农业图书情报学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 20-32.doi: 10.13998/j.cnki.issn1002-1248.24-0721
所属专题: 人工智能
人工智能素养视域下高校学生用户使用AIGC信息行为分析
- 北京理工大学 教育学院,北京 100081
-
收稿日期:2024-10-09出版日期:2024-11-05发布日期:2025-04-09 -
通讯作者:赵锦涛 -
作者简介:崔宇红(1972- ),女,教授,博士生导师,北京理工大学教育学院,研究方向为科学计量与科技评价、大数据分析与情报研究、人工智能教育应用
-
基金资助:2023年度教育部人文社会科学研究规划基金项目“开放科学场域中高校青年科研人员学术行为及治理机制研究”(23YJAZH021)
AIGC Using Behavior Analysis from the Perspective of Artificial Intelligence Literacy
- Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081
-
Received:2024-10-09Online:2024-11-05Published:2025-04-09 -
Contact:Jintao ZHAO
摘要:
[目的/意义] AIGC技术为创造包容与广泛的学习环境提供机遇,针对滥用AIGC工具潜在风险,分析人工智能素养背景下影响学生用户使用AIGC工具的因素,探究学生用户使用影响因素模型框架与关联路径,为图书馆人工智能素养教育推进提供理论依据。 [方法/过程] 借鉴TAM构建概念关系模型,提出基本假设,通过结构方程模型和中介分析进行验证解释。 [结果/结论] 研究表明,努力期望直接影响学生用户对AIGC工具的实际使用,并且通过绩效期望和行为意图连续间接地增加他们对于AIGC工具的实际使用。此外,人工智能素养可以显著提高学生用户AIGC实际使用的转化率。研究弥补学生用户使用AIGC信息行为研究,揭示影响因素的内在关联路径,为图书馆人工智能素养培育提供科学的建议与启示。
中图分类号: G40
引用本文
崔宇红, 赵锦涛. 人工智能素养视域下高校学生用户使用AIGC信息行为分析[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(11): 20-32.
Yuhong CUI, Jintao ZHAO. AIGC Using Behavior Analysis from the Perspective of Artificial Intelligence Literacy[J]. Journal of Library and Information Science in Agriculture, 2024, 36(11): 20-32.
表1
使用AIGC影响因素变量测量题项"
| 变量 | 题项 |
|---|---|
| 努力期望EE | 学习如何使用AIGC对我来说很容易 |
| 与AIGC的互动通俗易懂 | |
| AIGC易于使用来管理与发现知识 | |
| AIGC使用用户界面友好 | |
| AIGC易于访问 | |
| 绩效期望PE | AIGC在日常学习中提供所寻求的完整的相关信息 |
| AIGC是搜索引擎的更好替代品 | |
| 使用AIGC可以帮助我提高生产力更快完成任务 | |
| 使用AIGC有助于理解与工作/学术相关的概念 | |
| 使用AIGC有助于提高我的科研水平 | |
| 行为意图BI | 我会选择从AIGC获取知识与信息资源 |
| 值得向其他人推荐AIGC | |
| 我有兴趣在未来工作/科研更频繁地使用AIGC | |
| 人工智能素养AI | 有足够的专业知识为自己使用AIGC提供技术支持 |
| 我能够利用AIGC找到需要的信息和内容 | |
| 我知道如何验证AIGC生成内容是否可信 | |
| 使用后能够评估当前AIGC产品的能力和局限性 | |
| 实际使用AU | 您实际使用AIGC工具的频率 |
表2
信度检验结果"
| 潜变量 | 观测变量 | 标准化因子载荷 |
|---|---|---|
| EE(感知易用性) | Cronbach α=0.936 | |
| 学习如何使用AIGC对我来说很容易 | 0.808 | |
| 与AIGC互动通俗易懂 | 0.905 | |
