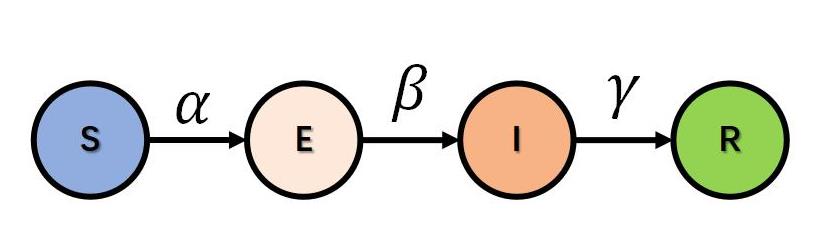
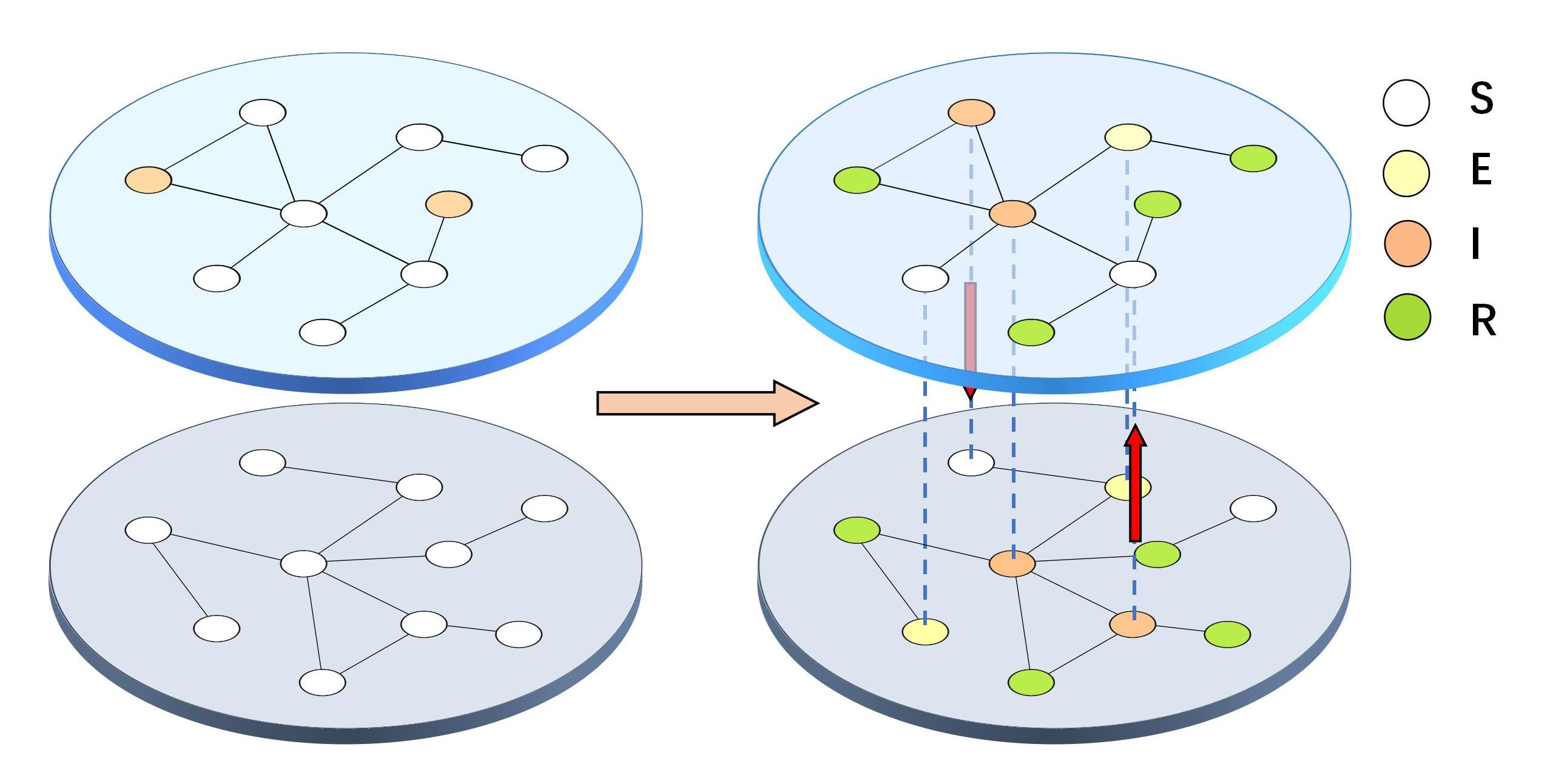
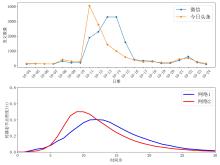
| 1 |
中国互联网络信息中心. 第52 次中国互联网络发展状况统计报告[EB/OL]. [2024-03-22].
|
| 2 |
QuestMobile研究院. 2023年新媒体生态洞察[EB/OL]. [2023-11-21].
|
| 3 |
KERMACK W O, MCKENDRICK A G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics[J]. Proceedings of the royal society of London series A, containing papers of a mathematical and physical character, 1927, 115(772): 700-721.
|
| 4 |
李思佳, 张鹏, 夏一雪, 等. 基于信息吸引力和相关性的双网络舆情交互传播建模与仿真研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2023, 42(5): 119-128.
|
|
LI S J, ZHANG P, XIA Y X, et al. Interactive propagation mode and simulation of dual network public opinions based on information attraction and relevance[J]. Journal of intelligence, 2023, 42(5): 119-128.
