农业图书情报学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 34-49.doi: 10.13998/j.cnki.issn1002-1248.24-0390
图书馆AI聊天机器人持续使用意愿研究——基于情感体验的中介
- 山东大学 图书馆,济南 250100
-
收稿日期:2024-05-03出版日期:2024-06-05发布日期:2024-09-30 -
通讯作者:程川生 -
作者简介:马海婷(1997- ),女,硕士,助理馆员,研究方向为图书馆服务与用户研究、数据分析
-
基金资助:山东大学教改项目“数智时代未来学习生态建设”(2023Z21)
Continuance Intention to Use AI Chatbots in Libraries: Mediation Based on Emotional Experience
Haiting MA, Chuansheng CHENG( )
)
- Shandong University Library, Jinan 250100
-
Received:2024-05-03Online:2024-06-05Published:2024-09-30 -
Contact:Chuansheng CHENG
摘要:
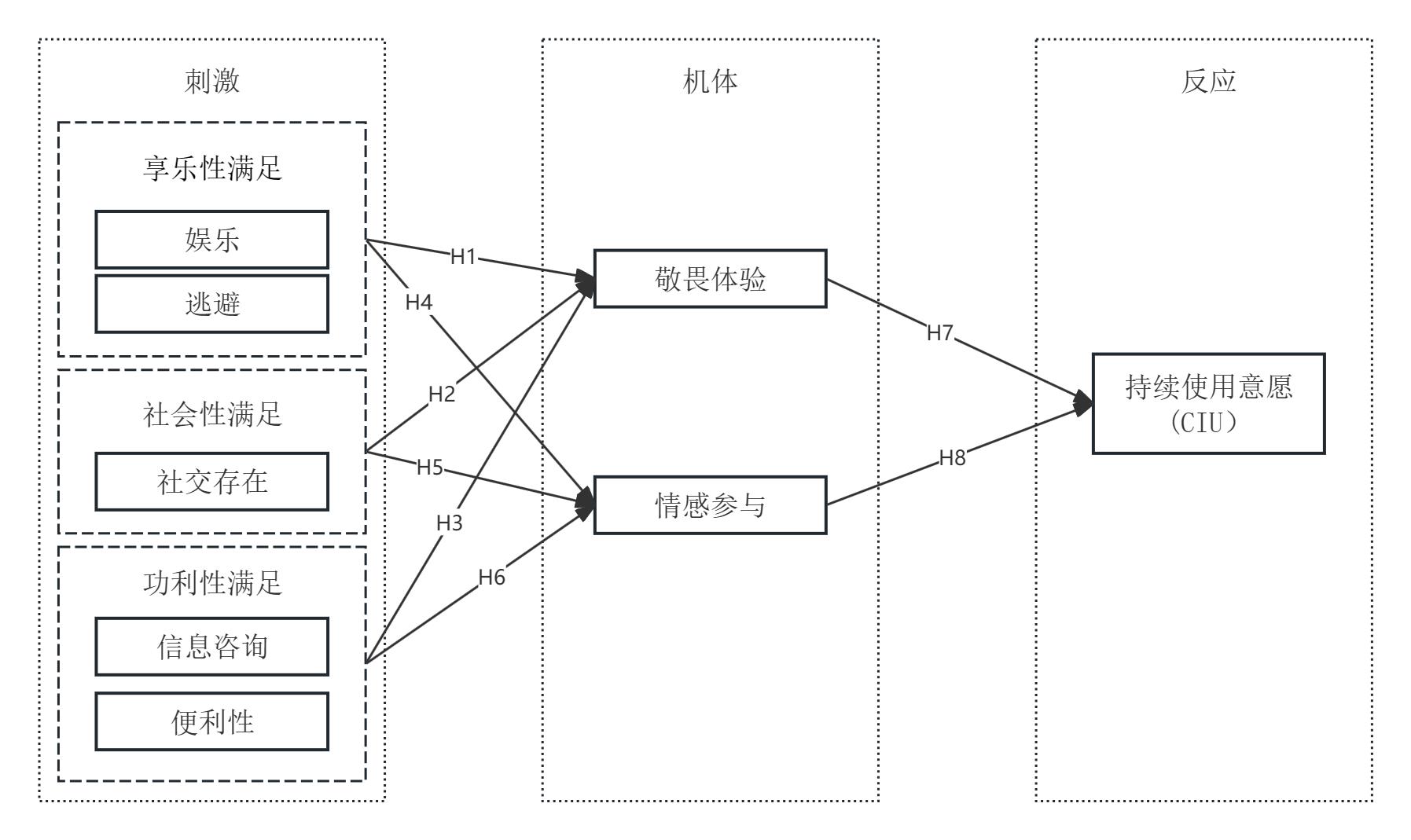
[目的/意义] 探究用户持续使用图书馆AI聊天机器人意愿的影响因素,更好地理解用户的持续性思维,并为未来学习生态下图书馆AI聊天机器人的进一步发展带来启示。 [方法/过程] 基于使用与满足理论和“刺激-机体-反应”框架,建立图书馆AI聊天机器人用户持续使用意愿概念模型。采用问卷调查法收集数据,再结合PLS-SEM和fsQCA混合研究方法对模型中所含变量与假设进行验证。 [结果/结论] 研究结果表明,享乐性(娱乐和逃避)、社会性(社交存在)和功利性(便利性和信息咨询)3种类型的满足对情感体验(敬畏体验和情感参与)有显著正向影响,其中逃避对敬畏体验影响最大,社交存在对情感参与影响最大;情感体验对持续使用意愿有显著正向影响,其中敬畏体验对持续使用意愿影响最大;情感体验作为作用机制影响了用户满足感和使用意愿。
中图分类号: G258.6
引用本文
马海婷, 程川生. 图书馆AI聊天机器人持续使用意愿研究——基于情感体验的中介[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(6): 34-49.
Haiting MA, Chuansheng CHENG. Continuance Intention to Use AI Chatbots in Libraries: Mediation Based on Emotional Experience[J]. Journal of Library and Information Science in Agriculture, 2024, 36(6): 34-49.
表1
AI聊天机器人用户持续使用意愿因素测量选项"
| 研究变量 | 测量选项 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 娱乐 | EN1.我喜欢使用AI聊天机器人,因为它给我带来了很多乐趣 | [ |
| EN2.我通常会花时间和AI聊天机器人在一起,因为它们很有趣 | ||
| EN3.我无聊的时候会用AI聊天机器人打发时间 | ||
| 逃避 | ES1.AI聊天机器人帮助我忘记烦恼和压力 | [ |
| ES2.AI聊天机器人帮助我避免孤独 | ||
| ES3.AI聊天机器人帮助我逃离现实世界 | ||
| 社交存在 | SP1.与AI聊天机器人的互动让我感受到了社交生活 | [ |
| SP2.我对AI聊天机器人有一种人类敏感性 | ||
| SP3.在我与AI聊天机器人的互动中,我能够做自己,展示我到底是什么样的人 | ||
