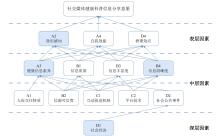
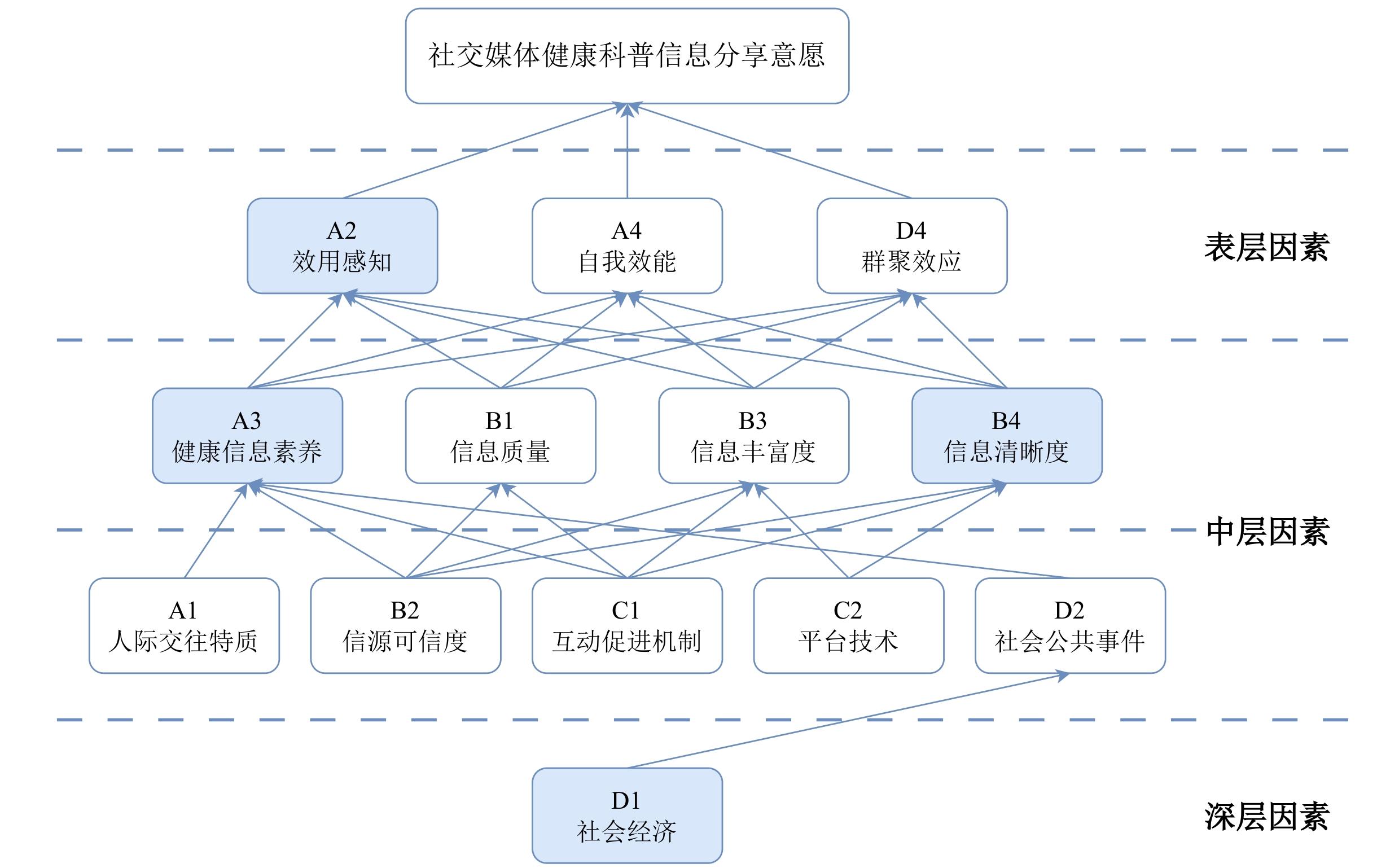
| [1] |
中共中央, 国务院. “健康中国2030”规划纲要[EB/OL]. [2024-12-05].
