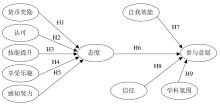
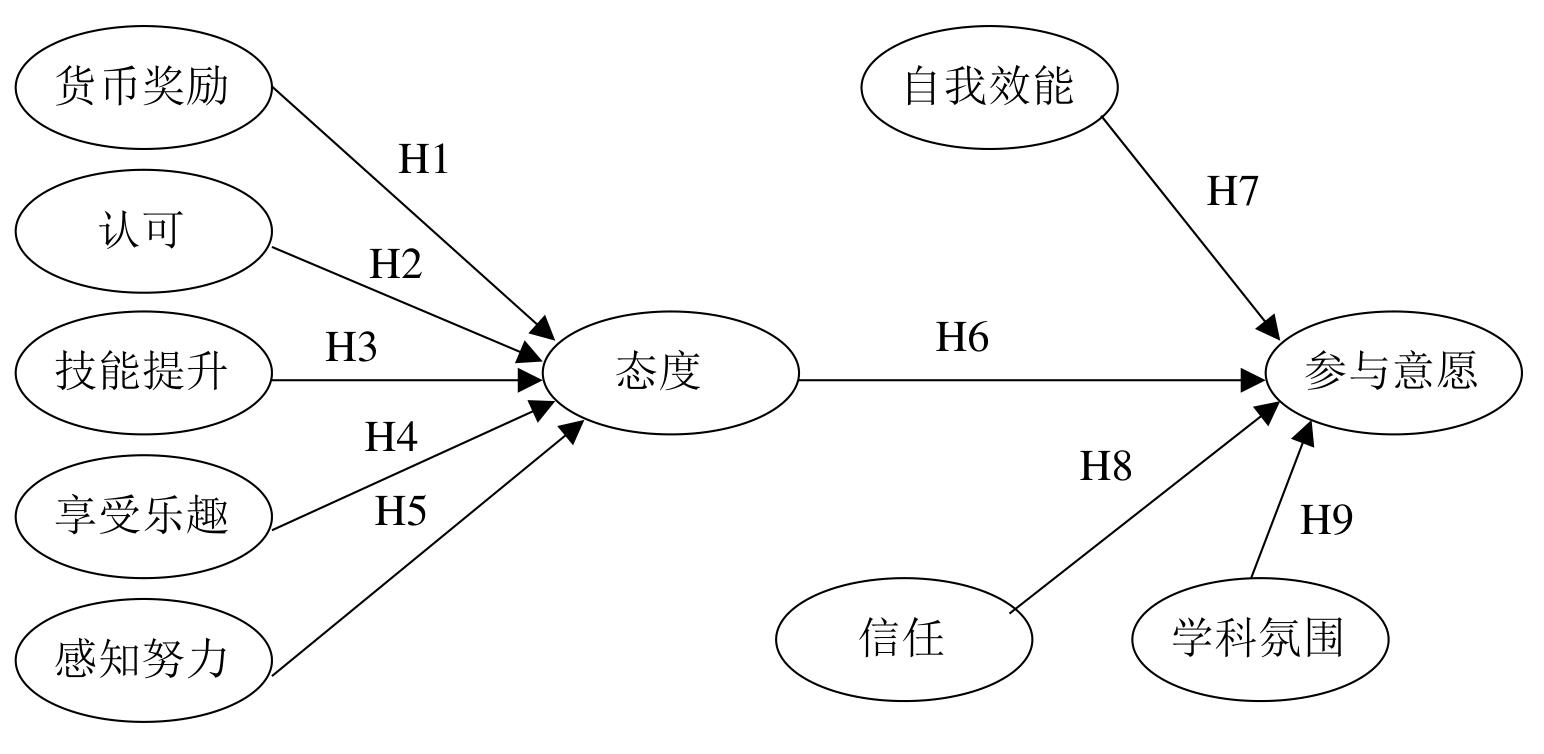
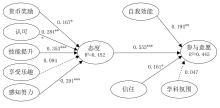
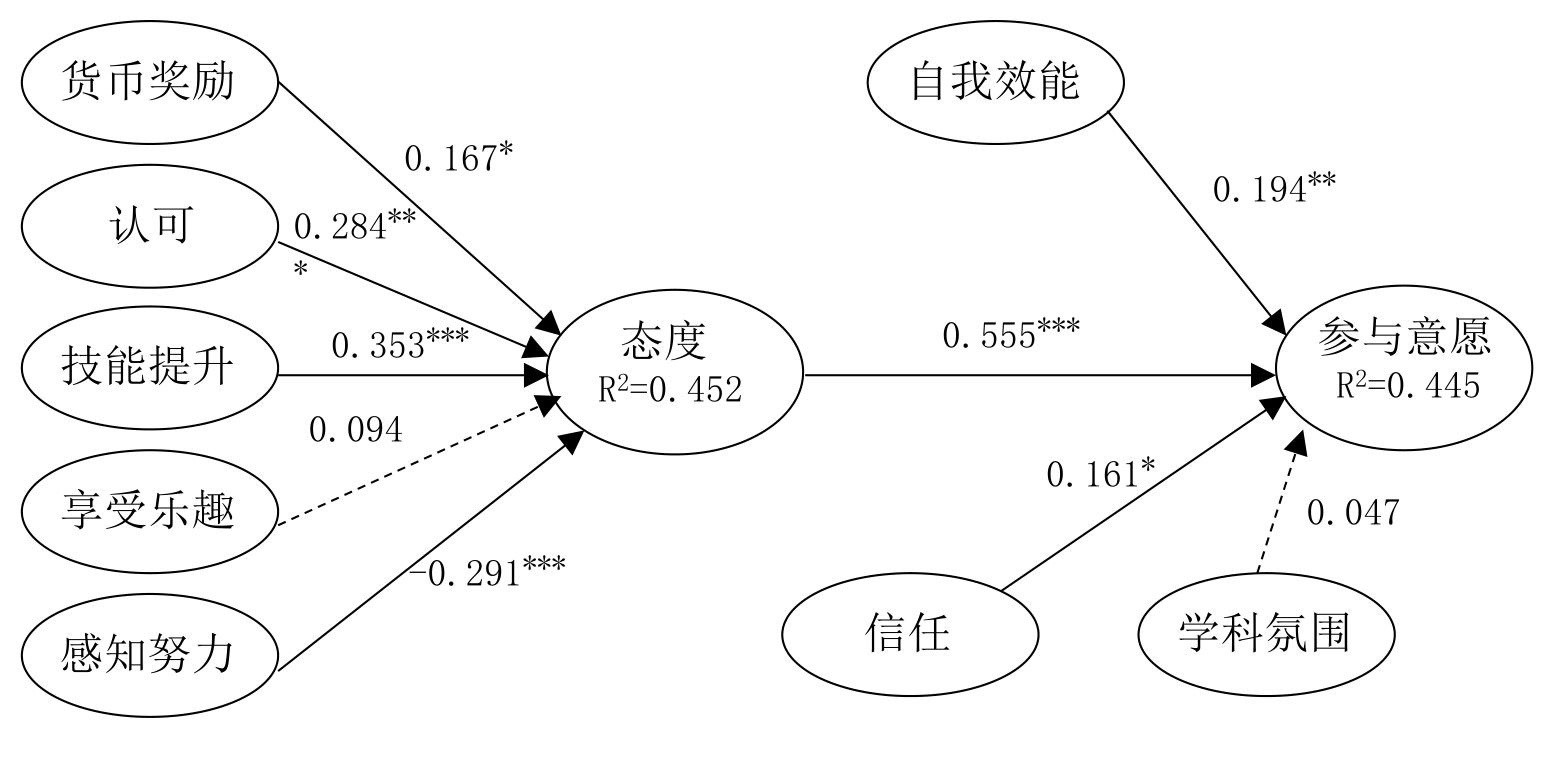
| 1 |
李晓, 曲建升, 寇蕾蕾. 众包在证据合成中的实践应用研究: 以Cochrane Crowd公民科学项目中的众包应用为例[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(2): 95-104.
|
|
LI X, QU J S, KOU L L. Applications of crowdsourcing in evidence synthesis: A case study of cochrane crowd[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2023, 35(2): 95-104.
|
| 2 |
BROWN A W, ALLISON D B. Using crowdsourcing to evaluate published scientific literature: Methods and example[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e100647.
|
| 3 |
SUN Y, CHENG P, WANG S, et al. Crowdsourcing information extraction for biomedical systematic reviews[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2016.
|
| 4 |
MORTENSEN M L, ADAM G P, TRIKALINOS T A, et al. An exploration of crowdsourcing citation screening for systematic reviews[J]. Research synthesis methods, 2017, 8(3): 366-386.
|
| 5 |
NAMA N, SAMPSON M, BARROWMAN N, et al. Crowdsourcing the citation screening process for systematic reviews: Validation study[J]. Journal of medical Internet research, 2019, 21(4): e12953.
|
| 6 |
NAMA N, ILIRIANI K, XIA M Y, et al. A pilot validation study of crowdsourcing systematic reviews: Update of a searchable database of pediatric clinical trials of high-dose vitamin D[J]. Translational pediatrics, 2017, 6(1): 18-26.