| SP4.与AI聊天机器人的互动让我感觉很舒服,就像和朋友在一起一样 | ||
| 信息咨询 | IS1.我使用AI聊天机器人来获取我需要的信息 | [ |
| IS2.我确实使用AI聊天机器人作为信息来源 | ||
| IS3.使用AI聊天机器人可以提高我对所提问题的理解 | ||
| IS4.使用AI聊天机器人可以解决我的疑虑 | ||
| 便利性 | CON1.我认为AI聊天机器人使用起来很方便 | [ |
| CON2.我可以在电脑或智能手机上随时随地使用AI聊天机器人 | ||
| CON3.使用AI聊天机器人时,我可以用更少的努力得到我想要的东西 | ||
| 敬畏体验 | 当我使用AI聊天机器人产品时 | [ |
| AE1.我总是有一种与它联系在一起的感觉 | ||
| AE2.我总是和它有一种合一的感觉 | ||
| AE3.有时,我感到浩瀚无垠,惊得下巴都掉下来了 | ||
| AE4.有时,我发现很难完全理解这段经历 | ||
| AE5.有时,我觉得自己置身于某种宏伟的事物中,并试图理解我所经历的 | ||
| AE6.有时,我会起鸡皮疙瘩,喘不过气来 | ||
| 情感参与 | EI1.当我使用AI聊天机器人产品时,我会深深地感受到它 | [ |
| EI2.在我结束与AI聊天机器人的对话后,我可能会保留一段时间的使用记忆 | ||
| EI3.当我使用AI聊天机器人产品时,我会沉浸于聊天机器人 | ||
| 持续使用 | CIU1.我想继续使用AI聊天机器人,而不是停止使用 | [ |
| CIU2.如果可能的话,我打算继续使用AI聊天机器人 | ||
| CIU3.我将来会继续使用AI聊天机器人 |
表2
受访者特征描述性统计"
| 项目 | 变量 | 数量 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 男 | 175 | 44.4 |
| 女 | 219 | 55.6 | |
| 总计 | 394 | 100.0 | |
| 年龄 | 19岁及以下 | 45 | 11.4 |
| 20~29岁 | 157 | 39.8 | |
| 30~39岁 | 120 | 30.5 | |
| 40~49岁 | 63 | 16.0 | |
| 50岁及以上 | 9 | 2.3 | |
| 总计 | 394 | 100.0 | |
| 受教育程度 | 本科 | 246 | 62.4 |
| 硕士及以上 | 148 | 37.6 | |
| 总计 | 394 | 100.0 | |
| 聊天机器人的使用频率(h/天) | 0.5h及以下 | 153 | 38.8 |
| 0.5~1h | 105 | 26.6 | |
| 1~2h | 89 | 22.6 | |
| 2~5h | 37 | 9.4 | |
| 5h及以上 | 10 | 2.5 | |
| 总计 | 394 | 100.0 |
表3
信度效度结果"
| Construct | Cronbach's α | VIF | AVE | CR | MSV | ASV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN | 0.839 | 1.575 | 0.755 | 0.902 | 0.346 | 0.510 |
| ES | 0.845 | 1.852 | 0.763 | 0.906 | 0.346 | 0.540 |
| SP | 0.864 | 1.665 | 0.710 | 0.907 | 0.403 | 0.573 |
| IS | 0.868 | 1.733 | 0.717 | 0.910 | 0.403 | 0.557 |
| CON | 0.829 | 1.601 | 0.744 | 0.897 | 0.337 | 0.547 |
| AE | 0.899 | 1.599 | 0.664 | 0.922 | 0.380 | 0.534 |
