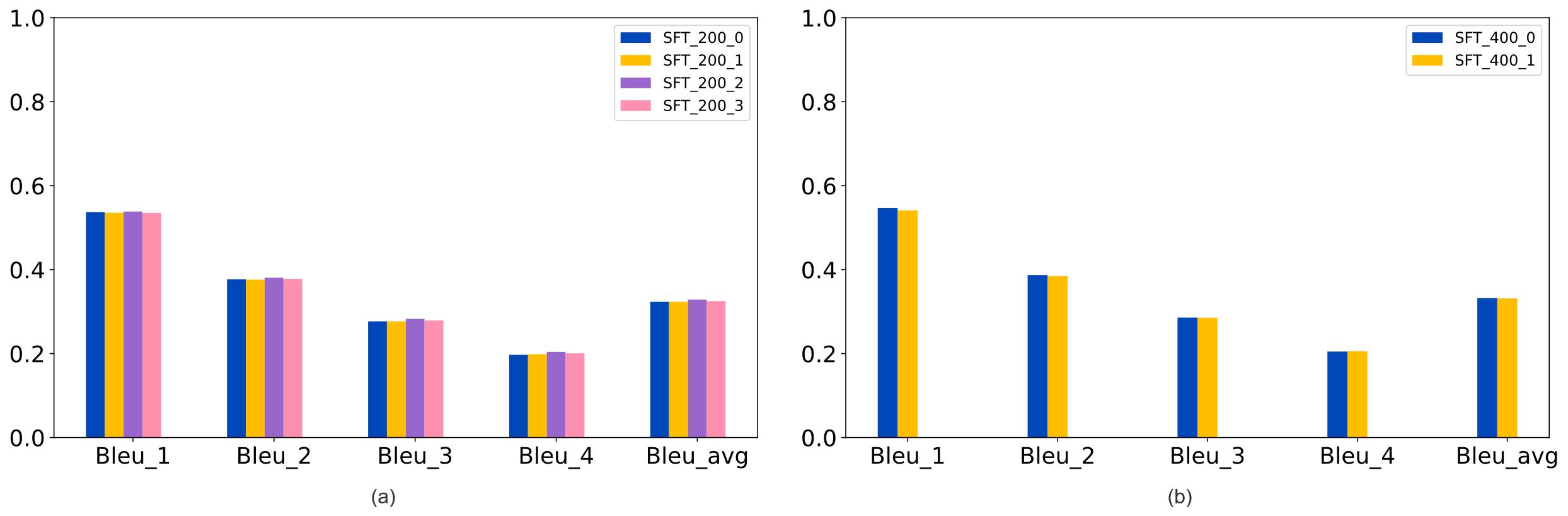
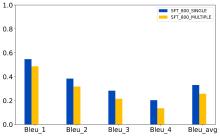
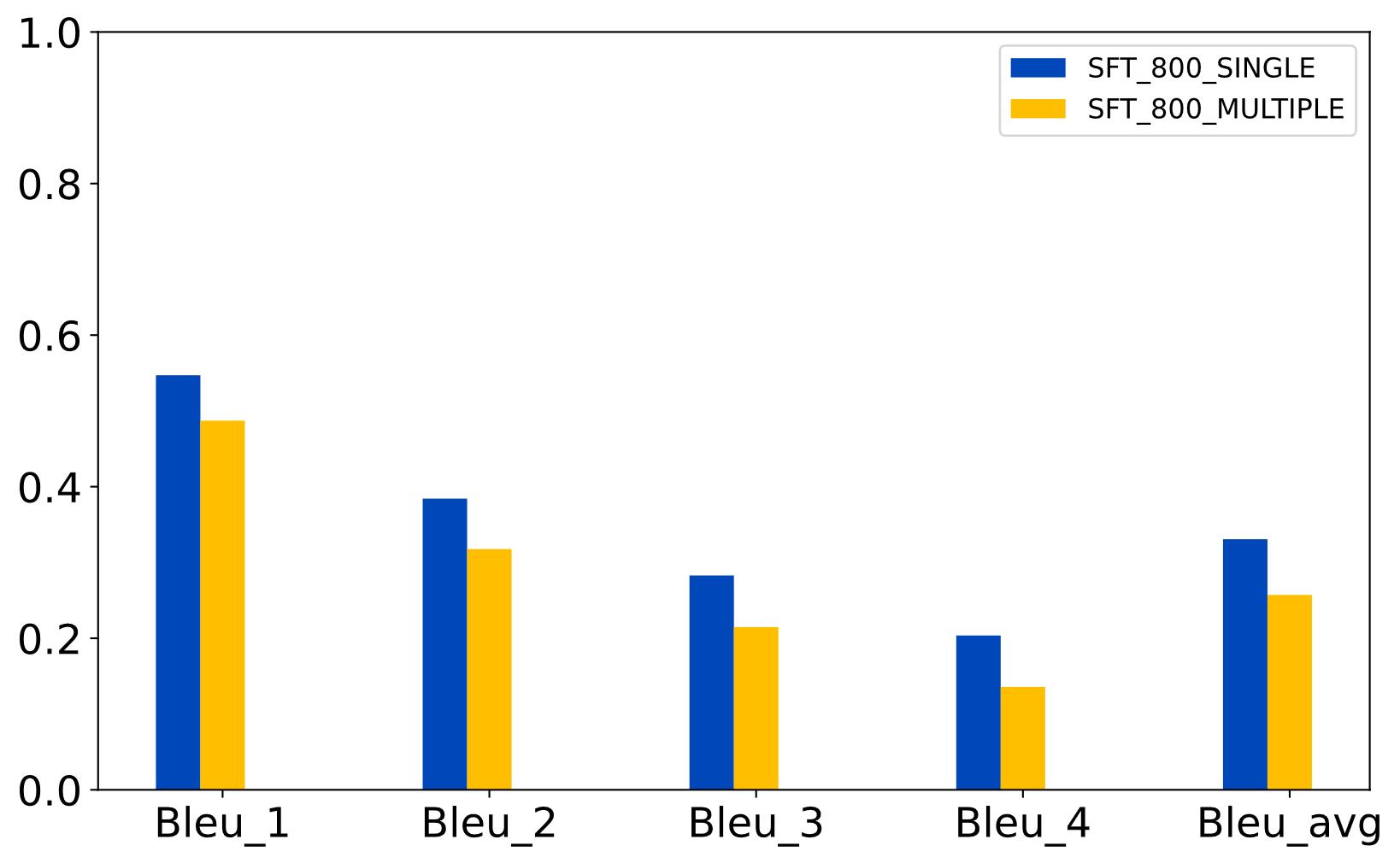
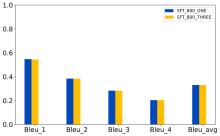
