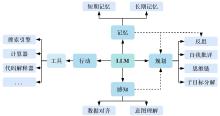
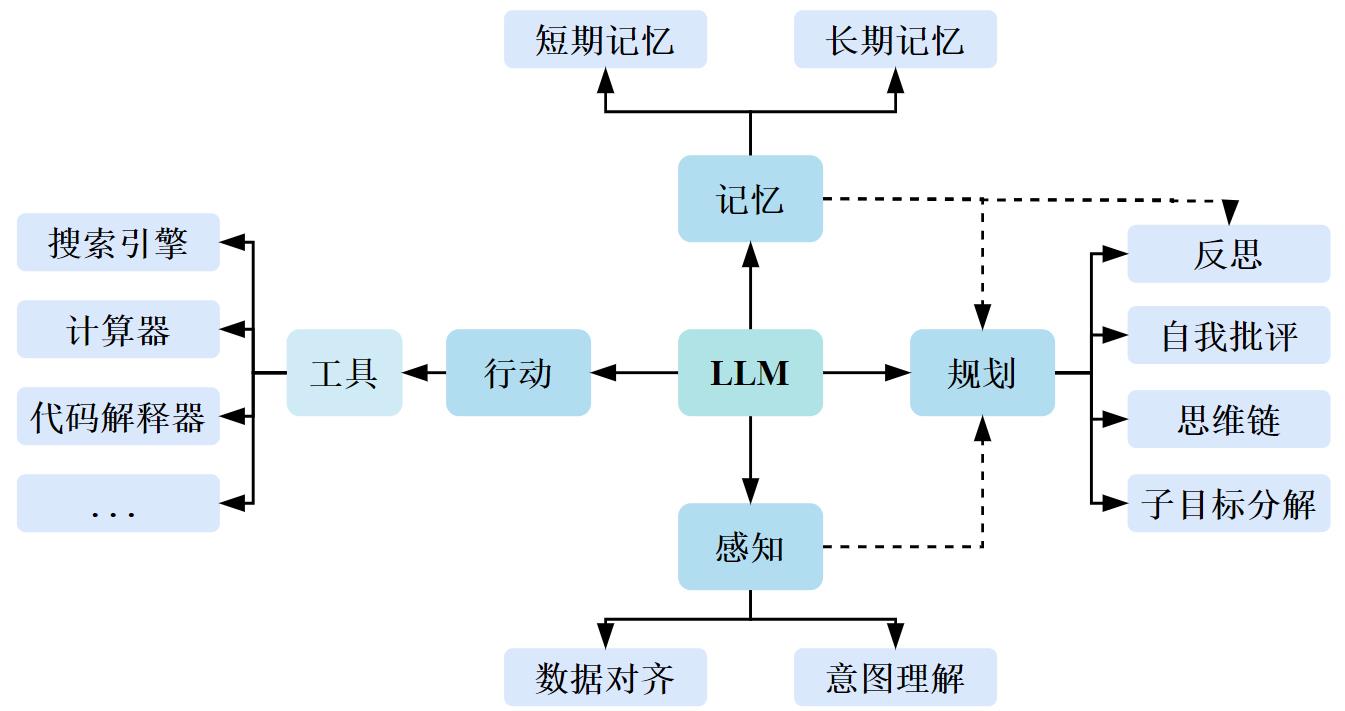
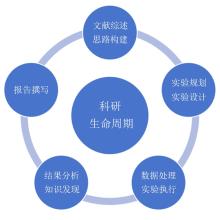
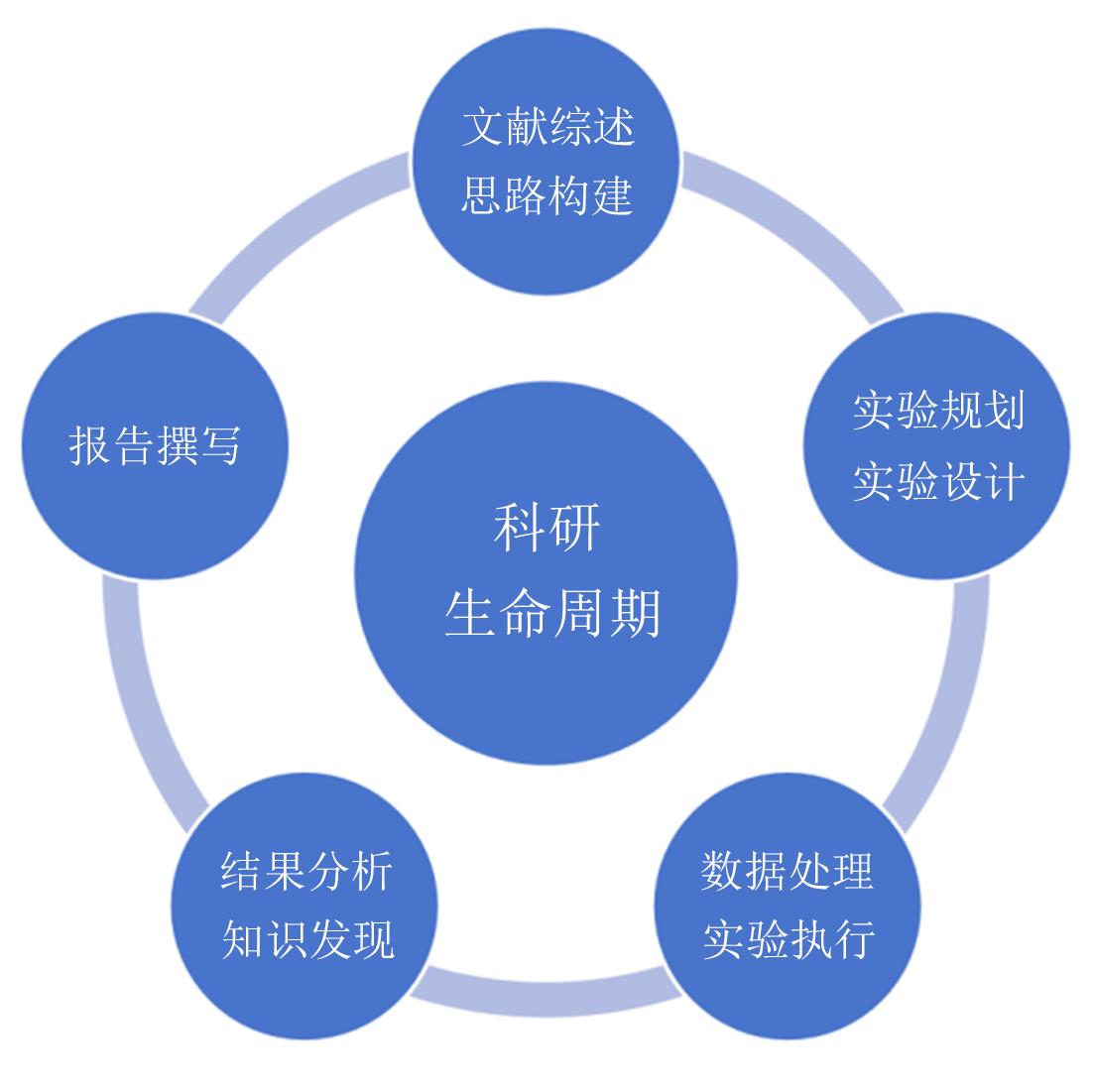
| [1] |
YANG J, LI A, FARAJTABAR M, et al. Learning to incentivize other learning agents[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2020. .
|
| [2] |
LAIRD J E, NEWELL A, ROSENBLOOM P S. SOAR: An architecture for general intelligence[J]. Artificial intelligence, 1987, 33(1): 1-64.
|
| [3] |
WOOLDRIDGE M, JENNINGS N R. Intelligent agents: Theory and practice[J]. The knowledge engineering review, 1995, 10(2): 115-152.
|
| [4] |
WANG L, MA C, FENG X Y, et al. A survey on large language model based autonomous agents[J]. Frontiers of computer science, 2024, 18(6): 186345.
|
| [5] |
KHOT T, TRIVEDI H, FINLAYSON M, et al. Decomposed prompting: A modular approach for solving complex tasks[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2022. .
|
| [6] |
YAO S, ZHAO J, YU D, et al. ReAct: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2022. .
|
| [7] |
HOU X, YANG M, JIAO W, et al. CoAct: A global-local hierarchy for autonomous agent collaboration[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024.
