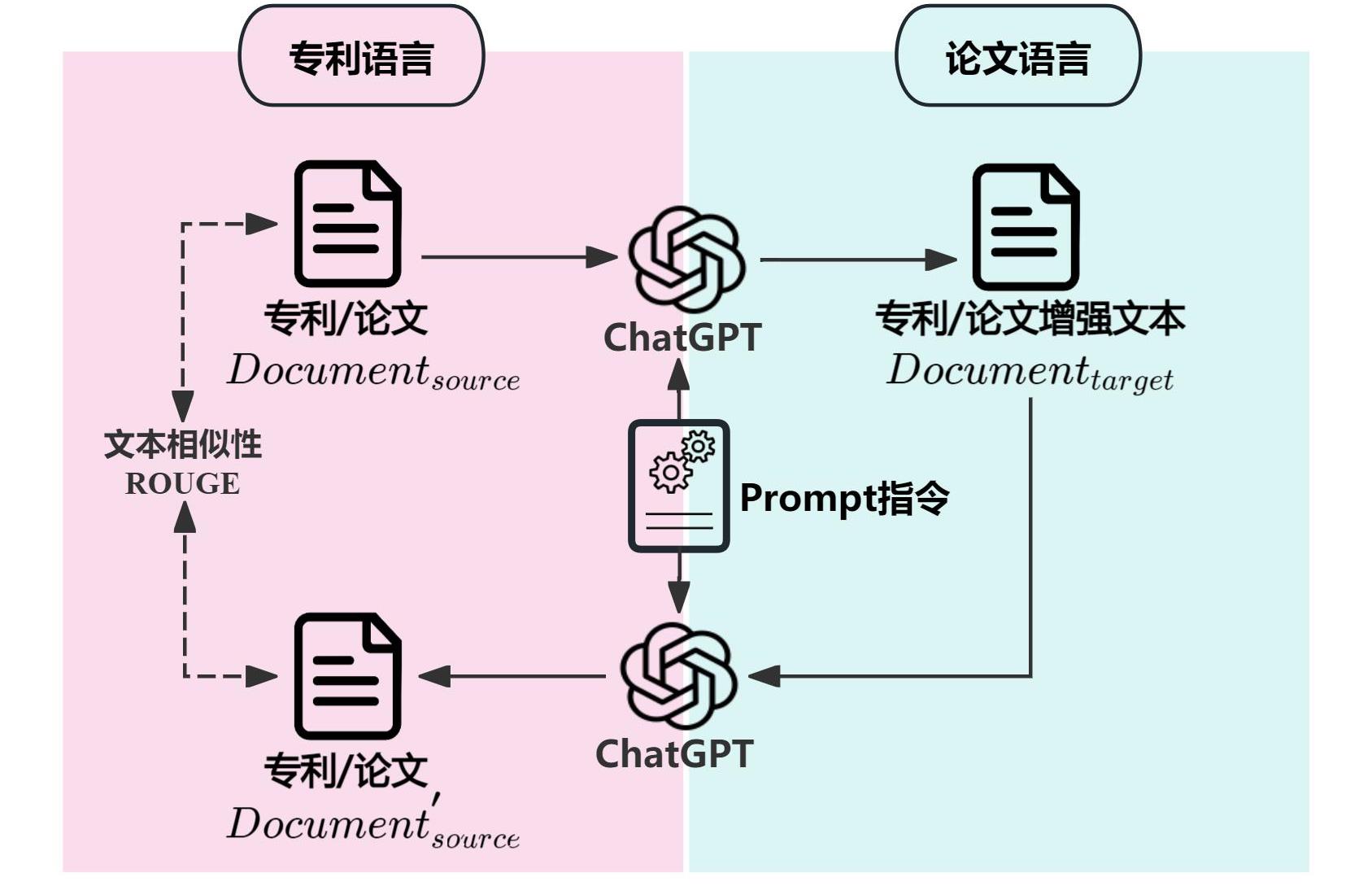
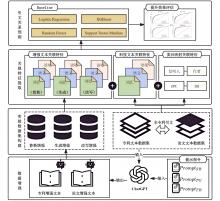
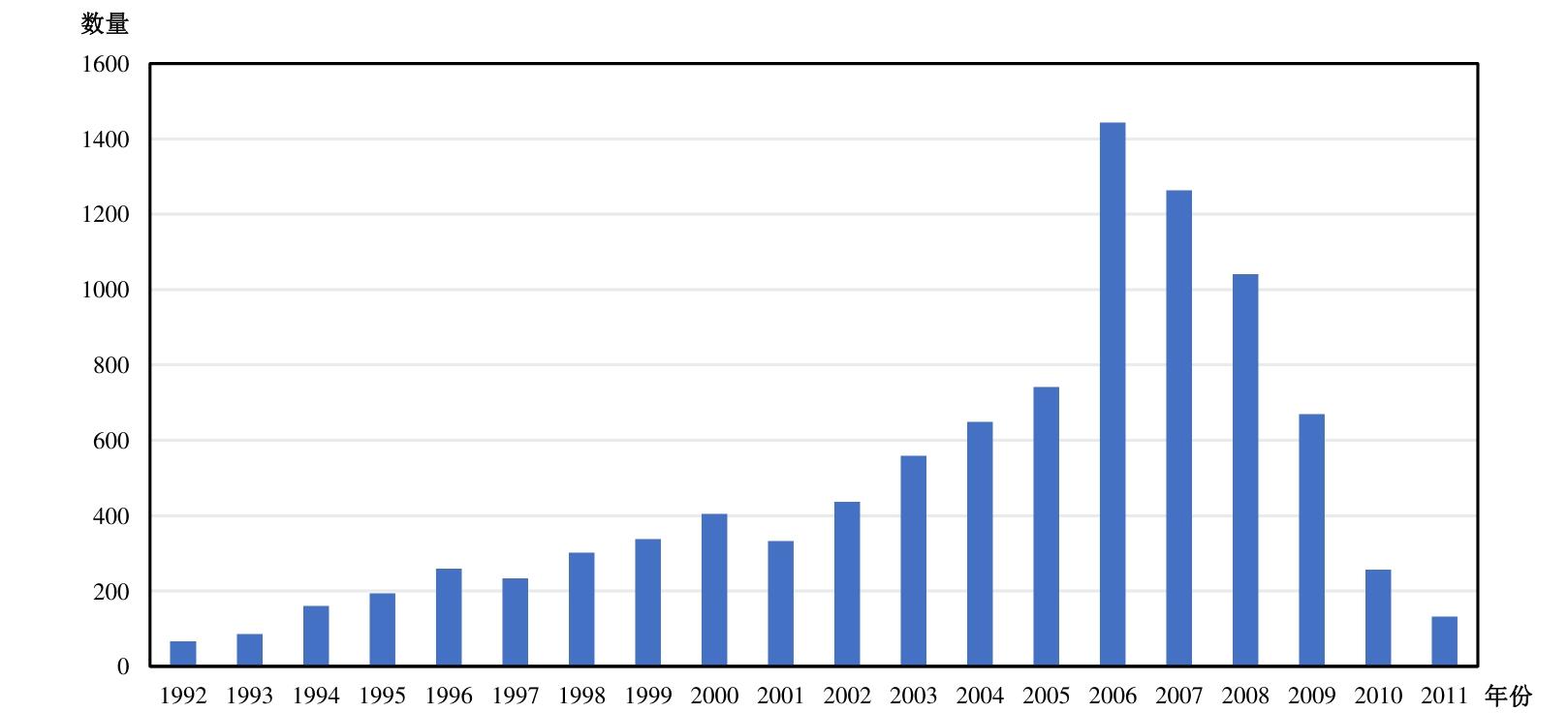
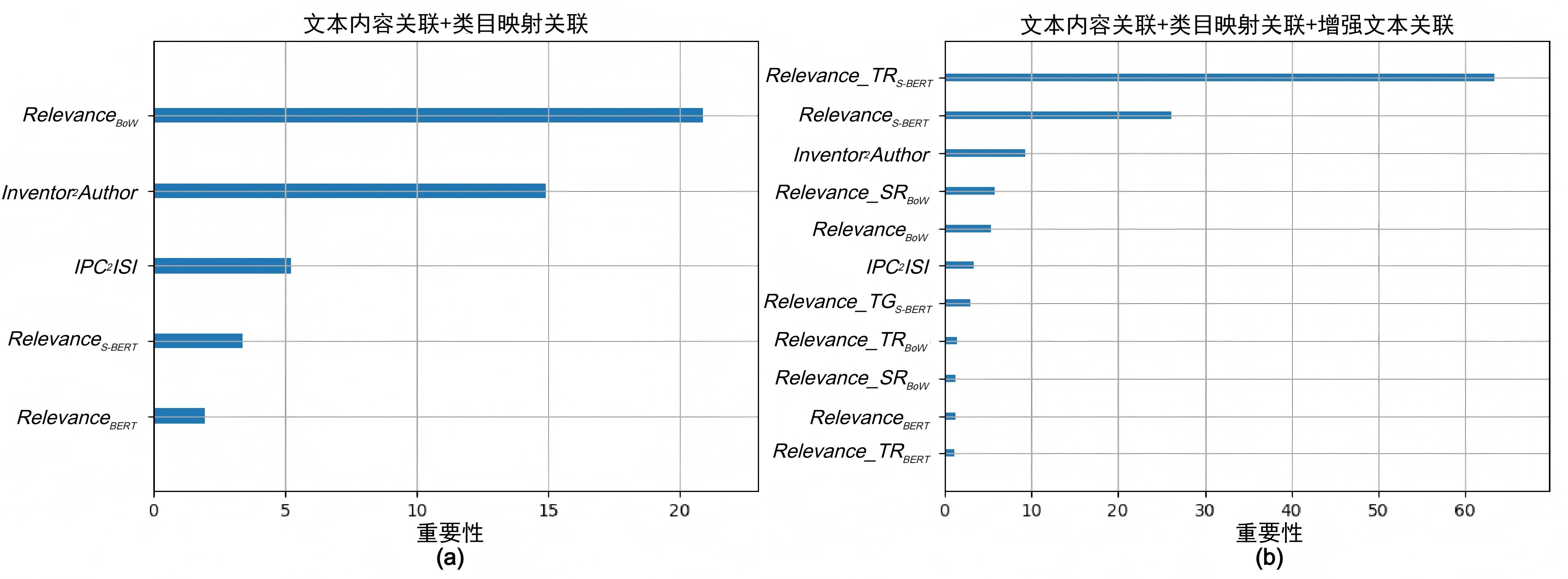
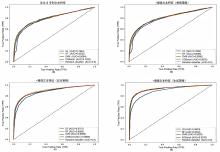
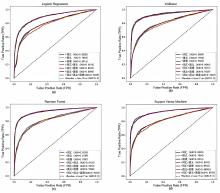
| [1] |
黄璐, 蔡依洁, 陈翔, 等. 组合优化视角下的科技关联识别方法研究[J]. 科学学与科学技术管理, 2024, 45(4): 118-136.
|
|
HUANG L, CAI Y J, CHEN X, et al. Looking for the best allocation of scientific and technological resources: A perspective of combinatorial optimization[J]. Science of science and management of S & T, 2024, 45(4): 118-136.
|
| [2] |
赵志耘, 雷孝平. 我国生物科技领域技术创新与基础研究关联分析: 从专利引文分析的角度[J]. 情报学报, 2012, 31(12): 1283-1289.
|
|
ZHAO Z Y, LEI X P. Analysis of scientific linkage between China's technology innovation and basic research in biotechnology industry based on patent citation[J]. Journal of the China society for scientific and technical information, 2012, 31(12): 1283-1289.
|
| [3] |
VERBEEK A, DEBACKERE K, LUWEL M, et al. Linking science to technology: Using bibliographic references in patents to build linkage schemes[J]. Scientometrics, 2002, 54(3): 399-420.
|
| [4] |
AHMADPOOR M, JONES B F. The dual frontier: Patented inventions and prior scientific advance[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6351): 583-587.