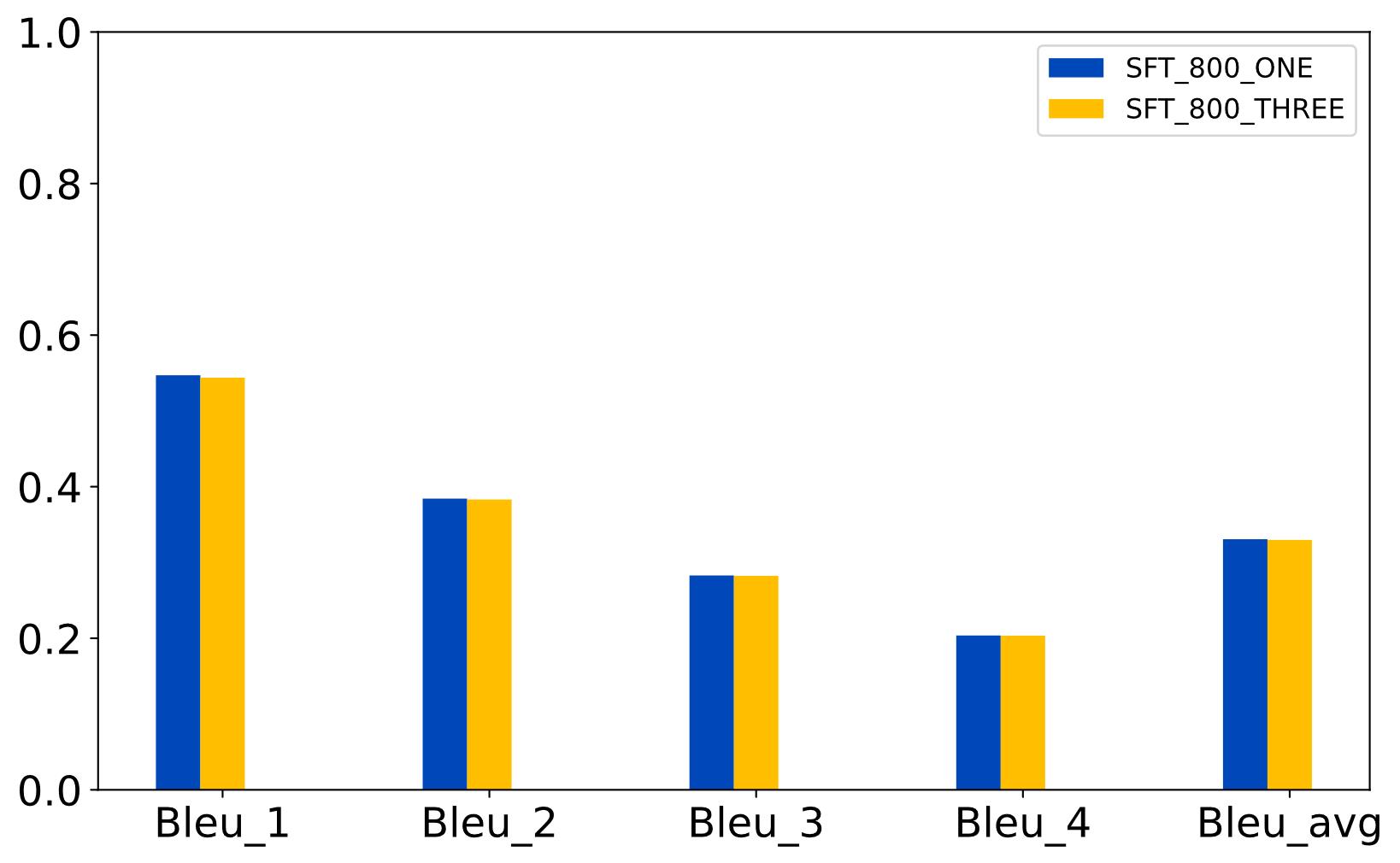
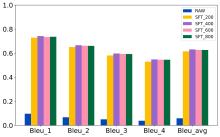
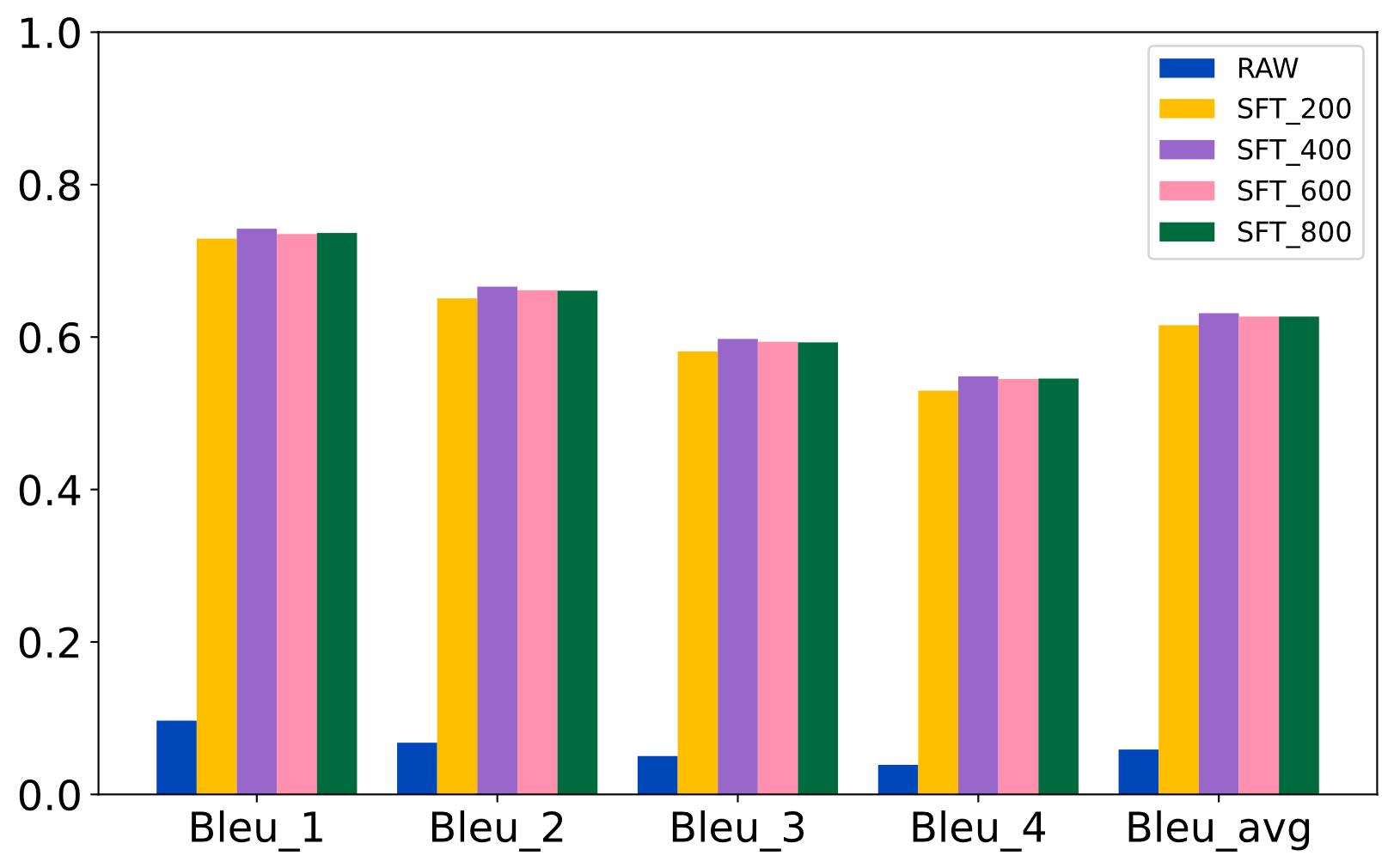
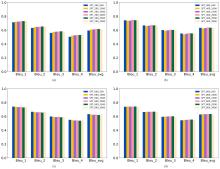
