农业图书情报学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 66-80.doi: 10.13998/j.cnki.issn1002-1248.25-0032
AIGC平台“Z世代”用户持续使用意愿影响因素研究
苟芮可, 罗卫
- 湘潭大学 公共管理学院,湘潭 411105
-
收稿日期:2025-01-20出版日期:2025-03-05发布日期:2025-06-10 -
作者简介:苟芮可(1998- ),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为用户信息行为
罗卫(1979- ),男,讲师,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为知识对象化、信息与数据资源开发利用、传统信息服务数智化转型研究 -
基金资助:湖南省司法厅重点项目“湖南省智慧公共法律服务体系建设研究”(HNSF23B05)
Influencing Factors of Continuous Use Intention of "Generation Z" Users of an AIGC Platform
GOU Ruike, LUO Wei
- School of Public Administration, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan 411105
-
Received:2025-01-20Online:2025-03-05Published:2025-06-10
摘要:
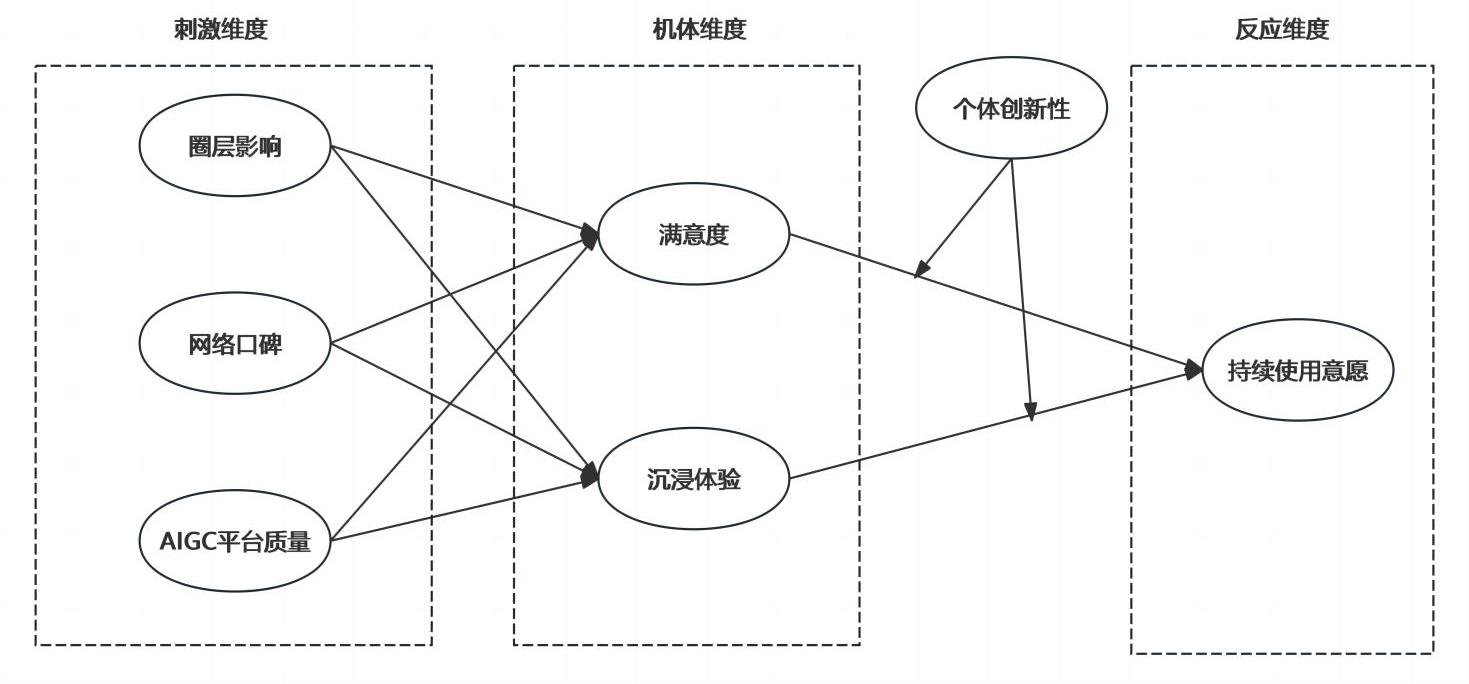
[目的/意义] 以“Z世代”为研究对象,剖析其持续使用意愿的影响因素及其内在作用机理,助力AIGC平台更精准地掌握这一核心用户群体的特征,以期在激烈的市场竞争中,为增强用户持续使用意愿,提高平台竞争优势提供参考建议。 [方法/过程] 基于SOR理论框架,构建AIGC平台“Z世代”用户持续使用意愿影响因素模型,通过问卷调查法收集数据并利用结构方程进行实证分析。 [结果/结论] 圈层影响、网络口碑、平台质量是通过满意度与沉浸体验影响Z世代用户持续使用意愿的重要因素,个体创新性对满意度和持续使用意愿之间的调节作用不显著,但正向调节沉浸体验与持续使用意愿之间的关系。据此,提出优化网络口碑,强化圈层运营,加强创新性引导等促进用户持续使用意愿的建议。
中图分类号: G252.0
引用本文
苟芮可, 罗卫. AIGC平台“Z世代”用户持续使用意愿影响因素研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2025, 37(3): 66-80.