|
| 5 |
马宇彤, 胡平. 考虑“关键用户”影响力及“热点问题”识别的改进SEIR知识传播模型[J]. 预测, 2021, 40(5): 48-55.
|
|
MA Y T, HU P. The improved SEIR knowledge dissemination model based on key user and hot spots influences[J]. Forecasting, 2021, 40(5): 48-55.
|
| 6 |
曾荣燊, 李弼程, 陈刚, 等. 基于线上-线下超网络模型的舆论演化仿真分析[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2024, 41(2): 507-514.
|
|
ZENG R S, LI B C, CHEN G, et al. Analysis of public opinion evolution based on online-offline supernetwork model[J]. Application research of computers, 2024, 41(2): 507-514.
|
| 7 |
卢友军, 吴森, 魏嘉银, 等. 带时间延迟和强制静默的SICR谣言传播模型[J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版), 2024, 45(6): 83-91.
|
|
LU Y J, WU S, WEI J Y, et al. A SICR rumor propagation model with time delay and enforced silence[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (engineering science), 2024, 45(6): 83-91.
|
| 8 |
陈帅. 基于多层耦合网络的舆情传播控制研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2020, 32(12): 2353-2361.
|
|
CHEN S. Research on dissemination and control of public opinion based on multilayer coupled network[J]. Journal of system simulation, 2020, 32(12): 2353-2361.
|
| 9 |
陈帅. 基于SEIR的双层社交网络舆情传播研究[J]. 情报探索, 2020(9): 29-36.
|
|
CHEN S. Research on public opinion communication in two-tier social network based on SEIR[J]. Information research, 2020(9): 29-36.
|
| 10 |
卓新建, 李晓燕, 徐文哲. 基于多层网络的舆情传播模型[J/OL]. 系统科学与数学, 2024: 1-18.
|
|
ZHUO X J, LI X Y, XU W Z. Public opinion propagation model based on multi-layer network[J/OL]. Journal of systems science and mathematical sciences, 2024: 1-18.
|
| 11 |
杨磊, 封永雪, 侯贵生, 等. 个体因素与外部环境共同作用下的跨平台社交网络舆情传播模型研究[J]. 现代情报, 2021, 41(3): 138-147, 158.
|
|
YANG L, FENG Y X, HOU G S, et al. Research on cross-platform social network public opinion propagation model under the joint action of individual factors and external environment[J]. Journal of modern information, 2021, 41(3): 138-147, 158.
|
| 12 |
罗章凯, 裴忠民, 熊伟, 等. 双层均质耦合网络信息传播动力学研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(1): 43-47.
|
|
LUO Z K, PEI Z M, XIONG W, et al. Research on dynamics of information spreading on double-layer coupled networks[J]. Computer simulation, 2023, 40(1): 43-47.
|
| 13 |
魏静, 张耀曾, 朱恒民, 等. 基于动态权值和不对称耦合网络的改进Deffuant模型舆情演化解析[J]. 情报杂志, 2021, 40(8): 142-151, 158.
|
|
WEI J, ZHANG Y Z, ZHU H M, et al. Analysis of the evolution of improved deffuant model of public opinion based on dynamic weights and asymmetric coupling networks[J]. Journal of intelligence, 2021, 40(8): 142-151, 158.
|
| 14 |
刘继, 郭一凡. 基于耦合网络的舆情观点演化机制分析[J/OL]. 情报杂志, 2024: 1-9.
|
|
LIU J, GUO Y F. Analysis of the evolution mechanism of public opinion viewpoints based on coupled neworks[J/OL]. Journal of intelligence, 2024: 1-9.
|
| 15 |
NEWMAN M E J. Assortative mixing in networks[J]. Physical review letters, 2002, 89(20): 208701.
|
| 16 |
田占伟, 王亮, 刘臣. 基于复杂网络的微博信息传播机理分析与模型构建[J]. 情报科学, 2015, 33(9): 15-21.
|
|
TIAN Z W, WANG L, LIU C. Information dissemination mechanism analysis and model construction of micro-blog based on complex network[J]. Information science, 2015, 33(9): 15-21.
|
| 17 |
韩一士, 徐雨欣, 卢甜甜. 一种基于耦合网络的RD-IHSAT网络谣言传播模型[J]. 电信科学, 2023, 39(2): 118-131.
|
|
HAN Y S, XU Y X, LU T T. A model of RD-IHSAT rumor dissemination based on coupling network[J]. Telecommunications science, 2023, 39(2): 118-131.
|
| 18 |
BULDYREV S V, PARSHANI R, PAUL G, et al. Catastrophic cascade of failures in interdependent networks[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7291): 1025-1028.
|
| 19 |
BULDYREV S V, SHERE N W, CWILICH G A. Interdependent networks with identical degrees of mutually dependent nodes[J]. Physical review E, Statistical, nonlinear, and soft matter physics, 2011, 83(1 Pt 2): 016112.
|
| 20 |
SIDOROV S, FAIZLIEV A, TIKHONOVA S. An extension of the susceptible–infected model and its application to the analysis of information dissemination in social networks[J]. Modelling, 2023, 4(4): 585-599.
|
| 21 |
XIA L L, JIANG G P, SONG B, et al. Rumor spreading model considering hesitating mechanism in complex social networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical mechanics and its applications, 2015, 437: 295-303.
|
| 22 |
梁冉, 徐雅斌. 基于改进SEIR模型的网络舆情传播研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(5): 333-340.
|
|
LIANG R, XU Y B. Research on network public opinion communication based on improved SERI model[J]. Computer simulation, 2023, 40(5): 333-340.
|

 ), Jianlong ZHENG1, Zhaoxin WANG2
), Jianlong ZHENG1, Zhaoxin WANG2