| EI | 0.837 | 1.627 | 0.754 | 0.902 | 0.360 | 0.545 |
| CIU | 0.820 | 1.634 | 0.736 | 0.893 | 0.380 | 0.552 |
表6
PLS-SEM结果"
| 项目 | 假设 | 路径系数 | t统计量 | p值 | 是否支持假设 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN→AE | H1a | 0.109 | 2.032 | 0.042 | Yes* |
| EN→EI | H1b | 0.135 | 2.619 | 0.009 | Yes** |
| ES→AE | H2a | 0.190 | 3.685 | <.001 | Yes*** |
| ES→EI | H2b | 0.132 | 2.491 | 0.013 | Yes* |
| SP→AE | H3a | 0.145 | 2.498 | 0.013 | Yes* |
| SP→EI | H3b | 0.224 | 3.927 | <.001 | Yes*** |
| IS→AE | H4a | 0.190 | 3.159 | 0.002 | Yes** |
| IS→EI | H4b | 0.159 | 3.000 | 0.003 | Yes** |
| CON→AE | H5a | 0.168 | 3.413 | 0.001 | Yes** |
| CON→EI | H5b | 0.159 | 2.985 | 0.003 | Yes** |
| AE→CIU | H6 | 0.404 | 9.228 | <.001 | Yes*** |
| EI→CIU | H7 | 0.304 | 6.548 | <.001 | Yes*** |
表7
调节结果"
| 项目 | 直接效应 | p值 | 间接效应 | 95%置信区间 | SE值 | 调节类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN→AE→CIU | 0.066 | 0.143 | 0.152 | (0.104, 0.205) | 0.026 | 间接调节 |
| EN→EI→CIU | 0.066 | 0.143 | 0.119 | (0.075, 0.166) | 0.024 | 间接调节 |
| ES→AE→CIU | 0.125 | 0.006 | 0.158 | (0.109, 0.214) | 0.027 | 补充调节 |
| ES→EI→CIU | 0.125 | 0.006 | 0.112 | (0.067, 0.161) | 0.024 | 补充调节 |
| SP→AE→CIU | 0.184 | <.001 | 0.159 | (0.110, 0.212) | 0.026 | 补充调节 |
| SP→EI→CIU | 0.184 | <.001 | 0.119 | (0.031, 0.110) | 0.027 | 补充调节 |
| IS→AE→CIU | 0.243 | <.001 | 0.146 | (0.026, 0.126) | 0.025 | 补充调节 |
| IS→EI→CIU | 0.243 | <.001 | 0.102 | (0.098, 0.198) | 0.025 | 补充调节 |
| CON→AE→CIU | 0.203 | <.001 | 0.146 | (0.100, 0.198) | 0.025 | 补充调节 |
| CON→EI→CIU | 0.203 | <.001 | 0.105 | (0.061, 0.152) | 0.023 | 补充调节 |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
沈鹏熠, 李金雄, 万德敏. “以情动人”还是“以理服人”? 人工智能聊天机器人角色对顾客情感依恋的影响研究[J/OL]. 南开管理评论, 2024: 1-20.