| AIGC易于用来管理和发现知识 | 0.913 | |
| AIGC使用的用户界面友好 | 0.898 | |
| AIGC易于访问 | 0.809 | |
| PE(感知有用性) | Cronbach α=0.947 | |
| AIGC能在日常学习中提供所寻求的完整信息 | 0.878 | |
| 使用AIGC可以帮助我提高生产力更快完成任务 | 0.890 | |
| 使用AIGC有助于理解与工作/科研中相关的概念 | 0.907 | |
| 使用AIGC有助于提高我的科研水平 | 0.903 | |
| BI(行为意图) | Cronbach α=0.953 | |
| 我会选择继续从AIGC工具获取知识与信息资源 | 0.919 | |
| 我愿意推荐其他人使用AIGC工具 | 0.899 | |
| 我会保持或增加使用AIGC工具频率 | 0.912 | |
| 我支持提供AIGC工具 | 0.928 | |
| AI(人工智能素养) | Cronbach α=0.939 | |
| 有足够的专业知识为自己使用AIGC提供技术支持 | 0.893 | |
| 我能够利用AIGC找到需要的信息和内容 | 0.889 | |
| 我知道如何验证AIGC生成内容是否可信 | 0.885 | |
| 使用后能够评估当前AIGC产品的能力和局限性 | 0.899 | |
| AU(实际使用) | Cronbach α=0.968 | |
| 使用AIGC是搜索引擎的更好替代品? | 0.869 | |
| 您使用生成式人工智能工具频率如何? | 0.614 | |
表3
假设模型路径分析"
| 假设 | 假设路径 | 估计值 | SE | CR值 | 显著性 | 假设判断 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
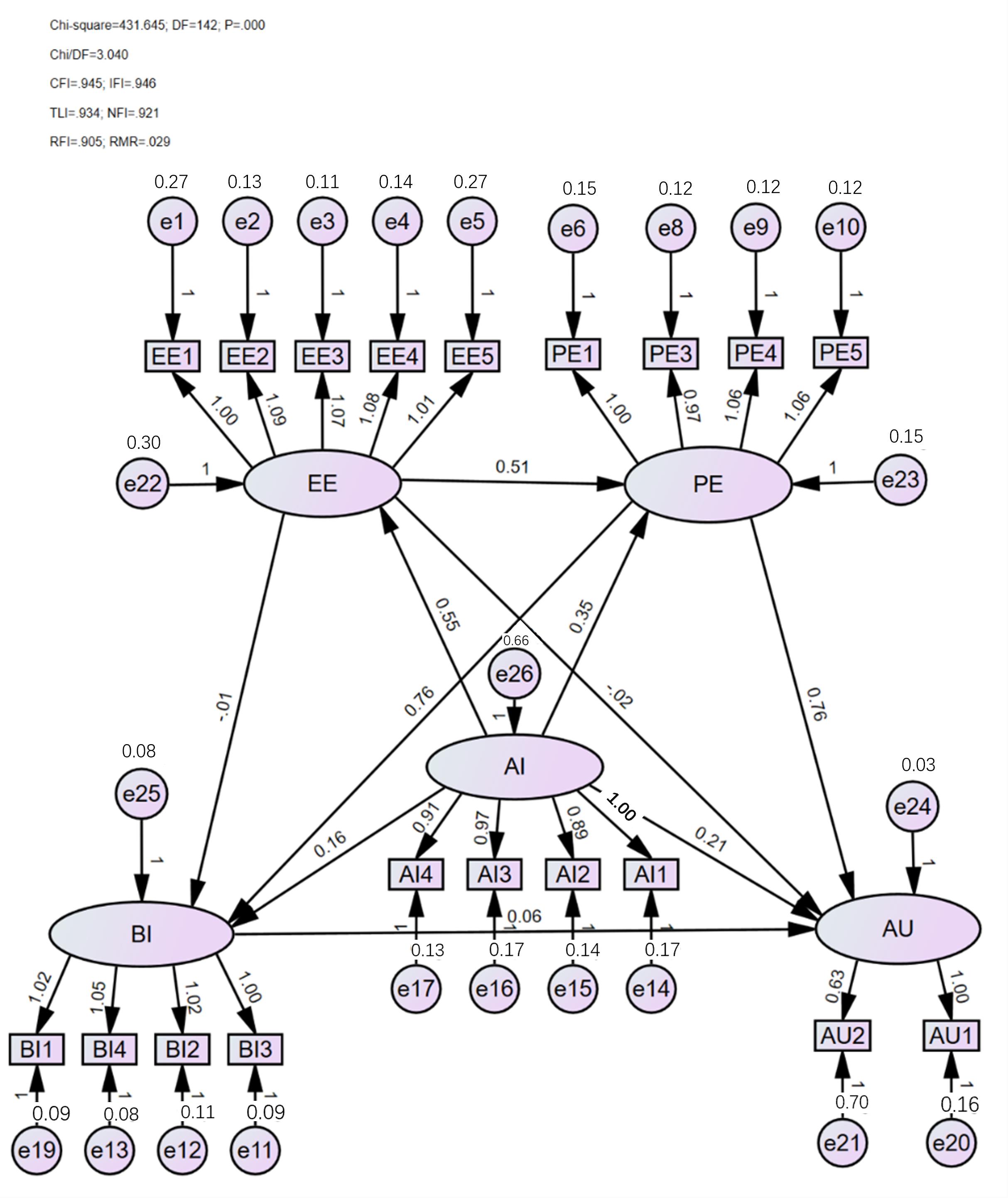
| H1:努力期望与绩效期望呈正相关 | EE→PE | 0.514 | 0.061 | 8.323 | *** | 支持 |
| H2:努力期望与使用AIGC行为意图呈正相关 | EE→BI | -0.009 | 0.053 | -0.159 | .874 | 不支持 |
| H3:努力期望与AIGC的实际使用呈正相关 | EE→AU | -0.023 | 0.069 | -0.340 | .734 | 不支持 |
| H4:绩效期望与使用AIGC行为意图呈正相关 | PE→BI | 0.777 | 0.070 | 10.755 | *** | 支持 |
| H5:绩效期望与AIGC的实际使用情况呈正相关 | PE→AU | 0.751 | 0.137 | 5.548 | *** | 支持 |
| H8:行为意图与AIGC的实际使用呈正相关 | BI→AU | 0.058 | 0.126 | 0.479 | .632 | 不支持 |
| H10a:人工智能素养与绩效期望呈正相关 | AI→EE | 0.635 | 0.055 | 0.996 | *** | 支持 |
| H10b:人工智能素养与绩效期望呈正相关 | AI→PE | 0.402 | 0.050 | 6.951 | *** | 支持 |
| H10c:人工智能素养与行为意图呈正相关 | AI→BI | 0.187 | 0.043 | 3.610 | *** | 支持 |
| H10d:人工智能素养与实际使用呈正相关 | AI→AU | 0.237 | 0.058 | 3.546 | *** | 支持 |
| 1 |
刘金海. 2023十大新兴技术[J]. 世界科学, 2023(9): 34-39.
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
张一春, 钟秋菊, 任屹远. 高校教学信息化创新发展的核心内容与实践进路——基于教育数字化转型的TASH视角[J]. 电化教育研究, 2024, 45(2): 71-76, 83.
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
肖银洁, 吕宏山. 教育数字化赋能高校教学新形态的风险审视与纾解路向[J]. 大学教育科学, 2023, 14(2): 24-32, 92.
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