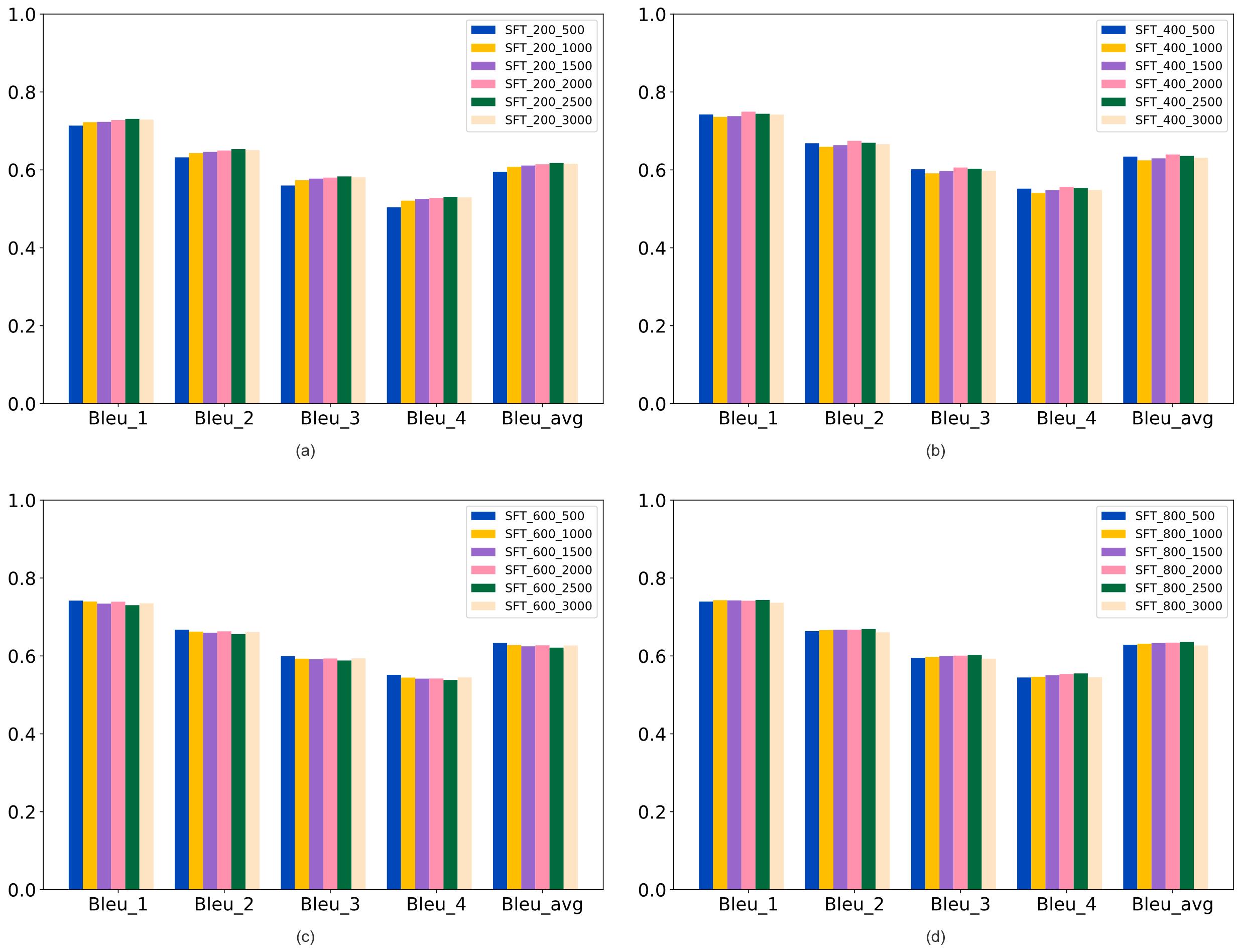
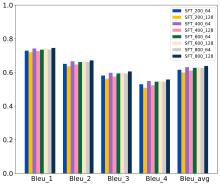
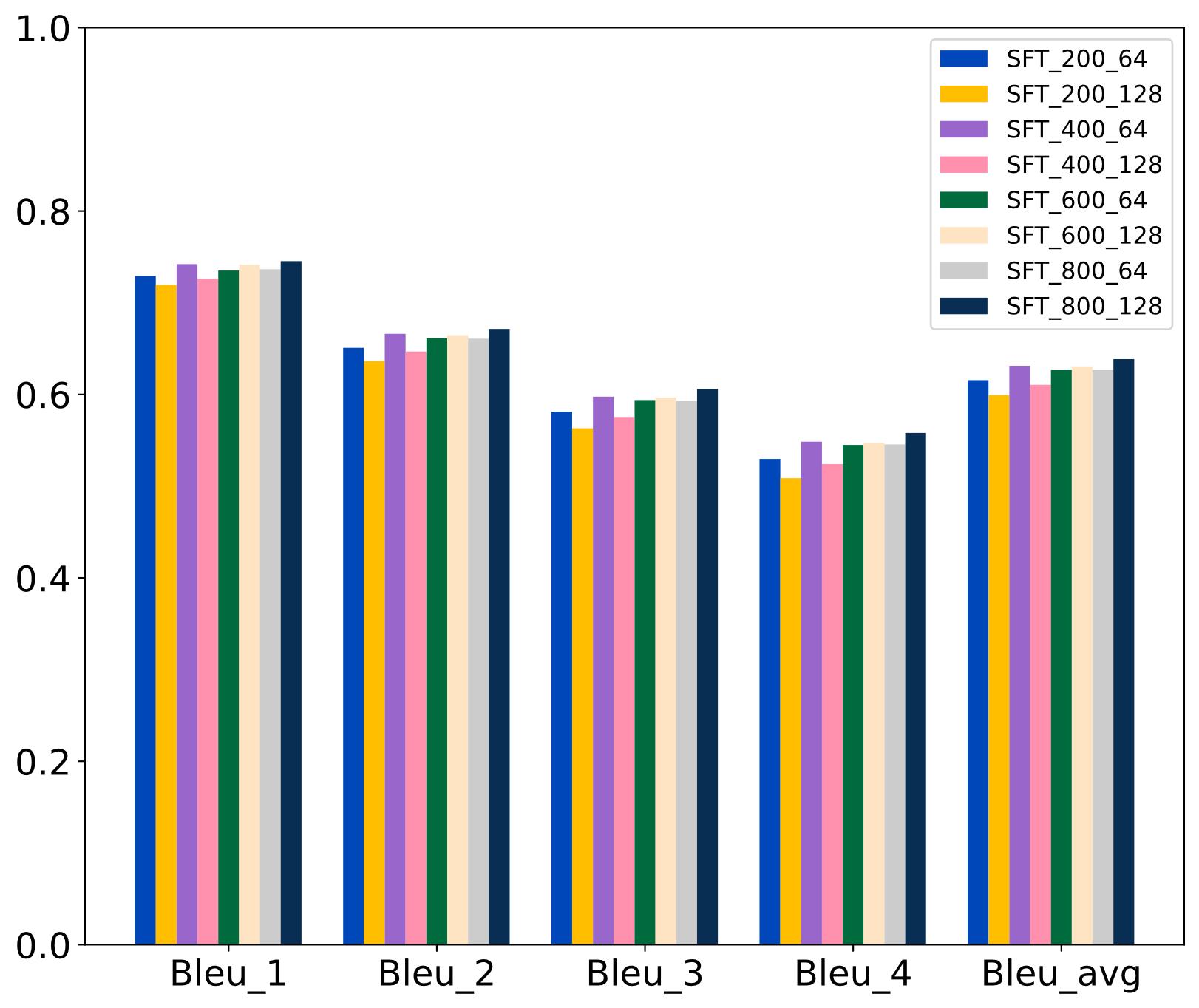
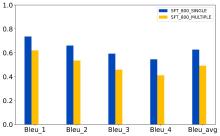