GOU Ruike, LUO Wei. Influencing Factors of Continuous Use Intention of "Generation Z" Users of an AIGC Platform[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2025, 37(3): 66-80.
表1
变量及测量题项"
| 变量 | 测量题项 | 参考来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 网络口碑(IW) | IW1:网上对AIGC平台的关注度很高 IW2:近期我看到过很多针对AIGC平台的口碑信息 IW3:该网络口碑内容客观、公正地描述了AIGC平台的相关信息 IW4:AIGC平台有大量正面口碑时,我会选择继续使用该平台 | 刘筱婷[ |
| 平台质量(PQ) | PQ1:AIGC平台提供的信息准确且全面 PQ2:AIGC平台提供的信息能满足我的需求 PQ3:AIGC平台的系统能可靠且稳定地运行 PQ4:在AIGC平台遇到使用问题时平台能及时响应并解决 | PARASURAMAN等[ 李睿智等[ 姜文博等[ |
| 圈层影响(SI) | SI1:我信任圈层中共享的信息 SI2:圈层中的好友们希望我使用AIGC平台 SI3:基于圈层中的见闻,我被鼓励去使用AIGC平台 | 张长亮[ 赵宇翔等[ 谭春辉等[ |
| 沉浸体验(IE) | IE1:我认为在AIGC平台上与机器以自然语言交流互动很有趣 IE2:AIGC平台上依据我的想法生成的信息、图像等很有意思 IE3:我在AIGC平台上查找信息时,我感觉到了探索的兴奋 | 孙祺宇等[ |
| 满意度(S) | S1:AIGC平台的体验使我感到愉悦 S2:我认为使用AIGC平台的服务是明智的选择 S3:AIGC平台基本满足我的需求,整体上感觉十分满意 | BHATTACHERJEE[ |
| 个体创新性(ID) | ID1:我很乐于接受新事物和新观点 ID2:我很乐意去尝试新的技术/产品/服务 ID3:我通常比周围的人更先尝试新技术/新产品 ID4:使用AIGC平台使我觉得好奇新鲜 | 石婷婷[ |
| 持续使用意愿(CI) | CI1:未来我打算继续使用AIGC平台 CI2:未来我会保持目前频率甚至增加频率使用AIGC平台 CI3:我愿意向身边的人推荐使用AIGC平台 | BHATTACHERJEE[ 谭春辉等[ |
表2
人口统计特征"
| 类别 | 选项 | 人数/人 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 男 | 170 | 47.75 |
| 女 | 186 | 52.25 | |
| 出生年份 | 1995年以前 | 15 | 4.21 |
| 1995—2000年 | 75 | 21.07 | |
| 2001—2005年 | 129 | 36.24 | |
| 2006—2009年 | 128 | 35.96 | |
| 2009年以后 | 9 | 2.53 | |
| 学历 | 高中及以下 | 144 | 40.45 |
| 专科 | 60 | 16.85 | |
| 本科 | 91 | 25.56 | |
| 硕士 | 48 | 13.48 | |
| 博士 | 13 | 3.65 | |
| 使用历史 | 3个月以内 | 87 | 24.44 |
| 3个月到半年 | 135 | 37.92 | |
| 半年到一年 | 98 | 27.53 | |
| 一年到两年 | 36 | 10.11 | |
| 使用频率 | 每周1次甚至更少 | 26 | 7.30 |
| 每周2~3次 | 80 | 22.47 | |
| 每周4~6次 | 150 | 42.13 | |
| 每周6次以上 | 100 | 28.09 | |
| 每次使用时长 | 少于30分钟 | 31 | 8.71 |
| 0.5~1小时 | 120 | 33.71 | |
| 1~2小时 | 143 | 40.17 | |
| 2~3小时 | 36 | 10.11 | |
| 3小时以上 | 26 | 7.30 |
表3
信度与效度分析"
| 潜变量 | 题项 | 标准化载荷 | 克隆巴赫(α) | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 圈层影响 | SI1 | 0.816 | 0.877 | 0.877 | 0.640 |
| SI2 | 0.783 | ||||
| SI3 | 0.795 | ||||
| SI4 | 0.806 | ||||
| 网络口碑 | IW1 | 0.780 | 0.874 | 0.874 | 0.634 |
| IW2 | 0.802 | ||||
| IW3 | 0.773 | ||||
| IW4 | 0.829 | ||||
| 平台质量 | PQ1 | 0.789 | 0.870 | 0.870 | 0.626 |
| PQ2 | 0.809 | ||||
| PQ3 | 0.751 | ||||
| PQ4 | 0.815 | ||||
| 个体创新性 | PI1 | 0.797 | 0.861 | 0.861 | 0.608 |
| PI2 | 0.756 | ||||
| PI3 | 0.781 | ||||
| PI4 | 0.785 | ||||
| 沉浸体验 | IE1 | 0.793 | 0.875 | 0.832 | 0.623 |
| IE2 | 0.794 | ||||
| IE3 | 0.780 | ||||
| 满意度 | S1 | 0.782 | 0.832 | 0.876 | 0.638 |
| S2 | 0.801 | ||||
| S3 | 0.787 | ||||
| S4 | 0.824 | ||||
| 持续使用意愿 | CI1 | 0.805 | 0.884 | 0.884 | 0.657 |
| CI2 | 0.808 | ||||
| CI3 | 0.830 | ||||
| CI4 | 0.798 |
表6
模型路径系数及假设检验结果"
| 研究假设 | 作用关系 | 标准化影响因素 | S.E. | C.R. | P | 是否成立 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
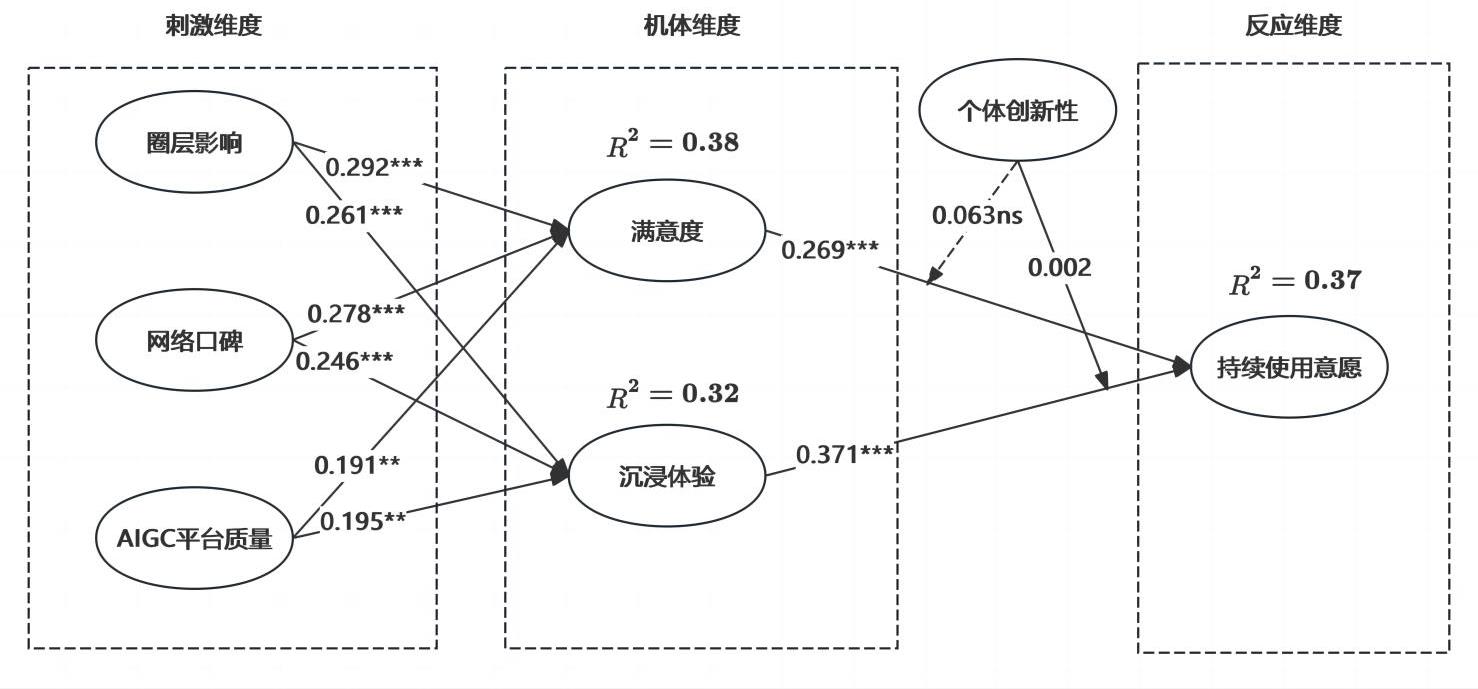