吴青, 刘毓文. ChatGPT时代的高等教育应对: 禁止还是变革[J]. 高校教育管理, 2023, 17(3): 32-41.
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
苗逢春. 生成式人工智能及其教育应用的基本争议和对策[J]. 开放教育研究, 2024, 30(1): 4-15.
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
盛大林, 吴星晔, 钟笑寒. 新高考改革中的科目选考机制: 一个博弈论分析[J]. 经济学(季刊), 2024, 24(1): 17-29.
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
袁曾. 生成式人工智能治理的法律回应[J]. 上海大学学报(社会科学版), 2024, 41(1): 28-39.
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
朱莎, 杨洒, 李嘉源, 等. 智慧课堂情境的课程核心素养评价范式[J]. 开放教育研究, 2024, 30(1): 83-88.
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
刘贵华, 孟照海. 论中国教育学自主知识体系建设[J]. 华东师范大学学报(教育科学版), 2024, 42(2): 1-17.
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
李帅帅, 何向真, 张跃洲, 等. 融合多情感的语音驱动虚拟说话人生成方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2024, 41(8): 2546-2553.
|
|
|
|
| 17 |
赵晓伟, 戴岭, 沈书生, 等. 促进高意识学习的教育提示语设计[J]. 开放教育研究, 2024, 30(1): 44-54.
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
郑旭东, 马云飞, 岳婷燕. 欧盟教师数字胜任力框架: 技术创新教师发展的新指南[J]. 电化教育研究, 2021, 42(2): 121-128.
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
邱燕楠, 李政涛. 挑战·融合·变革: “ChatGPT与未来教育” 会议综述[J]. 现代远程教育研究, 2023, 35(3): 3-12, 21.
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
李书宁, 刘一鸣. ChatGPT类智能对话工具兴起对图书馆行业的机遇与挑战[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2023, 43(5): 104-110.
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
卢宇, 余京蕾, 陈鹏鹤, 等. 生成式人工智能的教育应用与展望——以ChatGPT系统为例[J]. 中国远程教育, 2023, 43(4): 24-31, 51.
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
宋雪雁, 王萍. 信息采纳行为概念及影响因素研究[J]. 情报科学, 2010, 28(5): 760-762, 767.
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
JO H,
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
毛太田, 汤淦, 马家伟, 等. 人工智能生成内容(AIGC)用户采纳意愿影响因素识别研究——以ChatGPT为例[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(7): 126-136.
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
曹晶, 叶继元, 朱强, 等. 影响用户访问全国信息资源保障平台行为意向的因素分析[J]. 图书馆杂志, 2023, 42(10): 104-116.