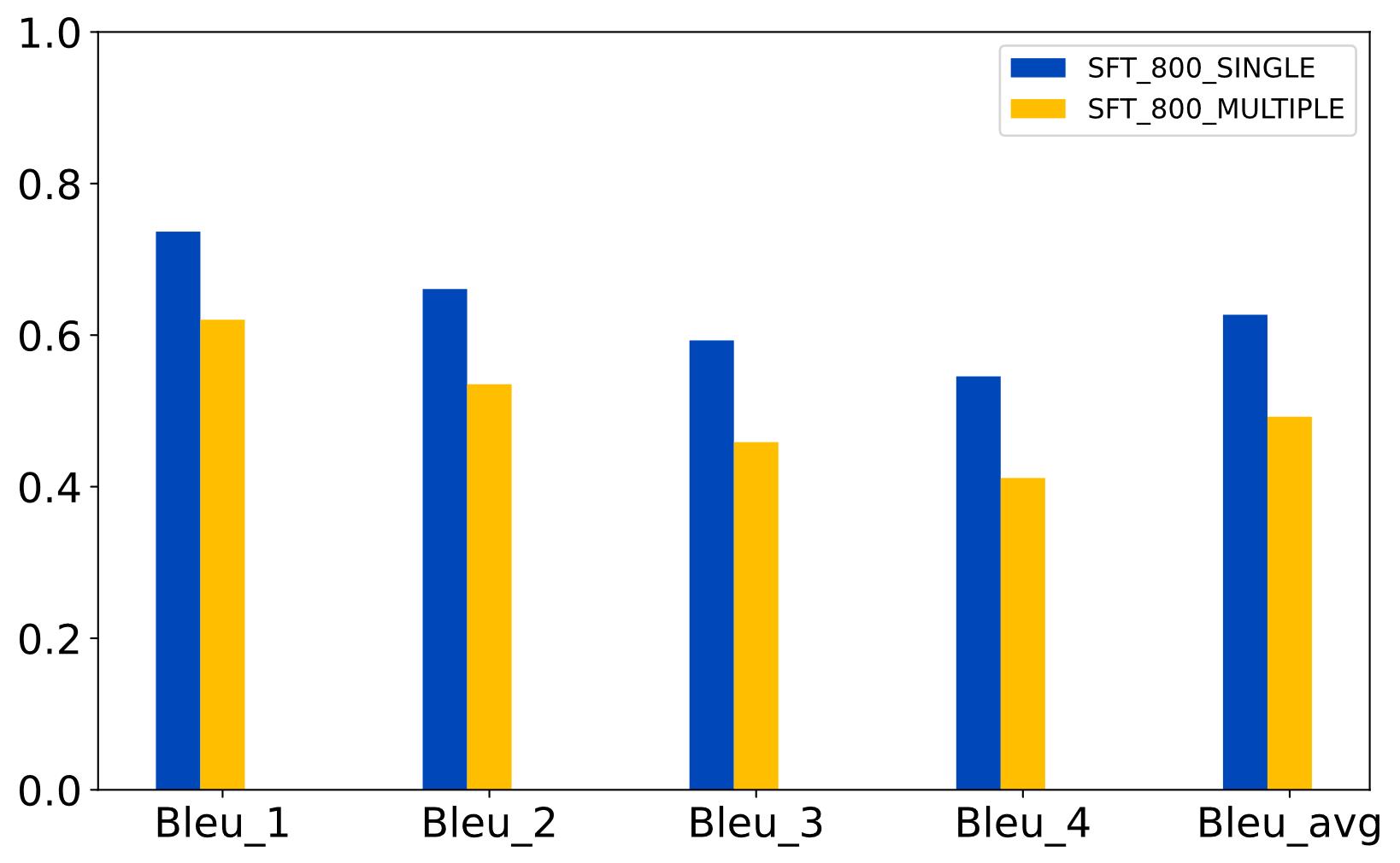
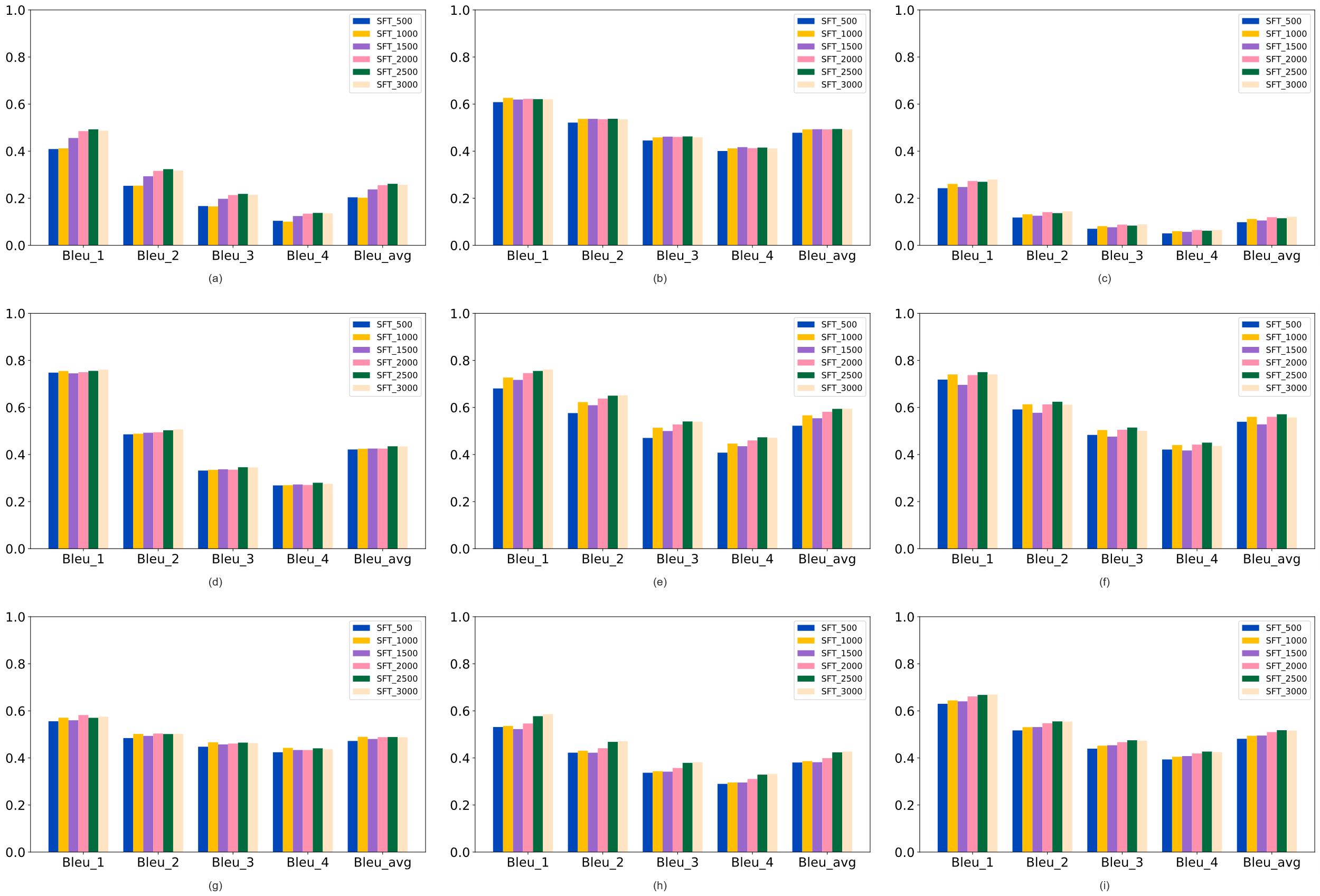
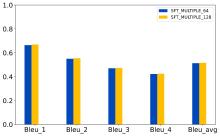
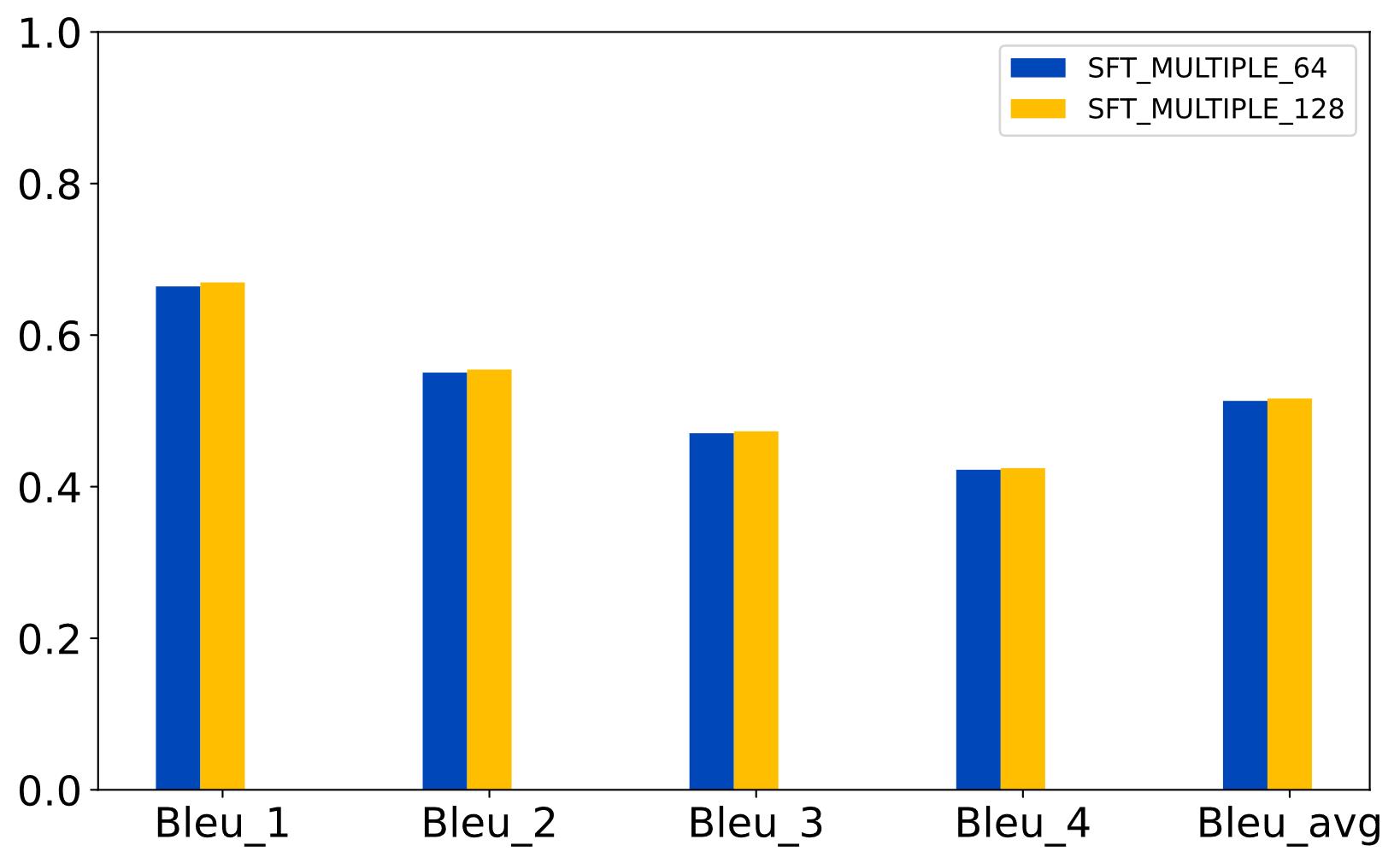
