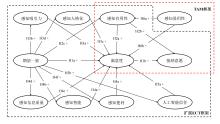
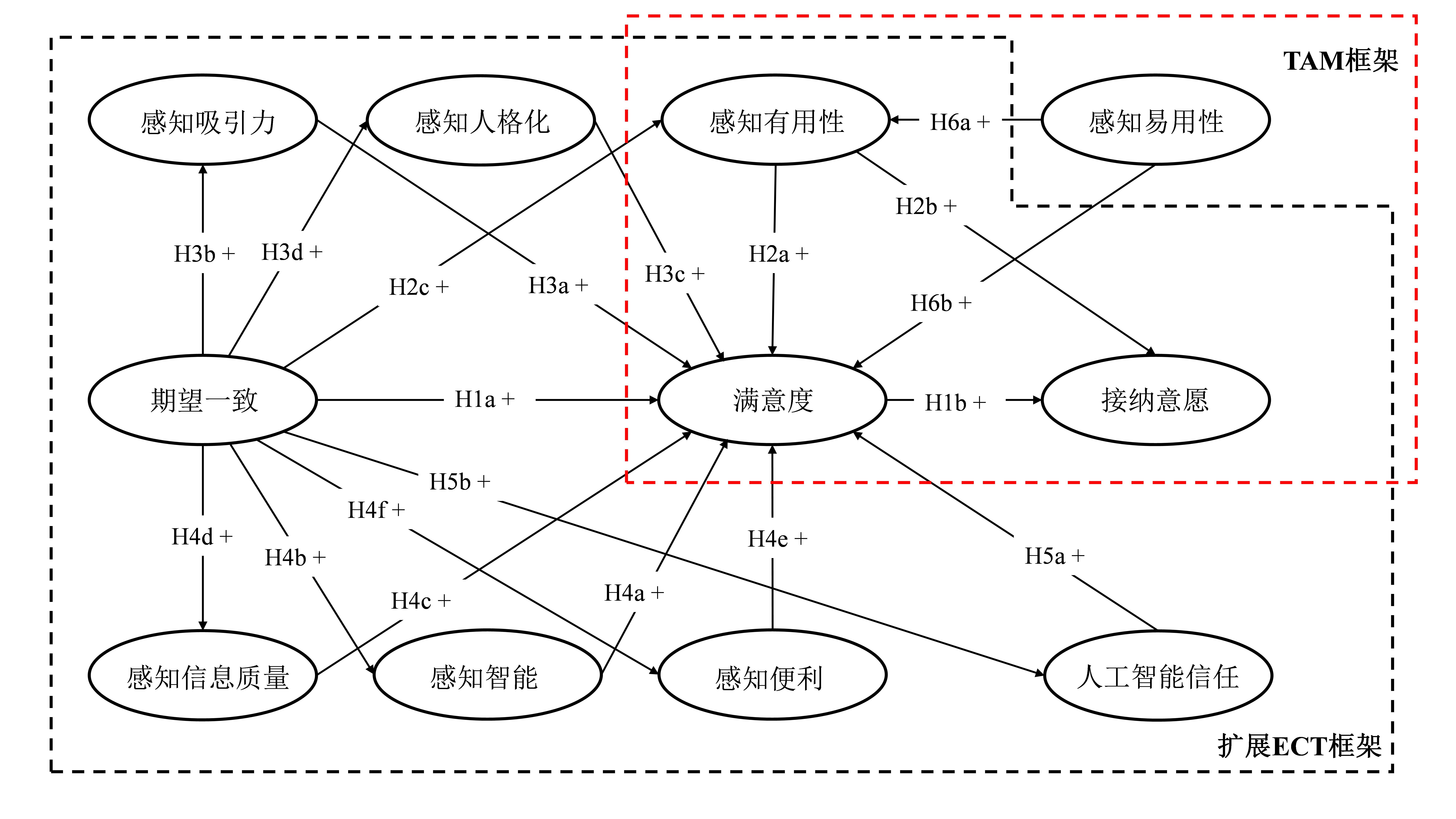
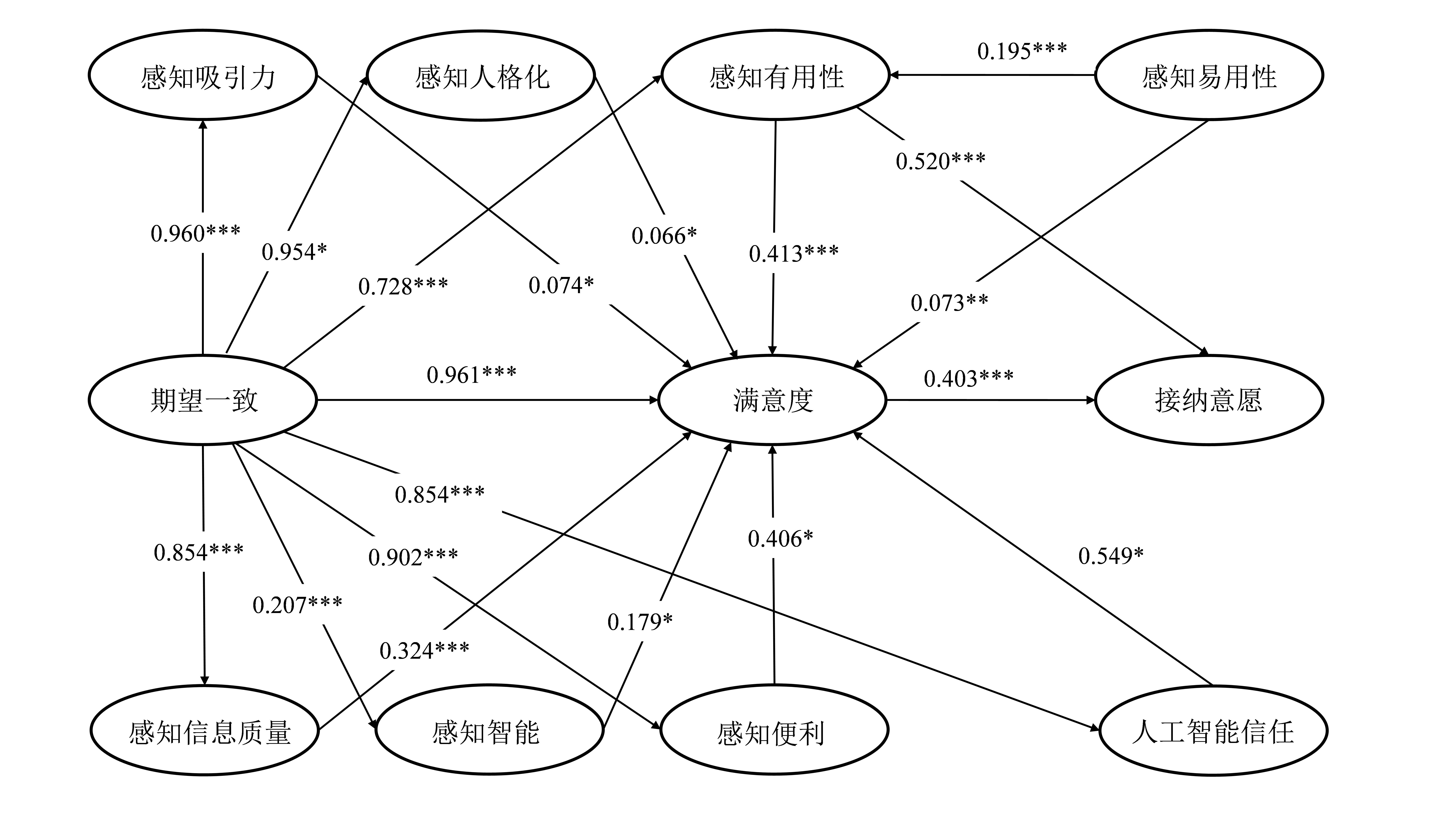
| 1 |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和2035年远景目标纲要[EB/OL]. [2021-03-13].
|
| 2 |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 数字中国建设整体布局规划[EB/OL]. [2023-02-27].
|
| 3 |
刘玮. ChatGPT类生成式人工智能嵌入数字政府建设: 可供、限制与优化——基于技术可供性视角[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2023, 46(10): 69-76.
