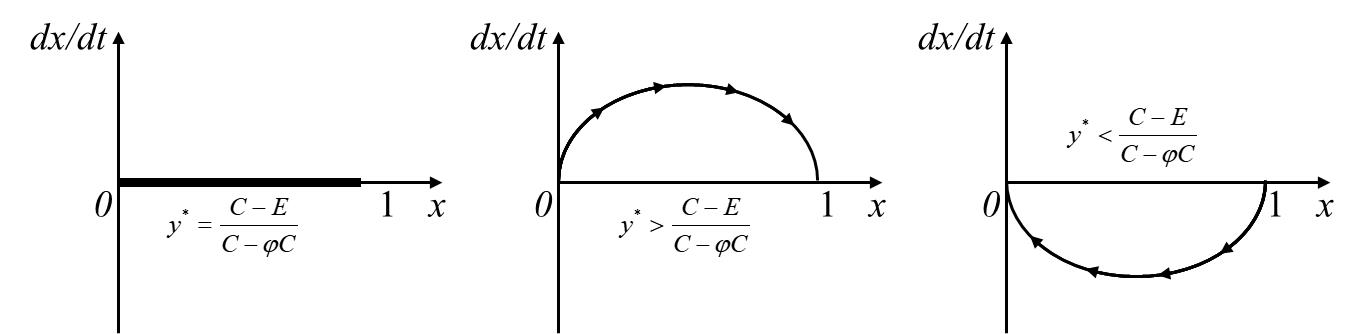
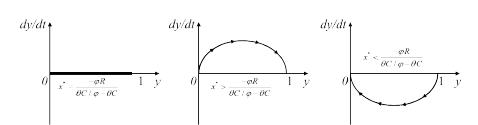
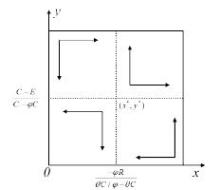
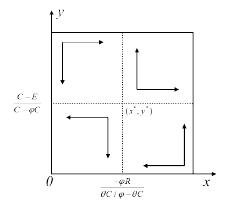
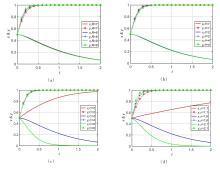
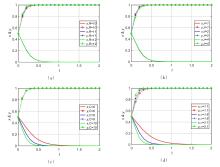
| [1] |
张铮, 刘晨旭. 海量信息下社交媒体用户数字囤积的心理机制初探[J]. 西南民族大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2024, 45(4): 135-142.
|
|
Zhang Zheng, Liu Chenxu. A preliminary study on the psychological mechanism of digital hoarding by social media users under massive information[J]. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 2024, 45(4): 135-142.
|
| [2] |
王琳, 杜田羽, 朱华健. 社交媒体环境下大学生数据囤积行为形成机理研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2022, 45(1): 22-29.
|
|
Wang Lin, Du Tianyu, Zhu Huajian. The formation mechanism of data hoarding behavior in social media context: Taking college students as an example[J]. Information Studies (Theory & Application), 2022, 45(1): 22-29.
|
| [3] |
Sedera D, Lokuge S, Grover V. Modern-day hoarding: A model for understanding and measuring digital hoarding[J]. Information & Management, 2022, 59(8): 103700.
|
| [4] |
国家互联网信息办公室, 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部, 中华人民共和国公安部, 等. 互联网信息服务算法推荐管理规定[EB/OL]. [2022-03-30].
|
| [5] |
Paasonen S. Affect, data, manipulation and price in social media[J]. Distinktion: Journal of Social Theory, 2018, 19(2): 214-229.
|
| [6] |
汤景泰, 星辰. 作为“武器”的谣言: 基于计算宣传的认知操纵[J]. 新闻大学, 2023(8): 16-30, 116-117.
|
|
Tang Jingtai, Xing Chen. Disinformation as "weapon": Cognitive manipulation based on computational propaganda[J]. Journalism Research, 2023(8): 16-30, 116-117.
|
| [7] |
袁静, 李柯. 移动社交媒体环境下用户信息焦虑行为研究进展[J]. 图书情报工作, 2020, 64(11): 133-144.
|
|
Yuan Jing, Li Ke. Research progress of user's information anxiety behavior in mobile social media environment[J]. Library and Information Service, 2020, 64(11): 133-144.
|
| [8] |
Shin D. How do users interact with algorithm recommender systems? The interaction of users, algorithms, and performance[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2020, 109: 106344.
|
| [9] |
张晓璐. 可供性视角下青年群体的数字囤积行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2024.
|
|
Zhang Xiaolu. Research on digital hoarding behavior of youth groups from the perspective of affordance[D]. Harbin: Helongjiang University, 2024.
|
| [10] |
谭春辉, 邹雅婷, 王仪雯, 等. 社交媒体用户的UGC数字囤积行为形成机理[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2025, 45(3): 130-140.
|
|
Tan Chunhui, Zou Yating, Wang Yiwen, et al. Formation mechanism of UGC digital hoarding behavior of social media users[J]. Library Tribune, 2025, 45(3): 130-140.