|
| [2] |
中共中央, 国务院. 关于实施健康中国行动的意见[EB/OL]. [2024-12-05].
|
| [3] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 关于建立健全全媒体健康科普知识发布和传播机制的指导意见[EB/OL]. [2024-12-05].
|
| [4] |
乔昆, 韩晔, 洪玮, 等. 医疗机构新媒体健康科普信息发布评价指标探索与构建[J]. 中国健康教育, 2023, 39(6): 488-492, 522.
|
|
Qiao Kun, Han Ye, Hong Wei, et al. Development of indexes for new media health popularization information dissemination in medical institutions[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Education, 2023, 39(6): 488-492, 522.
|
| [5] |
徐基田. 图书馆科普服务发展历程探究[J]. 数字与缩微影像, 2021(4): 18-20.
|
|
Xu Jitian. An exploration of the development history of library science popularization services[J]. Digital & Micrographic Imaging, 2021(4): 18-20.
|
| [6] |
徐基田. 图书馆科普服务路径选择研究[J]. 河南图书馆学刊, 2021, 41(7): 113-115.
|
|
Xu Jitian. Research on the path selection of library science popularization service[J]. The Library Journal of Henan, 2021, 41(7): 113-115.
|
| [7] |
周谦豪, 姚占雷, 许鑫. 图书馆健康信息素养教育的调研与分析[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2020(10): 77-86.
|
|
Zhou Qianhao, Yao Zhanlei, Xu Xin. Investigation and analysis of library education of health information literacy[J]. Research on Library Science, 2020(10): 77-86.
|
| [8] |
田崑, 宣雯霞, 魏文静, 等. 基于C-A-C理论的健康科普视频对用户持续使用意愿的影响研究[J]. 包装工程, 2023, 44(18): 293-302.
|
|
Tian Kun, Xuan Wenxia, Wei Wenjing, et al. Impact of health science video on users' intention to continue usage: An investigation from the perspective of the C-A-C theory[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2023, 44(18): 293-302.
|
| [9] |
武晓立. 微信用户健康信息分享行为的影响因素研究[J]. 国际新闻界, 2022, 44(10): 96-118.
|
|
Wu Xiaoli. Influence factors of users' health information sharing behavior on WeChat platform[J]. Journal of International Communication, 2022, 44(10): 96-118.
|
| [10] |
魏华, 高劲松, 代芳. 虚拟健康社区社会支持对用户知识分享意愿的影响: 一个有调节的链式中介模型[J]. 情报科学, 2021, 39(12): 146-154, 173.
|
|
Wei Hua, Gao Jinsong, Dai Fang. Impact of social support on users' knowledge sharing intention in virtual health community: A moderated chain mediation model[J]. Information Science, 2021, 39(12): 146-154, 173.
|
| [11] |
尤剑, 李新月, 朱庆华, 等. 基于内容分析法的社交媒体健康信息分享行为研究综述[J]. 现代情报, 2023, 43(6): 67-77, 107.
|
|
You Jian, Li Xinyue, Zhu Qinghua, et al. Health information sharing behavior of social media based on content analysis: A review[J]. Journal of Modern Information, 2023, 43(6): 67-77, 107.
|
| [12] |
田梅, 韩月茹, 刘菡. 社交媒体用户健康信息行为研究元人种志分析[J]. 情报杂志, 2023, 42(8): 177-184.
|
|
Tian Mei, Han Yueru, Liu Han. A meta-ethnographic analysis of social media users health information behavior research[J]. Journal of Intelligence, 2023, 42(8): 177-184.
|
| [13] |
张坤, 查先进, 严亚兰. 从众健康信息转发行为影响因素的扎根探测——以新浪微博为例[J]. 图书与情报, 2022(2): 10-18.
|
|
Zhang Kun, Zha Xianjin, Yan Yalan. Grounded detection on influencing factors for herd forwarding behavior of health information: The case of sina weibo[J]. Library and Information, 2022(2): 10-18.
|
| [14] |
Vardell E, Wang Ting. The information behaviour of individuals changing health insurance plans and an exploration of health insurance priorities[J]. Journal of Information Science, 2024, 50(3): 751-765.