|
| [8] |
DONGRE V, YANG X C, ACIKGOZ E C, et al. ReSpAct: Harmonizing reasoning, speaking, and acting towards building large language model-based conversational AI agents[J]. arXiv e-prints, 2024: arXiv: .
|
| [9] |
PAN J B, ZHANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. DynaThink: Fast or slow? A dynamic decision-making framework for large language models[C]//Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Miami, Florida, USA. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: ACL, 2024: 14686-14695.
|
| [10] |
LEANG J O J, GEMA A P, COHEN S B. CoMAT: Chain of mathematically annotated thought improves mathematical reasoning[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024.
|
| [11] |
SCHICK T, DWIVEDI-YU J, DESSÌ, et al. Toolformer: Language models can teach themselves to use tools[J]. arXiv e-prints, 2023: arXiv: .
|
| [12] |
DU Y, WEI F, ZHANG H. AnyTool: Self-reflective, hierarchical agents for large-scale api calls[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024. .
|
| [13] |
LIU X, PENG Z, YI X, et al. ToolNet: Connecting large language models with massive tools via tool graph[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024. .
|
| [14] |
MODARRESSI A, IMANI A, FAYYAZ M, et al. RET-LLM: Towards a general read-write memory for large language models[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2023. .
|
| [15] |
HONG S, ZHUGE M, CHEN J, et al. MetaGPT: Meta programming for a multi-agent collaborative framework[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2023. .
|
| [16] |
ANOKHIN P, SEMENOV N, SOROKIN A, et al. AriGraph: Learning knowledge graph world models with episodic memory for LLM agents[J]. arXiv e-prints, 2024: arXiv: .
|
| [17] |
TRAN K, DAO D, NGUYEN M, et al. Multi-agent collaboration mechanisms: A survey of LLMs[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2025. .
|
| [18] |
WU Q Y, BANSAL G, ZHANG J Y, et al. AutoGen: Enabling next-gen LLM applications via multi-agent conversation framework[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2023.
|
| [19] |
HE Y, HUANG G, FENG P, et al. PaSa: An LLM agent for comprehensive academic paper search[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2025. .
|
| [20] |
CHEN Z, LIU K, WANG Q, et al. MindSearch: Mimicking human minds elicits deep AI searcher[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024. .
|
| [21] |
SAMI M A, RASHEED Z, KEMELL K, et al. System for systematic literature review using multiple AI agents: Concept and an empirical evaluation[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024. .
|
| [22] |
BAEK J, JAUHAR S K, CUCERZAN S, et al. ResearchAgent: Iterative research idea generation over scientific literature with large language models[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024. .
|
| [23] |
GOTTWEIS J, WENG W, DARYIN A, et al. Towards an AI co-scientist[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2025. .
|
| [24] |
QU Y H, HUANG K X, COUSINS H, et al. CRISPR-GPT An LLM agent for automated design of gene-editing experiments[J]. bioRxiv, 2024: 2024.04.25.591003.
|
| [25] |
NI B, BUEHLER M J. MechAgents: Large language model multi-agent collaborations can solve mechanics problems, generate new data, and integrate knowledge[J]. Extreme mechanics letters, 2024, 67: 102131.
|
| [26] |
CHRIS L, CONG L, ROBERT T L, et al. The AI scientist: Towards fully automated open-ended scientific discovery[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2024.
|
| [27] |
XIN Q, KONG Q, JI H, et al. BioInformatics Agent (BIA): Unleashing the power of large language models to reshape bioinformatics workflow[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024. .
|
| [28] |
BRAN A M, COX S, SCHILTER O, et al. Augmenting large language models with chemistry tools[J]. Nature machine intelligence, 2024, 6(5): 525-535.
|
| [29] |
GHAFAROLLAHI A, BUEHLER M J. ProtAgents: Protein discovery via large language model multi-agent collaborations combining physics and machine learning[J]. Digital discovery, 2024, 3(7): 1389-1409.
|
| [30] |
XIAO Y, LIU J, ZHENG Y, et al. CellAgent: An LLM-driven multi-agent framework for automated single-cell data analysis[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2024. .
|
| [31] |
SCHMIDGALL S, SU Y, WANG Z, et al. Agent laboratory: Using LLM agents as research assistants[J/OL]. ArXiv, 2025. .
|