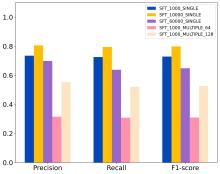
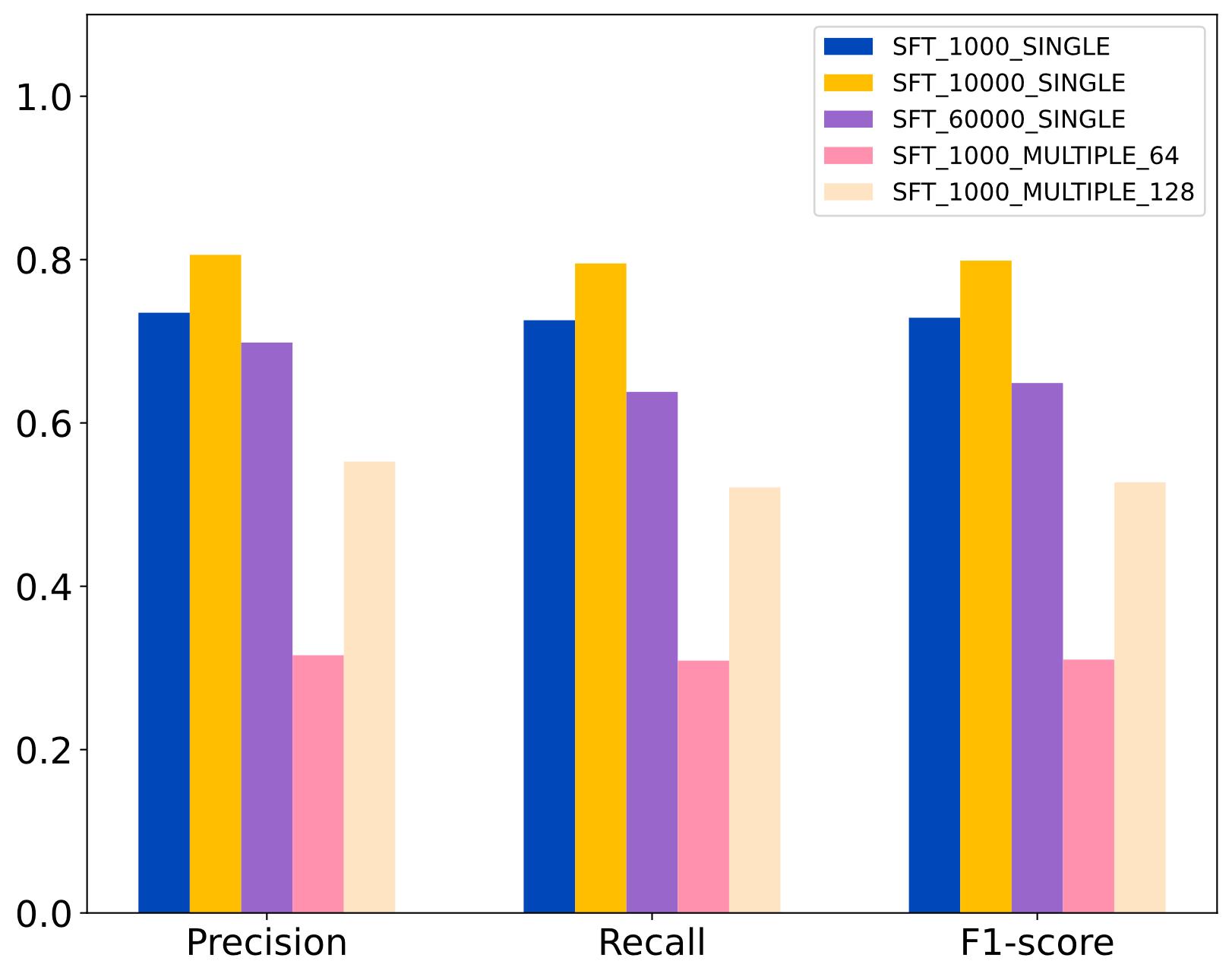
| [1] |
张旭, 雷孝平. 国内外专利情报分析方法、技术与应用研究进展[M]//情报学进展. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012, 9: 287-321.
|
|
Zhang Xu, Lei Xiaoping. Research progress on patent intelligence analysis methods, technologies and applications at home and abroad[M]//Progress in Information Science. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012, 9: 287-321.
|
| [2] |
吕璐成, 罗文馨, 许景龙, 等. 专利情报方法、工具、应用研究进展及新技术应用趋势[J]. 情报学进展, 2020, 13: 235-278.