|
|
LIU W. Embedding ChatGPT-like generative artificial intelligence in digital government construction: Affordances, constraints, and optimization - A perspective based on technological affordance[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2023, 46(10): 69-76.
|
| 4 |
SESTINO A, D'ANGELO A. My doctor is an avatar! The effect of anthropomorphism and emotional receptivity on individuals' intention to use digital-based healthcare services[J]. Technological forecasting and social change, 2023, 191: 122505.
|
| 5 |
NI M Q. Digital participation for inclusive growth: A case study of Singapore's collaborative digital governance model[M]//The Urban Book Series. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022: 323-337.
|
| 6 |
KATTEL R, MERGEL I. Estonia's digital transformation: Mission mystique and the hiding hand[M]//Great Policy Successes. Cambridge, UK: Oxford University Press, 2019: 143-160.
|
| 7 |
TWEED A. From Eliza to Ellie: the evolution of the AI therapist[EB/OL]. [2019-09-12].
|
| 8 |
BHATTACHERJEE A. An empirical analysis of the antecedents of electronic commerce service continuance[J]. Decision support systems, 2001, 32(2): 201-214.
|
| 9 |
BHATTACHERJEE A. Understanding information systems continuance: An expectation-confirmation model[J]. MIS quarterly, 2001, 25(3): 351.
|
| 10 |
LEE M C. Explaining and predicting users' continuance intention toward e-learning: An extension of the expectation–confirmation model[J]. Computers & education, 2010, 54(2): 506-516.
|
| 11 |
GUPTA A, DHIMAN N, YOUSAF A, et al. Social comparison and continuance intention of smart fitness wearables: An extended expectation confirmation theory perspective[J]. Behaviour & information technology, 2021, 40(13): 1341-1354.
|
| 12 |
YUEN K F, CAI L H, QI G Q, et al. Factors influencing autonomous vehicle adoption: An application of the technology acceptance model and innovation diffusion theory[J]. Technology analysis & strategic management, 2021, 33(5): 505-519.
|
| 13 |
HUARNG K H, YU T H K, LEE C F. Adoption model of healthcare wearable devices[J]. Technological forecasting and social change, 2022, 174: 121286.
|
| 14 |
OENTORO W. Mobile payment adoption process: A serial of multiple mediation and moderation analysis[J]. The bottom line, 2021, 34(3/4): 225-244.
|
| 15 |
YE J H, LEE Y S, WANG C L, et al. The continuous use intention for the online learning of Chinese vocational students in the post-epidemic era: The extended technology acceptance model and expectation confirmation theory[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(3): 1819.
|
| 16 |
HUANG Y K, YU Z Y. Understanding the continuance intention for artificial intelligence news anchor: Based on the expectation confirmation theory[J]. Systems, 2023, 11(9): 438.
|
| 17 |
赵雪芹, 刘雅宁. 在线视频用户关闭弹幕的影响因素研究[J]. 新闻与传播评论, 2018, 71(5): 16-26.
|
|
ZHAO X Q, LIU Y N. A study on the factors influencing online video users to turn off Danmaku[J]. Journalism & communication review, 2018, 71(5): 16-26.
|
| 18 |
STONE R W, BAKER-EVELETH L. Students' expectation, confirmation, and continuance intention to use electronic textbooks[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2013, 29(3): 984-990.
|
| 19 |
OGHUMA A P, LIBAQUE-SAENZ C F, WONG S F, et al. An expectation-confirmation model of continuance intention to use mobile instant messaging[J]. Telematics and informatics, 2016, 33(1): 34-47.
|
| 20 |
李望平, 苏冬燕, 陈晓星, 等. 基于技术接受模型和计划行为理论的内陆核电站重启公众接受度研究[J]. 科技管理研究, 2023, 43(1): 171-180.
|
|
LI W P, SU D Y, CHEN X X, et al. Study on public acceptance of restart of inland nuclear power plants based on technology acceptance model and theory of planned behavior[J]. Science and technology management research, 2023, 43(1): 171-180.