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
王永贵, 张静. 定制服务代理对消费者购买意愿的影响——基于AI聊天机器人与人工服务比较的实验研究[J]. 学习与探索, 2024(6): 145-159, 196.
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
刘莉, 邵波. 生成式AI赋能智慧图书馆的融合路径探析——以扎耶德大学图书馆为例[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2023(12): 34-43.
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
王文韬, 钱鹏博, 丁雨辰, 等. 个性化内容推荐关闭对移动社交媒体持续使用意愿的影响[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(11): 88-100.
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
雷承锋, 邢振江. AIGC重构消费行为: 持续使用意愿影响因素[J]. 技术经济与管理研究, 2024(6): 152-158.
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
脱润萱, 虞涵. 游戏化数字阅读App的使用意愿研究[J]. 当代传播, 2023(6): 49-55.
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
倪洁玲, 刘泽, 邵波. 下一代图书馆服务平台用户持续使用意愿影响因素研究[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2024(4): 112-123.
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
沈书生. 学习新生态: 构建信息化学习力[J]. 苏州大学学报(教育科学版), 2020, 8(1): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
中华人民共和国教育部教育部高等教育司2023年工作要点[EB/OL]. [2024-01-16].
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
|
| [1] | 李默, 杨彬. 从生成式人工智能到通用人工智能:赋能图书馆知识服务模式创新[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(6): 50-61. |
| [2] | 武茹, 张茹涵, 戴晨星, 鲁程. 基于创新人才培养的高校图书馆知识产权素养教育研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(6): 79-87. |
| [3] | 杨行. 美国佛罗里达大学图书馆提升馆员数字学术服务能力的实践与启示[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(5): 93-101. |
| [4] | 姜晔, 刘琼, 刘桂锋. AIGC赋能高校图书馆信息文化的培育框架研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(4): 36-44. |
| [5] | 周文杰. 信息资源序化整理的三次浪潮与图书馆统计评价体系的演进[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(3): 21-31. |
| [6] | 邹娅一. ChatGPT赋能图书馆智慧服务:机遇、挑战与发展策略[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(2): 71-80. |
| [7] | 易童, 罗国锋. 教育技术应用下高校图书馆馆员数字素养提升路径研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(2): 61-70. |
| [8] | 万乔. 多元协同视角下高校图书馆融合发展模式及思路[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(1): 97-104. |
| [9] | 杨玲梅. 高校图书馆服务乡村振兴的知识信息转移模型探讨[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(1): 71-82. |
| [10] | 夏义堃, 蒋洁, 张夏恒, 王建冬, 周文杰, 杨新涯, 李阳. 发展新质生产力的信息资源管理学科回应与思考[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(1): 4-32. |
| [11] | 万乔. 未来学习中心:育人范式、基本特性及空间构建[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(9): 57-65. |
| [12] | 张嘉宁, 宋西贵. ChatGPT与图书馆的领域动向[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(8): 19-29. |
| [13] | 谢燕洁. 中国公共图书馆老年人服务研究述评[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(7): 18-26. |
| [14] | 符荣鑫, 杨小华. AIGC语言模型分析及其高校图书馆应用场景研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(7): 27-38. |
| [15] | 许魁义, 卢珂琦, 陆和建. 中国公共图书馆参与文化遗产传承的策略研究——以公共图书馆古籍保护为例[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(7): 85-93. |
|
||