|
| [5] |
LI X, ZHAO D Z, HU X J. Gatekeepers in knowledge transfer between science and technology: An exploratory study in the area of gene editing[J]. Scientometrics, 2020, 124(2): 1261-1277.
|
| [6] |
CHANG S H. A pilot study on the connection between scientific fields and patent classification systems[J]. Scientometrics, 2018, 114(3): 951-970.
|
| [7] |
HAN F, MAGEE C L. Testing the science/technology relationship by analysis of patent citations of scientific papers after decomposition of both science and technology[J]. Scientometrics, 2018, 116(2): 767-796.
|
| [8] |
CALLAERT J, VAN LOOY B, VERBEEK A, et al. Traces of Prior Art: An analysis of non-patent references found in patent documents[J]. Scientometrics, 2006, 69(1): 3-20.
|
| [9] |
MEYER M. Does science push technology Patents citing scientific literature[J]. Research policy, 2000, 29(3): 409-434.
|
| [10] |
MARAUT S, MARTÍNEZ C. Identifying author–inventors from Spain: Methods and a first insight into results[J]. Scientometrics, 2014, 101(1): 445-476.
|
| [11] |
SHIBATA N, KAJIKAWA Y, SAKATA I. Detecting potential technological fronts by comparing scientific papers and patents[J]. Foresight, 2011, 13(5): 51-60.
|
| [12] |
BA Z C, LIANG Z T. A novel approach to measuring science-technology linkage: From the perspective of knowledge network coupling[J]. Journal of informetrics, 2021, 15(3): 101167.
|
| [13] |
XU S, ZHAI D S, WANG F F, et al. A novel method for topic linkages between scientific publications and patents[J]. Journal of the association for information science and technology, 2019, 70(9): 1026-1042.
|
| [14] |
SELVA BIRUNDA S, KANNIGA DEVI R. A review on word embedding techniques for text classification[C]//Innovative Data Communication Technologies and Application. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 267-281.
|
| [15] |
YU D J, YAN Z P. Combining machine learning and main path analysis to identify research front: From the perspective of science-technology linkage[J]. Scientometrics, 2022, 127(7): 4251-4274.
|
| [16] |
XU H Y, YUE Z H, PANG H S, et al. Integrative model for discovering linked topics in science and technology[J]. Journal of informetrics, 2022, 16(2): 101265.
|
| [17] |
车万翔, 窦志成, 冯岩松, 等. 大模型时代的自然语言处理: 挑战、机遇与发展[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(9): 1645-1687.
|
|
CHE W X, DOU Z C, FENG Y S, et al. Towards a comprehensive understanding of the impact of large language models on natural language processing: Challenges, opportunities and future directions[J]. Scientia sinica (informationis), 2023, 53(9): 1645-1687.
|
| [18] |
LIU X Z, XIA T, YU Y Y, et al. Cross social media recommendation[J]. Proceedings of the international AAAI conference on web and social media, 2016, 10(1): 221-230.
|
| [19] |
罗文, 王厚峰. 大语言模型评测综述[J]. 中文信息学报, 2024, 38(1): 1-23.
|
|
LUO W, WANG H F. Evaluating large language models: A survey of research progress[J]. Journal of Chinese information processing, 2024, 38(1): 1-23.
|
| [20] |
黄鲁成, 王静静, 李欣, 等. 基于论文和专利的钙钛矿太阳能电池的技术机会分析[J]. 情报学报, 2016, 35(7): 686-695.
|
|
HUANG L C, WANG J J, LI X, et al. Detecting technology opportunities based on papers and patents for perovskite solar cells[J]. Journal of the China society for scientific and technical information, 2016, 35(7): 686-695.
|
| [21] |
CHOUDHURY N, FAISAL F, KHUSHI M. Mining temporal evolution of knowledge graphs and genealogical features for literature-based discovery prediction[J]. Journal of informetrics, 2020, 14(3): 101057.
|
| [22] |
CHEN X, YE P F, HUANG L, et al. Exploring science-technology linkages: A deep learning-empowered solution[J]. Information processing & management, 2023, 60(2): 103255.