| H1a | 圈层影响显著正向影响用户满意度 | 0.290 | 0.067 | 4.140 | *** | 是 |
| H1b | 圈层影响显著正向影响用户的沉浸体验 | 0.260 | 0.068 | 3.461 | *** | 是 |
| H2a | 网络口碑显著正向影响用户满意度 | 0.280 | 0.065 | 4.630 | *** | 是 |
| H2b | 网络口碑显著正向影响用户的沉浸体验 | 0.250 | 0.066 | 3.894 | *** | 是 |
| H3a | 平台质量显著正向影响用户满意度 | 0.200 | 0.070 | 2.866 | 0.004 | 是 |
| H3b | 平台质量显著正向影响用户的沉浸体验 | 0.200 | 0.072 | 2.70 | 0.007 | 是 |
| H4 | 满意度显著正向影响用户的持续使用意愿 | 0.370 | 0.058 | 5.972 | *** | 是 |
| H6 | 沉浸体验显著正向影响用户的持续使用意愿 | 0.370 | 0.062 | 5.791 | *** | 是 |
| 1 | 张海, 段荟, 王东波. 信息资源管理领域生成式人工智能: 研究现状、研究主题及研究展望[J]. 情报杂志, 2024, 43(10): 150-156. |
| ZHANG H, DUAN H, WANG D B. Artificial intelligence generative content in information resource management: Research status, research topics and research prospect[J]. Journal of intelligence, 2024, 43(10): 150-156. | |
| 2 | 艾瑞咨询. 中国生成式人工智能(AIGC)行业发展研究报告[EB/OL]. [2024-09-12]. . |
| 3 | 中国网信网. 生成式人工智能服务管理暂行办法[EB/OL]. [2024-09-12]. . |
| 4 | 张智雄, 曾建勋, 夏翠娟, 等. 回应AIGC的信息资源管理学人思考[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(1): 4-25. |
| ZHANG Z X, ZENG J X, XIA C J, et al. Information resource management researchers' thinking about the opportunities and challenges of AIGC[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2023, 35(1): 4-25. | |
| 5 | 中国发展改革网. 《2024Z世代AIGC态度报告》发布, 三分之一的年轻人愿意和AI做朋友[EB/OL]. [2024-09-13]. . |
| 6 | 陈杰. 洞察“Z世代” 消费趋势[J]. 知识经济, 2019(26): 66-69. |
| CHEN J. Insight into the consumption trend of "Z generation"[J]. Knowledge economy, 2019(26): 66-69. | |
| 7 | QuestMobile研究院. Z世代洞察报告[EB/OL]. [2024-09-14]. . |
| 8 | DAVIS F D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology[J]. MIS quarterly, 1989, 13(3): 319. |
| 9 | BHATTACHERJEE A. Understanding information systems continuance: An expectation-confirmation model[J]. MIS quarterly, 2001, 25(3): 351. |
| 10 | HSU M H, CHIU C M, JU T L. Determinants of continued use of the WWW: An integration of two theoretical models[J]. Industrial management & data systems, 2004, 104(9): 766-775. |
| 11 | 刘佳静, 匡莉, 潘婕, 等. 省级公共文化云微信用户持续使用意愿研究[J]. 图书馆杂志, 2022, 41(7): 47-57. |
| LIU J J, KUANG L, PAN J, et al. Research on users' continuance intention for provincial public cultural cloud WeChat[J]. Library journal, 2022, 41(7): 47-57. | |
| 12 | 郭财强, 明均仁. 移动图书馆用户持续使用意愿整合模型及其实证研究[J]. 现代情报, 2020, 40(9): 79-89. |
| GUO C Q, MING J R. Integrated model and empirical study on users' continuous usage willingness of mobile library[J]. Journal of modern information, 2020, 40(9): 79-89. | |
| 13 | 孟猛,朱庆华.移动视觉搜索用户体验模型构建与实证研究[J].图书情报工作,2022,66(5):80-92. |
| MENG M, ZHU Q H. Construction and empirical research on mobile visual search user experience model[J]. Library and information service, 2022,66(5):80–92. | |
| 14 | SAXENA A, DOLECK T. A structural model of student continuance intentions in ChatGPT adoption[J]. Eurasia journal of mathematics, science and technology education, 2023, 19(12): em2366. |