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
王超, 顾小清. OMO教学的推进: 以中小学生在线学习参与意愿为切入点突破在线教学困境: 基于技术接受模型的实证研究[J]. 现代教育技术, 2022, 32(2): 72-80.
|
|
|
|
| 31 |
王军, 程文婷. 教育类移动应用技术接受模型构建[J]. 图书情报工作, 2017, 61(16): 60-65.
|
|
|
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
张晓丹, 江洪, 王可慧. 学术APP用户采纳意愿影响因素实证研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2018, 62(18): 90-101.
|
|
|
|
| 36 |
李武, 胡泊, 季丹. 电子书阅读客户端的用户使用意愿研究: 基于UTAUT和VAM理论视角[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2018, 38(4): 103-110.
|
|
|
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
祝智庭, 戴岭, 胡姣. AIGC技术赋能高等教育数字化转型的新思路[J]. 中国高教研究, 2023(6): 12-19, 34.
|
|
|
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
王树胜, 王俊菊. 动机驱动的AI赋能外语学习接受度研究——基于技术接受模型[J]. 外语电化教学, 2024(6): 23-29, 108.
|
|
|
|
| 43 |
洪学婷, 张宏梅, 张业臣. Airbnb平台的使用意愿与使用行为: 对技术接受模型的扩展[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2021, 40(4): 91-95, 117.
|
|
|
|
| 44 |
万力勇, 杜静, 熊若欣. 人机共创: 基于AIGC的数字化教育资源开发新范式[J]. 现代远程教育研究, 2023, 35(5): 12-21.
|
|
|
|
| 45 |
钟柏昌, 刘晓凡, 杨明欢. 何谓人工智能素养: 本质、构成与评价体系[J]. 华东师范大学学报(教育科学版), 2024, 42(1): 71-84.
|
|
|
|
| 46 |
罗国锋, 刘清生, 易童. 新质人才培养视域下高校图书馆人工智能素养教育内容与策略研究[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2025(1): 85-93.
|
|
|
|
| 47 |
郭亚军, 寇旭颍, 冯思倩, 等. 人工智能素养: 内涵剖析与评估标准构建[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2025, 45(2): 42-50.
|
|
|
|
| 48 |
|
| 49 |
|
| 50 |
VENKATESH, THONG, XU. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology[J]. MIS quarterly, 2012, 36(1): 157.
|
| 51 |
|
| 52 |
|
| 53 |
|
| 54 |
|
| [1] | 罗学妹, 林予哲. AIGC驱动下研究生数字素养教育提升路径探索[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(9): 70-77. |
| [2] | 袁帆, 李佳. 生成式人工智能在图书馆信息素养教育中的机遇、挑战与发展方向——一项范围综述[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(9): 44-57. |
| [3] | 李华明. 机遇与挑战:ChatGPT赋能图书馆知识服务中的应用研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(8): 96-105. |
| [4] | 李白杨, 孙榕. 基于“知识-技能”导航的人工智能素养通识教育课程构建[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(8): 34-42. |
| [5] | 吴丹, 孙昕玦. 以人为本的人工智能素养教育探究:UNESCO教师和学生人工智能能力框架的解读与启示[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(8): 4-19. |
| [6] | 罗国锋, 刘清生. ChatGPT赋能高校信息素养教育应用场景与实践研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(4): 91-101. |
| [7] | 王伟正, 乔鸿, 李肖俊, 王静静. 基于AIDUA框架的生成式人工智能使用意愿研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(2): 36-50. |
| [8] | 邹娅一. ChatGPT赋能图书馆智慧服务:机遇、挑战与发展策略[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(2): 71-80. |
| [9] | 张铭洁, 赵瑞雪. ChatGPT驱动的智慧图书馆情感感知与服务优化[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(12): 74-88. |
| [10] | 张嘉宁, 宋西贵. ChatGPT与图书馆的领域动向[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(8): 19-29. |
| [11] | 符荣鑫, 杨小华. AIGC语言模型分析及其高校图书馆应用场景研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(7): 27-38. |
| [12] | 王超, 孔祥辉. 大型预训练语言模型在网络健康信息鉴别中的应用探讨[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(6): 51-59. |
| [13] | 吕瑞娟, 张静蓓, 严丹, 蔡迎春. AIGC与GLAM创新发展综述——基于“生成未来·AIGC与GLAM创新发展”前沿学术论坛[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(5): 27-36. |
| [14] | 李鹏, 宋西贵. AIGC技术赋能图书馆阅读推广工作的创新应用[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(12): 84-93. |
| [15] | 郭鹏睿, 文庭孝. 大语言模型对信息检索系统与用户检索行为影响研究[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2023, 35(11): 13-22. |
|
||