|
|
Lucheng Lyu, Luo Wenxin, Xu Jinglong, et al. Research progress of patent intelligence methods, tools, applications and application trends of new technologies[J]. Progress in Information Science, 2020, 13: 235-278.
|
| [3] |
胡雅敏, 吴晓燕, 陈方. 基于机器学习的技术术语识别研究综述[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2022, 6(2): 7-17.
|
|
Hu Yamin, Wu Xiaoyan, Chen Fang. Review of technology term recognition studies based on machine learning[J]. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 2022, 6(2): 7-17.
|
| [4] |
吕璐成, 韩涛, 周健, 等. 基于深度学习的中文专利自动分类方法研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2020, 64(10): 75-85.
|
|
Lucheng Lyu, Han Tao, Zhou Jian, et al. Research on the method of Chinese patent automatic classification based on deep learning[J]. Library and Information Service, 2020, 64(10): 75-85.
|
| [5] |
马俊, 吕璐成, 赵亚娟, 等. 基于预训练语言模型的中文专利自动分类研究[J]. 中华医学图书情报杂志, 2022, 31(11): 20-28.
|
|
Ma Jun, Lucheng Lyu, Zhao Yajuan, et al. Research on automatic classification of Chinese patents based on pre-trained language models[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Library and Information Science, 2022, 31(11): 20-28.
|
| [6] |
孙蒙鸽, 韩涛, 王燕鹏, 等. GPT技术变革对基础科学研究的影响分析[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2023, 38(8): 1212-1224.
|
|
Sun Mengge, Han Tao, Wang Yanpeng, et al. Impact analysis of GPT technology revolution on fundamental scientific research[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy Of Sciences, 2023, 38(8): 1212-1224.
|
| [7] |
张智雄, 于改红, 刘熠, 等. ChatGPT对文献情报工作的影响[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2023, 7(3): 36-42.
|
|
Zhang Zhixiong, Yu Gaihong, Liu Yi, et al. The influence of chat GPT on library & information services[J]. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 2023, 7(3): 36-42.
|
| [8] |
张铭洁, 赵瑞雪. ChatGPT驱动的智慧图书馆情感感知与服务优化[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(12): 74-88.
|
|
Zhang Mingjie, Zhao Ruixue. Emotion perception and serviceoptimization in ChatGPT-driven smart libraries[J]. Journal of Library and Information Science in Agriculture, 2024, 36(12): 74-88.
|
| [9] |
Bai Z L, Zhang R J, Chen L Q, et al. PatentGPT: A large language model for intellectual property[PP/OL]. V5. arXiv (2024-06-05)[2025-09-15].
|
| [10] |
Ren R T, Ma J, Luo J X. Large language model for patent concept generation[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2025, 65: 103301.
|
| [11] |
Lee J S. InstructPatentGPT: Training patent language models to follow instructions with human feedback[J]. Artificial Intelligence and Law, 2025, 33(3): 739-782.
|
| [12] |
Liu C, Fomin N I, Xiao S T, et al. How ChatGPT is shaping next-generation patent solutions[J]. Buildings, 2025, 15(13): 2273.
|
| [13] |
Pelaez S, Verma G, Ribeiro B, et al. Large-scale text analysis using generative language models: A case study in discovering public value expressions in AI patents[J]. Quantitative Science Studies, 2024, 5(1): 153-169.
|
| [14] |
Kosonocky C W, Wilke C O, Marcotte E M, et al. Mining patents with large language models elucidates the chemical function landscape[J]. Digital Discovery, 2024, 3(6): 1150-1159.
|
| [15] |
Zhang W, Wang Q G, Kong X T, et al. Fine-tuning large language models for chemical text mining[J]. Chemical Science, 2024, 15(27): 10600-10611.
|
| [16] |
Liu X, Ji K X, Fu Y C, et al. P-tuning: Prompt tuning can be comparable to fine-tuning across scales and tasks[C]//Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers). Stroudsburg, PA, USA: ACL, 2022: 61-68.
|
| [17] |
Hu E J, Shen Y L, Wallis P, et al. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models[PP/OL]. V2. arXiv (2021-10-16)[2025-09-15].
|
| [18] |
李鑫鑫, 马雨萌, 鞠孜涵, 王敬. 基于大语言模型的科技政策评论方面级情感分析研究——以新能源汽车产业为例[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2025, 37(10): 53-66.
|
|
Li Xinxin, Ma Yumeng, Ju Zihan, et al. Aspect-level sentiment analysis of science and technology policy reviews based on large language models: A case study of the new energy vehicle industry[J]. Journal of Library and Information Science in Agriculture, 2025, 37(10): 53-66.
|
| [19] |
赵建飞, 陈挺, 王小梅, 等. 基于大语言模型知识自蒸馏的无标注专利关键信息抽取[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2024, 8(8): 133-143.
|
|
Zhao Jianfei, Chen Ting, Wang Xiaomei, et al. Extracting key information from unlabeled patents based on knowledge self-distillation of large language model[J]. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 2024, 8(8): 133-143.
|
| [20] |
时宗彬, 朱丽雅, 乐小虬. 基于本地大语言模型和提示工程的材料信息抽取方法研究[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2024, 8(7): 23-31.
|
|
Shi Zongbin, Zhu Liya, Le Xiaohong. Material information extraction based on local large language model and prompt engineering[J]. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 2024, 8(7): 23-31.
|
| [21] |
Prottasha N J, Mahmud A, Sobuj M S I, et al. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning of large language models using semantic knowledge tuning[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: 30667.
|