|
| 7 |
NOEL-STORR A H, REDMOND P, LAMÉ G, et al. Crowdsourcing citation-screening in a mixed-studies systematic review: A feasibility study[J]. BMC medical research methodology, 2021, 21(1): 88.
|
| 8 |
NOEL-STORR A, GARTLEHNER G, DOOLEY G, et al. Crowdsourcing the identification of studies for COVID-19-related cochrane rapid reviews[J]. Research synthesis methods, 2022, 13(5): 585-594.
|
| 9 |
THOMAS J, NOEL-STORR A, MARSHALL I, et al. Living systematic reviews: Combining human and machine effort[J]. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 2017, 91: 31-37.
|
| 10 |
STRANG L, SIMMONS R K. Citizen science: Crowdsourcing for systematic reviews[M]. Cambridge: THIS Institute, 2018.
|
| 11 |
FELIZARDO K R, DE SOUZA E F, LOPES R, et al. Crowdsourcing in systematic reviews: A systematic mapping and survey[C]//2020 46th Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA). August 26-28, 2020. Portoroz, Slovenia. IEEE, 2020: 404-412.
|
| 12 |
MOREAU D, GAMBLE B. Conducting a meta-analysis in the age of open science: Tools, tips, and practical recommendations[J]. Psychological methods, 2022, 27(3): 426.
|
| 13 |
WEISS M, ABUALHAOL I, AMIN M. A leader-driven open collaboration platform for exploring new domains[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Open Collaboration. Berlin Germany. ACM, 2016: 1-4.
|
| 14 |
WEISS M. Crowdsourcing literature reviews in new domains[J]. Technology innovation management review, 2016, 6(2): 5-14.
|
| 15 |
NAMA N, BARROWMAN N, O’HEARN K, et al. Quality control for crowdsourcing citation screening: The importance of assessment number and qualification set size[J]. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 2020, 122: 160-162.
|
| 16 |
KRIVOSHEEV E, CASATI F, CAFORIO V, et al. Crowdsourcing paper screening in systematic literature reviews[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on human computation and crowdsourcing, 2017, 5: 108-117.
|
| 17 |
KRIVOSHEEV E, CASATI F, BENATALLAH B. Crowd-based multi-predicate screening of papers in literature reviews[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference on World Wide Web - WWW '18. Lyon, France: ACM, 2018: 55-64.
|
| 18 |
SAMPSON M, NAMA N, O'HEARN K, et al. Creating enriched training sets of eligible studies for large systematic reviews: The utility of PubMed's Best Match algorithm[J]. International journal of technology assessment in health care, 2020, 37: e7.
|
| 19 |
RAMIREZ J, KRIVOSHEEV E, BAEZ M, et al. Crowdrev: A platform for crowd-based screening of literature reviews[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2018.
|
| 20 |
SANTOS V, IWAZAKI A, SOUZA É, et al. CrowdSLR: A tool to support the use of crowdsourcing in systematic literature reviews[C]//Brazilian Symposium on Software Engineering. Joinville Brazil. ACM, 2021: 341-346.
|
| 21 |
NOEL-STORR A, DOOLEY G, ELLIOTT J, et al. An evaluation of Cochrane Crowd found that crowdsourcing produced accurate results in identifying randomized trials[J]. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 2021, 133: 130-139.
|
| 22 |
PIANTA M J, MAKRAI E, VERSPOOR K M, et al. Crowdsourcing critical appraisal of research evidence (CrowdCARE) was found to be a valid approach to assessing clinical research quality[J]. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 2018, 104: 8-14.
|
| 23 |
ASHKANASE J, NAMA N, SANDARAGE R V, et al. Identification and evaluation of controlled trials in pediatric cardiology: Crowdsourced scoping review and creation of accessible searchable database[J]. Canadian journal of cardiology, 2020, 36(11): 1795-1804.
|
| 24 |
SHAH N, GUO Y J, WENDELSDORF K V, et al. A crowdsourcing approach for reusing and meta-analyzing gene expression data[J]. Nature biotechnology, 2016, 34(8): 803-806.
|
| 25 |
荷兰心理统计联盟. 共建管理学元分析数据库[EB/OL]. [2022-03-22]. .
|
|
Netherlands Society for Psychometrics and Statistics. Co-constructing a meta-analysis database for management research[EB/OL]. [2022-03-22]. .
|
| 26 |
BOSCO F A, UGGERSLEV K L, STEEL P. MetaBUS as a vehicle for facilitating meta-analysis[J]. Human resource management review, 2017, 27(1): 237-254.
|
| 27 |
LEBEL E P, MCCARTHY R J, EARP B D, et al. A unified framework to quantify the credibility of scientific findings[J]. Advances in methods and practices in psychological science, 2018, 1(3): 389-402.