|
| [11] |
张征, 贺伟. 大学生数字囤积行为的影响因素及组态路径研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2023, 46(1): 108-114.
|
|
Zhang Zheng, He Wei. Research on the factors influencing digital hoarding behavior of college students and the configuration path[J]. Information Studies (Theory & Application), 2023, 46(1): 108-114.
|
| [12] |
赵栋祥. 个人的数字囤积行为研究进展与展望[J]. 情报杂志, 2022, 41(8): 194-200, 184.
|
|
Zhao Dongxiang. Review and outlook of personal digital hoarding behaviors[J]. Journal of Intelligence, 2022, 41(8): 194-200, 184.
|
| [13] |
贾明霞, 赵宇翔, 朱庆华, 等. 双系统理论视角下用户数字囤积行为的形成机理与演化路径研究[J]. 情报学报, 2024, 43(3): 339-356.
|
|
Jia Mingxia, Zhao Yuxiang, Zhu Qinghua, et al. Formation and evolution path of user's digital hoarding behavior: A dual-system theory perspective[J]. Journal of the China Society for Scientific AndTechnical Information, 2024, 43(3): 339-356.
|
| [14] |
刘亚丽, 范逢春. 社交媒体用户数字囤积行为要素识别与影响路径研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2023, 46(7): 87-97.
|
|
Liu Yali, Fan Fengchun. Factor identification and influence path of social media users' digital hoarding behavior[J]. Information Studies (Theory & Application), 2023, 46(7): 87-97.
|
| [15] |
李龙飞, 张国良. 算法时代“信息茧房”效应生成机理与治理路径——基于信息生态理论视角[J]. 电子政务, 2022(9): 51-62.
|
|
Li Longfei, Zhang Guoliang. Generation mechanism and governance path of "information cocoon room" effect in algorithm era - Based on the perspective of information ecology theory[J]. E-Government, 2022(9): 51-62.
|
| [16] |
姜婷婷, 许艳闰. 国外过滤气泡研究: 基础、脉络与展望[J]. 情报学报, 2021, 40(10): 1108-1117.
|
|
Jiang Tingting, Xu Yanrun. Filter bubbles - Induced by personalized recommendation algorithms: A review of related research[J]. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 2021, 40(10): 1108-1117.
|
| [17] |
刘强, 赵茜. 算法中选择的同化与异化——国外回音室效应研究20年述评与展望[J]. 新闻界, 2021(6): 29-38.
|
|
Liu Qiang, Zhao Qian, Xi. Assimilation and alienation in the algorithm of choice - Review and prospect of the research on echo chamber effect abroad[J]. Press Circles, 2021(6): 29-38.
|
| [18] |
朱丽丽, 姜红莉. 消极绩效主义实践: 基于社交平台青年群体数字囤积行为的研究[J]. 国际新闻界, 2024, 46(6): 154-176.
|
|
Zhu Lili, Jiang Hongli. The practice of negative-performancism: A study based on the digital hoarding behavior of young people in social platforms[J]. Chinese Journal of Journalism & Communication, 2024, 46(6): 154-176.
|
| [19] |
张艳丰, 刘敏. 移动社交媒体用户数字囤积行为生成机理与引导策略研究[J]. 情报资料工作, 2024, 45(2): 48-56.
|
|
Zhang Yanfeng, Liu Min. Research on the formation mechanism and guiding strategies of digital hoarding behavior of mobile social media users[J]. Information and Documentation Services, 2024, 45(2): 48-56.
|
| [20] |
van Bennekom M J, Blom R M, Vulink N, et al. A case of digital hoarding[J]. BMJ Case Reports, 2015, 2015: bcr2015210814.
|
| [21] |
Neave N, Briggs P, McKellar K, et al. Digital hoarding behaviours: Measurement and evaluation[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2019, 96: 72-77.
|
| [22] |
邓胜利, 贾哲宇, 夏苏迪, 等. 网络用户算法推荐服务接受意愿与使用行为背离研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(2): 3-13.
|
|
Deng Shengli, Jia Zheyu, Xia Sudi, et al. Research on the deviation between acceptance willingness and usage behavior of online users' algorithmic, recommendation service[J]. Library and Information Service, 2023, 67(2): 3-13.
|
| [23] |
Kim T, Im I. Understanding users' AI manipulation intention: An empirical investigation of the antecedents in the context of AI recommendation algorithms[J]. Information & Management, 2025, 62(1): 104061.
|
| [24] |
Fink L, Newman L, Haran U. Let me decide: Increasing user autonomy increases recommendation acceptance[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2024, 156: 108244.
|
| [25] |
赵栋祥. 在线健康社区信息服务质量优化研究——基于演化博弈的分析[J]. 情报科学, 2018, 36(8): 149-154.
|
|
Zhao Dongxiang. Research on online health community information service quality optimization: Based on evolutionary game theory[J]. Information Science, 2018, 36(8): 149-154.