| 15 | 熊强, 李文元, 陈晓燕, 等. 在线教学平台交互性、体验价值和持续使用意愿的关系研究: 一个有调节的中介效应[J]. 管理评论, 2022, 34(6): 153-161. |
| XIONG Q, LI W Y, CHEN X Y, et al. Research on the relationship among interaction, experience value and user stickiness of online teaching platform: A moderated mediation effect model[J]. Management review, 2022, 34(6): 153-161. | |
| 16 | 张嵩, 王安娜, 陈昊. 冷漠依赖与沉浸体验: 移动短视频用户持续使用意愿研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2022, 66(14): 89-100. |
| ZHANG S, WANG A N, CHEN H. Apathy dependence and immersive experience: Research on the users' continuous use intention of mobile short video APPs[J]. Library and information service, 2022, 66(14): 89-100. | |
| 17 | 贺莉. Z世代: 缘起、特征与影响[EB/OL]. [2024-09-13]. . |
| 18 | ROSLI M S, SALEH N S, MD ALI A, et al. Factors determining the acceptance of E-wallet among gen Z from the lens of the extended technology acceptance model[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(7): 5752. |
| 19 | WIANGKHAM A, KIEANWATANA K, VONGVIT R. A comparative study of baby boomers and gen Z on virtual reality adoption for travel intentions: A PLS-MGA and GRNN model[J]. International journal of human–computer interaction, 2024: 1-22. |
| 20 | 栗蕊蕊, 王淼. Z世代大学生网络社交: 行为特征与引导策略[J]. 思想理论教育, 2024(7): 107-111. |
| LI R R, WANG M. Social networking of generation Z college students: Behavior characteristics and guidance strategies[J]. Ideological & theoretical education, 2024(7): 107-111. | |
| 21 | 张潇月. “副号即隐私”: Z世代用户社交媒体信息发布行为特点研究[J]. 情报资料工作, 2024, 45(3): 60-69. |
| ZHANG X Y. Alternate account is privacy: Research on the features of generation Z users social media information posting behaviors[J]. Information and documentation services, 2024, 45(3): 60-69. | |
| 22 | 杨宇辰. Z世代网络互动仪式的生成机制分析[J]. 中国特色社会主义研究, 2024, 15(3): 105-113. |
| YANG Y C. Analysis on generative mechanism of generation Z's online interactive ceremony[J]. Studies on socialism with Chinese characteristics, 2024, 15(3): 105-113. | |
| 23 | 刘蒙之, 王麓乔, 张瑞杰. “Z世代”群体道德消费行为的影响因素与态度-行为差距成因分析[J]. 中国青年研究, 2023(10): 55-62. |
| LIU M Z, WANG L Q, ZHANG R J. Influencing factors of moral consumption behavior of generation Z group and analysis of attitude-behavior gap[J]. China youth study, 2023(10): 55-62. | |
| 24 | 张铮, 刘晨旭. 建构数字自我意识: “Z世代”青年数字形象消费中的新认同实践[J]. 福建论坛(人文社会科学版), 2023(8): 30-39. |
| ZHANG Z, LIU C X. Constructing digital self-consciousness: New identity practice in digital image consumption of generation Z youth[J]. Fujian tribune, 2023(8): 30-39. | |
| 25 | 刘森林. “装在盒子里的人”: “Z世代”盲盒消费景观及其形成机制[J]. 中国青年研究, 2022(2): 78-84. |
| LIU S L. People in a box: Blind box consumption landscape and its formation mechanism of Z generation[J]. China youth study, 2022(2): 78-84. | |
| 26 | 中国人工智能学会. 人工智能生成内容(AIGC)白皮书(2022年)[EB/OL]. [2024-09-12]. . |