|
| [23] |
刘自强, 许海云, 罗瑞, 等. 基于主题关联分析的科技互动模式识别方法研究[J]. 情报学报, 2019, 38(10): 997-1011.
|
|
LIU Z Q, XU H Y, LUO R, et al. Research on scientific and technological interaction patterns based on topic relevance analysis[J]. Journal of the China society for scientific and technical information, 2019, 38(10): 997-1011.
|
| [24] |
冉从敬, 田文芳, 贾志轩. 基于混合方法的“科学论文-专利技术”关联关系模型构建: 以生物医药领域为例[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(6): 132-143.
|
|
RAN C J, TIAN W F, JIA Z X. Modeling of scientific paper-patent technology association relationship based on mixed methods: Taking the biomedical field as an example[J]. Information science, 2024, 42(6): 132-143.
|
| [25] |
REYNOLDS L, MCDONELL K. Prompt programming for large language models: Beyond the few-shot paradigm[C]//Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. May 8 - 13, 2021, Yokohama, Japan. ACM, 2021: 1-7.
|
| [26] |
YAO S Y, YU D, ZHAO J, et al. Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models[EB/OL]. 2023
|
| [27] |
陆伟, 刘寅鹏, 石湘, 等. 大模型驱动的学术文本挖掘: 推理端指令策略构建及能力评测[J]. 情报学报, 2024, 43(8): 946-959.
|
|
LU W, LIU Y P, SHI X, et al. Large language model-driven academic text mining: Construction and evaluation of inference-end prompting strategy[J]. Journal of the China society for scientific and technical information, 2024, 43(8): 946-959.
|
| [28] |
张颖怡, 章成志, 周毅, 等. 基于ChatGPT的多视角学术论文实体识别: 性能测评与可用性研究[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2023, 7(9): 12-24.
|
|
ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG C Z, ZHOU Y, et al. ChatGPT-based scientific paper entity recognition: Performance measurement and availability research[J]. Data analysis and knowledge discovery, 2023, 7(9): 12-24.
|
| [29] |
吴娜, 沈思, 王东波. 基于开源LLMs的中文学术文本标题生成研究: 以人文社科领域为例[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(7): 137-145.
|
|
WU N, SHEN S, WANG D B. Chinese academic text title generation based on open source large language models: Taking the field of humanities and social sciences as an example[J]. Information science, 2024, 42(7): 137-145.
|
| [30] |
DONG C H, LI Y H, GONG H F, et al. A survey of natural language generation[J]. ACM computing surveys, 2022, 55(8): 1-38.
|
| [31] |
DAI H X, LIU Z L, LIAO W X, et al. AugGPT: Leveraging ChatGPT for text data augmentation[J/OL]. arXiv: 2302.13007,2023.
|
| [32] |
张恒, 赵毅, 章成志. 基于SciBERT与ChatGPT数据增强的研究流程段落识别[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(1): 164-172, 153.
|
|
ZHANG H, ZHAO Y, ZHANG C Z. Recognition of research workflow paragraphs based on SciBERT and ChatGPT data augmentation[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2024, 47(1): 164-172, 153.
|
| [33] |
MENG K, BA Z C, MA Y X, et al. A network coupling approach to detecting hierarchical linkages between science and technology[J]. Journal of the association for information science and technology, 2024, 75(2): 167-187.
|
| [34] |
DING B S, QIN C W, ZHAO R C, et al. Data augmentation using LLMs: Data perspectives, learning paradigms and challenges[C]//Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics ACL 2024. Bangkok, Thailand and virtual meeting. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: ACL, 2024: 1679-1705.
|
| [35] |
LIN C Y. ROUGE: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries[C]//Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics., 2004
|
| [36] |
SHARMA P, LI Y B. Self-supervised contextual keyword and keyphrase retrieval with self-labelling[EB/OL]. [2025-06-12].
|
| [37] |
REIMERS N, GUREVYCH I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks[J/OL]. arXiv: 1908.10084, 2019.
|
| [38] |
DAIR AI. Prompt engineering guide[EB/OL]. [2023-12-14].
|