|
| [15] |
韩玺, 蒋佩瑶, 陈思然, 等. 评论特征对用户采纳在线医评信息意愿的影响机制——基于ELM模型和信任转移理论[J]. 现代情报, 2023, 43(9): 36-50.
|
|
Han Xi, Jiang Peiyao, Chen Siran, et al. The influence mechanism of review features on users' willingness to adopt online physician review information - Based on ELM model and trust transfer theory[J]. Journal of Modern Information, 2023, 43(9): 36-50.
|
| [16] |
刘玮, 陈锦博. 搜索即学习视角下知识捕获与学习效果的影响因素研究——以健康信息学习型搜索为例[J]. 信息资源管理学报, 2023, 13(6): 133-143, 155.
|
|
Liu Wei, Chen Jinbo. Identifying the influencial factors of knowledge capture and learning performance in learning-related search: A perspective of SAL[J]. Journal of Information Resources Management, 2023, 13(6): 133-143, 155.
|
| [17] |
王素芳, 周禹涵. 老年人社交媒体健康信息甄别能力及其提升影响因素研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2022, 66(24): 14-29.
|
|
Wang Sufang, Zhou Yuhan. Influencing factors of social media health information screening ability and its improving of the elderly[J]. Library and Information Service, 2022, 66(24): 14-29.
|
| [18] |
陈旖旎, 周晓英, 岳丽欣, 等. 健康焦虑人群信息行为的类型、特征及影响因素[J]. 图书情报知识, 2024, 41(5): 89-102.
|
|
Chen Yini, Zhou Xiaoying, Yue Lixin, et al. The types, characteristics and influencing factors of information behavior in people with health anxiety[J]. Document, Informaiton & Knowledge, 2024, 41(5): 89-102.
|
| [19] |
Vaghefi M S, Beheshti N, Jain H. Dissemination of health messages in online social network: A study of healthcare providers'content generation and dissemination on Twitter[J]. Information & Management, 2024, 61(2): 103925.
|
| [20] |
段尧清, 郑卓闻, 汪银霞, 等. 基于DEMATEL的数据要素属性结构关系分析[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2022, 45(7): 124-131, 123.
|
|
Duan Yaoqing, Zheng Zhuowen, Wang Yinxia, et al. Attributes structural relationship analysis of data as a factor of production based on DEMATEL[J]. Information Studies (Theory & Application), 2022, 45(7): 124-131, 123.
|
| [21] |
陈琦, 熊回香, 肖兵, 等. 高校学生在线健康信息搜寻行为影响因素研究: 全貌、关键及层级路径[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(23): 69-88.
|
|
Chen Qi, Xiong Huixiang, Xiao Bing, et al. A study on the influencing factors of college students' online health information seeking behavior: Panorama, key factors and hierarchical paths[J]. Library and Information Service, 2023, 67(23): 69-88.
|
| [22] |
李建玲. 基于DEMATEL的数字档案馆建设影响因素研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2021.
|
|
Li Jianling. Research on Influencing Factors of Digital Archives Construction Based on DEMATEL[D]. Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2021.
|
| [23] |
袁红, 王焘. 政府数据开放可持续发展关键影响因素识别与作用机理分析[J]. 图书情报工作, 2022, 66(9): 53-65.
|
|
Yuan Hong, Wang Tao. Critical influencing factors identification and action mechanism analysis of the sustainable development of government data openness[J]. Library and Information Service, 2022, 66(9): 53-65.
|
| [24] |
付少雄, 邓胜利, 陈晓宇. 国外健康信息素养研究现状与发展动态述评[J]. 信息资源管理学报, 2016, 6(3): 5-14, 33.
|
|
Fu Shaoxiong, Deng Shengli, Chen Xiaoyu. Review on the foreign research status and development trend of health information literacy[J]. Journal of Information Resources Management, 2016, 6(3): 5-14, 33.
|
| [25] |
姚丽琴, 杨光, 任雁洲. 我国公共图书馆健康信息服务研究[J]. 图书馆工作与研究, 2024(8): 83-91.
|
|
Yao Liqin, Yang Guang, Ren Yanzhou. Research on health information services in public libraries in China[J]. Library Work and Study, 2024(8): 83-91.
|