|
| 28 |
SHACKELFORD G E, KEMP L, RHODES C, et al. Accumulating evidence using crowdsourcing and machine learning: A living bibliography about existential risk and global catastrophic risk[J]. Futures, 2020, 116: 102508.
|
| 29 |
HONG Q N, BOUIX-PICASSO J, RUCHON C. Creation of an online inventory for choosing critical appraisal tools[J]. Education for information, 2022, 38(2): 205-210.
|
| 30 |
AJZEN I. From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior[M]//Action Control: From Cognition to Behavior. New York: Springer, 1985: 11-39.
|
| 31 |
AJZEN I. The theory of planned behavior[J]. Organizational behavior & human decision processes, 1991, 50(2): 179–211.
|
| 32 |
AJZEN I. Perceived behavioral control, self-efficacy, locus of control, and the theory of planned behavior[J]. Journal of applied social psychology, 2002, 32(4): 665-683.
|
| 33 |
DAVIS F D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology[J]. MIS quarterly, 1989, 13(3): 319.
|
| 34 |
PETRI H L, GOVERN J M. Motivation: Theory, research, and application[M]. Boston: Cengage Learning, 2012.
|
| 35 |
MILLER K A, DECI E L, RYAN R M. Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior[J]. Contemporary sociology, 1988, 17(2): 253.
|
| 36 |
ZHENG H C, LI D H, HOU W H. Task design, motivation, and participation in crowdsourcing contests[J]. International journal of electronic commerce, 2011, 15(4): 57-88.
|
| 37 |
NOV O, NAAMAN M, YE C. Analysis of participation in an online photo-sharing community: A multidimensional perspective[J]. Journal of the American society for information science and technology, 2010, 61(3): 555-566.
|
| 38 |
GOH D H, PE-THAN E P P, LEE C S. Perceptions of virtual reward systems in crowdsourcing games[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2017, 70: 365-374.
|
| 39 |
LAKHANI K R, JEPPESEN L B, LOHSE P A, et al. The value of openess in scientific problem solving[M]//Division of Research. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School, 2007.
|
| 40 |
KATZ D. The functional approach to the study of attitudes[J]. Public opinion quarterly, 1960, 24(2): 163-204.
|
| 41 |
ARMITAGE C J, CONNER M. Efficacy of the theory of planned behaviour: A meta-analytic review[J]. British journal of social psychology, 2001, 40(4): 471-499.
|
| 42 |
Collaboration Cochrane. Cochrane crowd[EB/OL]. [2022-06-18]. .
|
| 43 |
KE W L, ZHANG P. Motivations in open source software communities: The mediating role of effort intensity and goal commitment[J]. International journal of electronic commerce, 2009, 13(4): 39-66.
|
| 44 |
ACAR O A. Motivations and solution appropriateness in crowdsourcing challenges for innovation[J]. Research policy, 2019, 48(8): 103716.
|
| 45 |
OREG S, NOV O. Exploring motivations for contributing to open source initiatives: The roles of contribution context and personal values[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2008, 24(5): 2055-2073.
|
| 46 |
GARBARINO E C, EDELL J A. Cognitive effort, affect, and choice[J]. Journal of consumer research, 1997, 24(2): 147-158.
|
| 47 |
WANG M M. Encouraging solvers to sustain participation intention on crowdsourcing platforms: An investigation of social beliefs[J]. Information technology and management, 2022, 23(1): 39-50.
|
| 48 |
AJZEN I, FISHBEIN M. The influence of attitudes on behavior[M]//The Handbook of Attitudes. London, England: Psychology Press, 2014: 187-236.
|
| 49 |
TOHIDINIA Z, MOSAKHANI M. Knowledge sharing behaviour and its predictors[J]. Industrial management & data systems, 2010, 110(4): 611-631.
|
| 50 |
KANKANHALLI, TAN, WEI. Contributing knowledge to electronic knowledge repositories: An empirical investigation[J]. MIS quarterly, 2005, 29(1): 113.
|
| 51 |
BOCK, ZMUD, KIM, et al. Behavioral intention formation in knowledge sharing: Examining the roles of extrinsic motivators, social-psychological forces, and organizational climate[J]. MIS quarterly, 2005, 29(1): 87.
|
| 52 |
HAIR JR J F, HULT G T M, RINGLE C M, et al. A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling(PLS-SEM)[M]. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications, 2021.
|
| 53 |
STRAUB D, GEFEN D. Validation guidelines for IS positivist research[J]. Communications of the association for information systems, 2004, 13(1): 24.
|
| 54 |
FORNELL C, LARCKER D F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error[J]. Journal of marketing research, 1981, 18(1): 39-50.
|
| 55 |
CASRAI. 14 contributor roles[EB/OL]. [2022-08-22]. .
|