| 27 | 赵瑞雪,黄永文,马玮璐,等.ChatGPT对图书馆智能知识服务的启示与思考[J].农业图书情报学报,2023,35(1):29-38. |
| ZHAO R X, HUANG Y W, MA W L, et al. Insights and reflections of the impact of ChatGPT on intelligent knowledge services in libraries[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2023, 35(1): 29-38. | |
| 28 | Bahroun Z, Anane C, Ahmed V,et al.Transforming education:A comprehensive review of generative artificial intelligence in educational settings through bibliometric and content analysis[J].Sustainability,2023,15(17):12983. |
| 29 | BAHROUN Z, ANANE C, AHMED V, et al. Transforming education: A comprehensive review of generative artificial intelligence in educational settings through bibliometric and content analysis[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(17): 12983. |
| 30 | LUND B D, WANG T, MANNURU N R, et al. ChatGPT and a new academic reality: Artificial Intelligence-written research papers and the ethics of the large language models in scholarly publishing[J]. Journal of the association for information science and technology, 2023, 74(5): 570-581. |
| 31 | SAM S. Early applications of ChatGPT in medical practice, education and research[J]. Clinical medicine, 2023, 23(3): 278-279. |
| 32 | LO L S. The CLEAR path: A framework for enhancing information literacy through prompt engineering[J]. The journal of academic librarianship, 2023, 49(4): 102720. |
| 33 | 孙鹏, 王宇, 刘新勇. ChatGPT赋能图书馆: 现实基础、逻辑方向与应用场景[J]. 情报资料工作, 2024, 45(5): 100-106. |
| SUN P, WANG Y, LIU X Y. Empowering libraries with chat GPT: Realistic foundation, logical direction and application scenarios[J]. Information and documentation services, 2024, 45(5): 100-106. | |
| 34 | 杨晶晶. 生成式人工智能在档案数字场景中的应用研究[J]. 浙江档案, 2024(1): 45-47, 54. |
| YANG J J. Research on application of Generative Artificial Intelligence in archive digital scene[J]. Zhejiang archives, 2024(1): 45-47, 54. | |
| 35 | 陈凯泉, 胡晓松, 韩小利, 等. 对话式通用人工智能教育应用的机理、场景、挑战与对策[J]. 远程教育杂志, 2023, 41(3): 21-41. |
| CHEN K Q, HU X S, HAN X L, et al. The mechanism, scenarios, challenges and countermeasure of conversational artificial general intelligence in education[J]. Journal of distance education, 2023, 41(3): 21-41. | |
| 36 | 熊皓舒, 王鐾璇, 侯健, 等. 生成式人工智能(AI)在中药智能制造及供应链中的应用场景设计与展望[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2024, 49(14): 3963-3970. |
| XIONG H S, WANG B X, HOU J, et al. Application scenario design and prospect of generative artificial intelligence (AI) in intelligent manufacturing and supply chain of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. China journal of Chinese materia Medica, 2024, 49(14): 3963-3970. | |
| 37 | 张海,段荟,孔晔晗.高校图书馆用户未来学习中心采纳意愿影响因素研究[J].国家图书馆学刊,2024,33(3):49-58. |
| ZHANG H, DUAN H, KONG Y H. Research on influencing factors of users, adoption intention of future learning centers in academic libraries[J]. Journal of the national library of China, 2024, 33(3): 49-58. | |