|
| 21 |
TAM C, SANTOS D, OLIVEIRA T. Exploring the influential factors of continuance intention to use mobile Apps: Extending the expectation confirmation model[J]. Information systems frontiers, 2020, 22(1): 243-257.
|
| 22 |
吴晓波, 张伟齐, 李思涵, 等. 基于技术接受模型(TAM)的智能投资顾问用户采纳意愿链式影响机制研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2023, 53(7): 5-19.
|
|
WU X B, ZHANG W Q, LI S H, et al. A sequential mediation model of the factors influencing the user adoption of robo-advisor: A technology acceptance model (TAM) perspective[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (humanities and social sciences), 2023, 53(7): 5-19.
|
| 23 |
KAMAL S A, SHAFIQ M, KAKRIA P. Investigating acceptance of telemedicine services through an extended technology acceptance model (TAM)[J]. Technology in society, 2020, 60: 101212.
|
| 24 |
RAHI S, GHANI M ABD. Integration of expectation confirmation theory and self-determination theory in Internet banking continuance intention[J]. Journal of science and technology policy management, 2019, 10(3): 533-550.
|
| 25 |
庞洋. 生成式人工智能嵌入数字政府建设的系统性分析[J]. 学术交流, 2023(8): 148-162.
|
|
PANG Y. Systematic analysis of generative artificial intelligence embedded in digital government construction[J]. Academic exchange, 2023(8): 148-162.
|
| 26 |
杨舒文, 包林. 数字媒体艺术中的虚拟性身体形象建构[J]. 中国高校社会科学, 2023(4): 133-141.
|
|
YANG S W, BAO L. Construction of virtual body image in digital media art[J]. Social sciences in Chinese higher education institutions, 2023(4): 133-141.
|
| 27 |
LI J, HUANG J S, LI Y Q. Examining the effects of authenticity fit and association fit: A digital human avatar endorsement model[J]. Journal of retailing and consumer services, 2023, 71: 103230.
|
| 28 |
刘斌, 崔茉琳. ChatGPT时代的虚拟数字人: 拟主体对人类认知与行为的中介[J]. 西南民族大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2023, 44(11): 126-132.
|
|
LIU B, CUI M L. Virtual digital humans in the ChatGPT era: The mediating role of quasi-subjects on human cognition and behavior[J]. Journal of southwest Minzu university (humanities and social science), 2023, 44(11): 126-132.
|
| 29 |
BLUT M, WANG C, WÜNDERLICH N V, et al. Understanding anthropomorphism in service provision: A meta-analysis of physical robots, chatbots, and other AI[J]. Journal of the academy of marketing science, 2021, 49(4): 632-658.
|
| 30 |
BALAKRISHNAN J, ABED S S, JONES P. The role of meta-UTAUT factors, perceived anthropomorphism, perceived intelligence, and social self-efficacy in chatbot-based services?[J]. Technological forecasting and social change, 2022, 180: 121692.
|
| 31 |
GHASEMAGHAEI M, HASSANEIN K. Online information quality and consumer satisfaction: The moderating roles of contextual factors – A meta-analysis[J]. Information & management, 2015, 52(8): 965-981.
|
| 32 |
李桥. 高速铁路旅客感知便利性对旅客满意和忠诚的影响研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2021, 43(6): 1-7.
|
|
LI Q. Effects of perceived service convenience of high-speed railway passengers on passenger satisfaction and loyalty[J]. Journal of the China railway society, 2021, 43(6): 1-7.
|
| 33 |
汤志伟, 龚泽鹏, 韩啸, 等. 公众对智能政务服务和人工政务服务的感知与选择——基于调查实验的研究发现[J]. 电子政务, 2023(9): 105-116.
|
|
TANG Z W, GONG Z P, HAN X, et al. Public perception and choice between intelligent government services and human government services: Findings from a survey experiment[J]. E-Government, 2023(9): 105-116.
|
| 34 |
计纬, 戚海峰, 费鸿萍. 智能助手对消费者的推荐说服机制研究——基于社会角色视角[J/OL]. 南开管理评论, 2024: 1-23.
|
|
JI W, QI H F, FEI H P. A study on the persuasive mechanism of recommendations by intelligent assistants: Based on the social role perspective[J/OL]. Nankai business review, 2024: 1-23.