|
| [26] |
Hirshleifer J. Evolutionary models in economics and law: Cooperation versus conflict strategies[J]. Research in Law & Economics, 1982(4): 1-60.
|
| [27] |
张瑞, 赵栋祥, 唐旭丽, 等. 社交媒体用户倦怠行为演化博弈及仿真分析[J]. 现代情报, 2019, 39(11): 46-54, 68.
|
|
Zhang Rui, Zhao Dongxiang, Tang Xuli, et al. Evolutionary game and simulation analysis of user fatigue behavior on social media[J]. Modern Information, 2019, 39(11): 46-54, 68.
|
| [28] |
彭焕萍, 陈瑶. 短视频推荐中的算法操控及其协同治理[J]. 中国编辑, 2023(3): 86-90.
|
|
Peng Huanping, Chen Yao. Algorithm manipulation and collaborative governance in short video recommendation[J]. Chinese Editors Journal, 2023(3): 86-90.
|
| [29] |
刘天元, 贾煜. 青年群体数字囤积行为的形成机理及其结果效应——基于内部动因视角的分析[J]. 中国青年研究, 2023(2): 93-100.
|
|
Liu Tianyuan, Jia Yu. The formation mechanism and result effect of youth group's digital hoarding behavior—Based on the internal motivation perspective[J]. China Youth Study, 2023(2): 93-100.
|
| [30] |
孙梦阳, 孙琦, 陈隽旎. 社交媒体原创内容如何影响商业内容——基于微观数据的实证研究[J]. 南开管理评论, 2024, 27(4): 153-163.
|
|
Sun Mengyang, Sun Qi, Chen Junni. How does organic content on social media platform affect sponsored content: An empirical study based on micro-level data of influencers[J]. Nankai Business Review, 2024, 27(4): 153-163.
|
| [31] |
Weibull J W. Evolutionary Game Theory[M]. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 1995.
|
| [32] |
Friedman D. Evolutionary games in economics[J]. Econometrica, 1991, 59(3): 637-666.
|
| [33] |
倪珍妮, 张帅, 姚志臻. 信息过载效应下在线健康社区用户信息规避行为演化博弈分析[J]. 现代情报, 2022, 42(4): 77-87, 133.
|
|
Ni Zhenni, Zhang Shuai, Yao Zhizhen. Evolutionary game analysis of information avoidance behavior of users in online health community under information overload effect[J]. Journal of Modern Information, 2022, 42(4): 77-87, 133.
|
| [34] |
胡媛, 蒋天森, 古淋鑫, 等. 跨平台社交媒体用户生成内容差异研究[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(4): 69-78.
|
|
Hu Yuan, Jiang Tiansen, Gu Linxin, et al. Cross-platform social media user-generated content differences[J]. Information Science, 2024, 42(4): 69-78.
|
| [35] |
中国互联网络信息中心. 第54 次《中国互联网络发展状况统计报告》发布[EB/OL]. [2024-08-29].
|
| [36] |
李玥琪. 社交网络舆情多平台主题图谱构建及风险识别研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023.
|
|
Li Yueqi. Research on the Construction of Topic Graph and Risk Identification of Multi-Platform Social Network Public Opinion[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023.
|
| [37] |
李武, 姚婧雅, 梁悦. 问答社区平台与用户策略选择的创新路径演化博弈分析[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2022, 42(5): 140-149.
|
|
Li Wu, Yao Jingya, Liang Yue. An evolutionary game analysis of innovation paths of Q & a community platforms and user strategic choices[J]. Library Tribune, 2022, 42(5): 140-149.
|
| [38] |
莫祖英, 赵悦名, 王垲烁. 突发公共事件下社交媒体虚假信息自净化动态博弈模型演化分析[J]. 情报杂志, 2023, 42(9): 98-108.
|
|
Mo Zuying, Zhao Yueming, Wang Kaishuo. Evolutionary analysis of the dynamic game model for self-purification of social media disinformation under public emergencies[J]. Journal of Intelligence, 2023, 42(9): 98-108.
|
| [39] |
屈楠伟, 夏志杰, 王诣铭. 基于用户信息行为的社交媒体辟谣效果研究[J]. 情报科学, 2021, 39(1): 111-119.
|
|
Qu Nanwei, Xia Zhijie, Wang Yiming. Research on the rejection effect of social media based on user information behavior[J]. Information Science, 2021, 39(1): 111-119.
|
| [40] |
陈积银, 胡睿心. 把关与操纵: 中国主流媒体与商业社交媒体推荐算法价值的比较研究[J]. 福建师范大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2024(2): 105-117, 170-171.
|
|
Chen Jiyin, Hu Ruixin. Gatekeeping and manipulation: A comparative study of the values of recommendation algorithms in China's mainstream media and commercial social media[J]. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 2024(2): 105-117, 170-171.
|
| [41] |
Li D, Deng Ceyu, Wang Xiaoguang, et al. Joint inter-word and inter-sentence multi-relation modeling for summary-based recommender system[J]. Information Processing & Management, 2024, 61(3): 103631.
|