| 38 | 周涛, 张春雷, 邓胜利. 基于C-A-C的生成式AI用户间歇性中辍行为研究[J]. 现代情报, 2025, 45(3): 40-50, 64. |
| ZHOU T, ZHANG C L, DENG S L. Research on generative AI users' intermittent discontinuance based on the C-A-C[J]. Journal of modern information, 2025, 45(3): 40-50, 64. | |
| 39 | 张玥, 李青宇, 刘雨琪, 等. 组态视角下AIGC应用平台用户中辍行为影响因素研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(3): 130-137, 148. |
| ZHANG Y, LI Q Y, LIU Y Q, et al. A study on discontinuance behavior in the AIGC application platform based on the perspective of configuration[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2024, 47(3): 130-137, 148. | |
| 40 | 毛太田, 汤淦, 马家伟, 等. 人工智能生成内容(AIGC)用户采纳意愿影响因素识别研究: 以ChatGPT为例[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(7): 126-136. |
| MAO T T, TANG G, MA J W, et al. Factors influencing user adoption intention of artificial intelligence generated content(AIGC): A study on ChatGPT[J]. Information science, 2024, 42(7): 126-136. | |
| 41 | 孙清白. 论人工智能大模型训练数据风险治理的规范构建[J]. 电子政务, 2024(12): 41-52. |
| SUN Q B. On the normative construction of risk management of artificial intelligence big model training data[J]. E-Government, 2024(12): 41-52. | |
| 42 | 何炜. 生成式人工智能技术的伦理风险及负责任创新治理研究[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2024, 46(4): 548-559. |
| HE W. Research on ethical risks and responsible innovation governance of generative artificial intelligence technology[J]. World sci-tech R & D, 2024, 46(4): 548-559. | |
| 43 | 张旭芳. 生成式人工智能的算法安全风险及治理路径[J]. 江西社会科学, 2024, 44(8): 90-100. |
| ZHANG X F. Algorithm security risk and governance path of generative artificial intelligence[J]. Jiangxi social sciences, 2024, 44(8): 90-100. | |
| 44 | MEHRABIAN A. Individual differences in stimulus screening and arousability[J]. Journal of personality, 1977, 45(2): 237-250. |
| 45 | 徐孝娟, 赵宇翔, 史如菊, 等. SOR理论在国内图书情报学领域的采纳: 溯源、应用及未来展望[J]. 情报资料工作, 2022, 43(5): 98-105. |
| XU X J, ZHAO Y X, SHI R J, et al. The adoption of SOR theory in the field of library and information science in China: Traceability, application and future prospects[J]. Information and documentation services, 2022, 43(5): 98-105. | |
| 46 | 王文韬, 钱鹏博, 丁雨辰, 等. 个性化内容推荐关闭对移动社交媒体持续使用意愿的影响[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(11): 88-100. |
| WANG W T, QIAN P B, DING Y C, et al. The impact of personalized content recommendation close on continuous use intention of mobile social media[J]. Library and information service, 2023, 67(11): 88-100. | |
| 47 | 梅倩茹. 基于心流体验理论的非遗沉浸式体验设计研究[J]. 鞋类工艺与设计, 2023, 3(9): 158-161. |
| MEI Q R. Research on intangible cultural heritage immersive experience design based on the flow theory[J]. Shoes technology and design, 2023, 3(9): 158-161. | |
| 48 | 来有为, 周海伟, 厉基巍. 理解中国“Z世代”迎接消费新浪潮[J]. 发展研究, 2022, 39(3): 44-55. |