|
| 35 |
BEDUÉ P, FRITZSCHE A. Can we trust AI? An empirical investigation of trust requirements and guide to successful AI adoption[J]. Journal of enterprise information management, 2022, 35(2): 530-549.
|
| 36 |
YIGITCANLAR T, DEGIRMENCI K, INKINEN T. Drivers behind the public perception of artificial intelligence: Insights from major Australian cities[J]. AI & society, 2022: 1-21.
|
| 37 |
CHEN Y, PRENTICE C, WEAVEN S, et al. The influence of customer trust and artificial intelligence on customer engagement and loyalty - The case of the home-sharing industry[J]. Frontiers in psychology, 2022, 13: 912339.
|
| 38 |
HSIAO K L, CHEN C C. What drives continuance intention to use a food-ordering chatbot? An examination of trust and satisfaction[J]. Library hi tech, 2022, 40(4): 929-946.
|
| 39 |
DAVIS F D, BAGOZZI R P, WARSHAW P R. User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models[J]. Management science, 1989, 35(8): 982-1003.
|
| 40 |
HWANG J, CHOE J Y, KIM H M, et al. Human baristas and robot baristas: How does brand experience affect brand satisfaction, brand attitude, brand attachment, and brand loyalty?[J]. International journal of hospitality management, 2021, 99: 103050.
|
| 41 |
NA S, HEO S, CHOI W, et al. Firm size and artificial intelligence (AI)-based technology adoption: The role of corporate size in South Korean construction companies[J]. Buildings, 2023, 13(4): 1066.
|
| 42 |
刘春明, 王丹, 周杨. 高校教师移动学习平台信息采纳行为研究[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(2): 109-118.
|
|
LIU C M, WANG D, ZHOU Y. A study on university teachers' adoption behavior of mobile learning platform information[J]. Information science, 2024, 42(2): 109-118.
|
| 43 |
朱哲慧, 袁勤俭. 技术接受模型及其在信息系统研究中的应用与展望[J]. 情报科学, 2018, 36(12): 168-176.
|
|
ZHU Z H, YUAN Q J. Technology acceptance model and its application and prospect in the field of information system[J]. Information science, 2018, 36(12): 168-176.
|
| 44 |
FILIERI R, ACIKGOZ F, LI C Y, et al. Influencers' “organic” persuasion through electronic word of mouth: A case of sincerity over brains and beauty[J]. Psychology & marketing, 2023, 40(2): 347-364.
|
| 45 |
LIN C Y. Perceived convenience retailer innovativeness: How does it affect consumers?[J]. Management decision, 2016, 54(4): 946-964.
|
| 46 |
LANKTON N, MCKNIGHT D H, THATCHER J B. Incorporating trust-in-technology into expectation disconfirmation theory[J]. The journal of strategic information systems, 2014, 23(2): 128-145.
|
| 47 |
许孝君, 程光辉, 钱丹丹, 等. 数字经济下旅游商务网站信息生态链运行机制对用户感知的影响研究[J]. 情报科学, 2023, 41(9): 78-86.
|
|
XU X J, CHENG G H, QIAN D D, et al. The influence of the operation mechanism of the information ecological chain of tourism business websites on user perception under the digital economy[J]. Information science, 2023, 41(9): 78-86.
|
| 48 |
LI L, LEE K Y, EMOKPAE E, et al. What makes you continuously use chatbot services? Evidence from Chinese online travel agencies[J]. Electronic markets, 2021, 31(3): 575-599.
|
| 49 |
ASHFAQ M, YUN J, YU S B, et al. I, Chatbot: Modeling the determinants of users' satisfaction and continuance intention of AI-powered service agents[J]. Telematics and informatics, 2020, 54: 101473.
|
| 50 |
毕达天, 张雪, 米艳霖, 等. 算法感知视角下跨平台信息推荐用户接纳意愿研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(21): 100-110.
|
|
BI D T, ZHANG X, MI Y L, et al. A study on user acceptance intention of cross-platform information recommendations from the perspective of algorithm perception[J]. Library and information service, 2023, 67(21): 100-110.
|

 )
)