| LAI Y W, ZHOU H W, LI J W. Understanding China's "Z generation" and meeting the new wave of consumption[J]. Development research, 2022, 39(3): 44-55. | |
| 49 | 李赫, 乔晓嫚, 魏佳辛. 圈层视域下Z世代网络舆论引导进路研究[J]. 公关世界, 2024(10): 26-28. |
| LI H, QIAO X M /Y), WEI J X. Research on the guidance approach of Z generation network public opinion from the perspective of circles[J]. PR world, 2024(10): 26-28. | |
| 50 | 何绍辉. Z世代青年的形成背景与群体特征[J]. 中国青年研究, 2022(8): 14-20. |
| HE S H. The formation background and group characteristics of generation Z youth[J]. China youth study, 2022(8): 14-20. | |
| 51 | 揭秘Z世代15个特质, 掌握未来 4500亿消费潜力[EB/OL]. [2024-09-12]. . |
| 52 | 刘晨. “种草”式内容营销对用户购买意愿的影响: 以小红书为例[J]. 新闻传播, 2024(15): 35-37. |
| LIU C. Influence of "planting grass" content marketing on users' purchase intention: Taking Xiaohongshu as an example[J]. Journalism communication, 2024(15): 35-37. | |
| 53 | 张长亮, 李竟彤, 郭宇. 网络社群用户信息共享行为影响因素研究[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(2): 39-46, 87. |
| ZHANG C L, LI J T, GUO Y. Influencing factors of network community user's information sharing behavior[J]. Information science, 2020, 38(2): 39-46, 87. | |
| 54 | 张大伟, 陈彦馨, 王敏. 期望与确认: 短视频平台持续使用影响因素初探: 基于SEM与fsQCA的研究[J]. 现代传播(中国传媒大学学报), 2020, 42(8): 133-140. |
| ZHANG D W, CHEN Y X, WANG M. Factors influencing the continuous use of short video platform: Based on SEM and fsQCA[J]. Modern communication (journal of communication university of China), 2020, 42(8): 133-140. | |
| 55 | HOFFMAN D L, NOVAK T P. Flow online: Lessons learned and future prospects[J]. Journal of interactive marketing, 2009, 23(1): 23-34. |
| 56 | 孙祺宇, 李菲. 元宇宙视角下数字阅读持续使用意愿研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(22): 23-34. |
| SUN Q Y, LI F. Research on the continuous digital reading willingness from the perspective of metaverse[J]. Library and information service, 2023, 67(22): 23-34. | |
| 57 | 王水雄. 中国“Z世代”青年群体观察[J]. 人民论坛, 2021(25): 24-27. |
| WANG S X. Observation on "generation Z" youth groups in China[J]. People's tribune, 2021(25): 24-27. | |
| 58 | 刘筱婷. 网络口碑、消费者鼓舞与冲动型购买行为的关系研究[J]. 商业经济研究, 2023(16): 71-74. |
| LIU X T. Research on the relationship among online word of mouth, consumer encouragement and impulsive buying behavior[J]. Journal of commercial economics, 2023(16): 71-74. | |
| 59 | PARASURAMAN A, ZEITHAML V A, MALHOTRA A. ES-QUAL: A multiple-item scale for assessing electronic service quality[J]. Journal of service research, 2005, 7(3): 213-233. |
| 60 | 李睿智, 齐航, 相甍甍, 等. 在线付费问答平台用户持续使用行为影响因素研究[J]. 情报探索, 2021(9): 94-101. |
| LI R Z, QI H, XIANG M M, et al. Research on influencing factors of continuous using behaviors of online payment Q & A platform[J]. Information research, 2021(9): 94-101. | |
| 61 | 姜文博, 刘维尚, 李蕊池. 用户行为视角下高校图书馆智慧服务影响因素研究[J]. 包装工程, 2024, 45(20): 383-391. |
| JIANG W B, LIU W S, LI R C. Factors influencing smart services in university libraries from the perspective of user behavior[J]. Packaging engineering, 2024, 45(20): 383-391. | |
| 62 | 赵宇翔. 知识问答类SNS中用户持续使用意愿影响因素的实证研究[J]. 图书馆杂志, 2016, 35(9): 25-37. |
| ZHAO Y X. An empirical investigation on the influencing factors of users' continuance intention in question-and-answer SNS[J]. Library journal, 2016, 35(9): 25-37. | |
| 63 | 谭春辉, 王晓宇, 刁斐, 等. 基于fsQCA方法的社会化问答社区用户持续使用意愿影响机理研究[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2023(1): 74-86. |
| TAN C H, WANG X Y, DIAO F, et al. A research on the influence mechanism of the user's continuous use intention in the social Q & A community based on the fsQCA method[J]. Research on library science, 2023(1): 74-86. | |
| 64 | 石婷婷. 基于UTAUT模型的学术社交网站用户采纳行为研究[J]. 新世纪图书馆, 2019(12): 46-52. |
| SHI T T. Research on adoption behavior of academic social networking sites based on the UTAUT model[J]. New century library, 2019(12): 46-52. | |
| 65 | 敖成兵. Z世代消费理念的多元特质、现实成因及亚文化意义[J]. 中国青年研究, 2021(6): 100-106. |
| AO C B. Diversified characteristics, realistic causes and subcultural significance of generation Z's consumption concept[J]. China youth study, 2021(6): 100-106. |
| [1] | 是沁, 谢靖, 吴尚. 移动健康APP用户满意度影响因素与关联路径研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2025, 37(1): 33-46. |
| [2] | 游鸽, 李洁琳, 张帆顺. 信息生态视角下突发公共事件网络舆情热度生成机理研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2025, 37(1): 86-99. |
| [3] | 高国伟, 张珊珊, 于佳岚. 主题差异化视角下老年人健康信息行为研究综述[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(7): 34-49. |
| [4] | 姚丽琴, 张海. AIGC用户中辍行为影响因素模型构建与实证研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(5): 79-92. |
| [5] | 高春玲, 姜莉媛. 基于演化动力学的老年人在线健康信息搜寻行为研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(5): 65-78. |
| [6] | 刘洋, 吕树月, 黎若珺. 社交机器人在信息行为研究中的概念、任务及应用[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(3): 4-20. |
| [7] | 周鑫. 机器功能主义与数智鸿沟:演化路径、生成逻辑与规制策略[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(3): 59-71. |
| [8] | 石燕青, 李露, 是沁. 网络结构视角下用户异质性对知识协作效果的影响研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(3): 72-82. |
| [9] | 王月莹. 农村中老年人健康信息素养偏低的原因探析及其提升策略[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(2): 81-93. |
| [10] | 王伟正, 乔鸿, 李肖俊, 王静静. 基于AIDUA框架的生成式人工智能使用意愿研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(2): 36-50. |
| [11] | 王铮, 庄苗, 张宇迪, 张雅琪. 西部农村老年群体在线健康信息获取行为影响因素研究——来自陕西关中地区的田野调查[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(10): 23-37. |
| [12] | 万益嘉, 顾立平. 研究生使用AIGC工具的行为动机与影响因素:基于问卷调查的实证分析[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(10): 4-22. |
| [13] | 谢燕洁. 中国公共图书馆老年人服务研究述评[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(7): 18-26. |
| [14] | 李婧. 代际健康冲突信息行为成因及其在社会控制中的作用机制研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(5): 74-88. |
| [15] | 肖耘, 许欢欢, 肖雅元, 赵又霖, 庞航远. 基于CLV偏好挖掘模型的数字社区用户偏好挖掘研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(2): 45-60. |
|
||