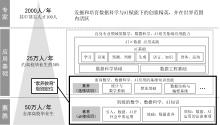
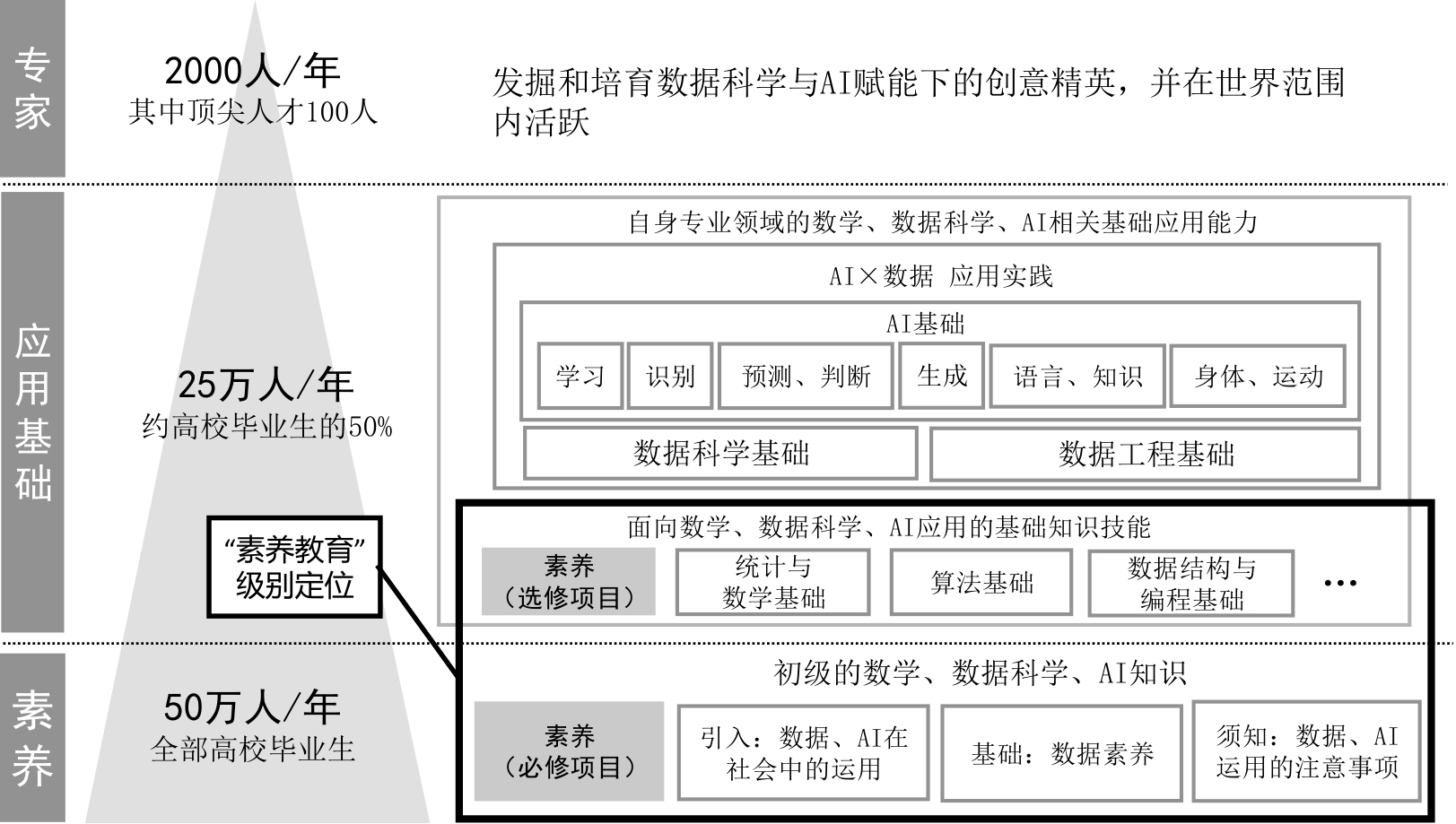
| [1] |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中共中央 国务院印发《教育强国建设规划纲要(2024-2035年)》[EB/OL]. [2025-01-21]. .
|
| [2] |
中华人民共和国教育部. 教育部等九部门关于加快推进教育数字化的意见[EB/OL]. [2025-01-21]. .
|
| [3] |
UNESCO. Artificial intelligence in education[EB/OL]. [2025-01-27]. .
|
| [4] |
UNESCO. International day of education[EB/OL] [2025-03-27]. .
|
| [5] |
张静蓓, 虞晨琳, 蔡迎春. 人工智能素养教育: 全球进展与展望[J]. 图书情报知识, 2024, 41(3): 15-26.
|
|
ZHANG J B, YU C L, CAI Y C. Artificial intelligence literacy education: Global progress and prospects[J]. Documentation, information & knowledge, 2024, 41(3): 15-26.
|
| [6] |
DIGITAL PROMISE. AI literacy: A framework to understand, evaluate, and use emerging technology[EB/OL]. [2025-01-22]. .
|
| [7] |
MyDIGITAL. AI untuk rakyat[EB/OL]. .
|
| [8] |
CHOICE. White paper - Building an AI literacy framework: perspectives from instruction librarians and current information literacy tools[EB/OL]. [2025-01-22]. .
|
| [9] |
日本内阁府. AI戦略2019[EB/OL]. [2025-01-28]. .
|
| [10] |
日本文部科学省. 数理・データサイエンス・AI教育プログラム認定制度[EB/OL]. [2025-01-28]. .
|
| [11] |
龚超, 王冀. 日本人工智能教育战略的研究与分析[J]. 中国教育信息化, 2022, 28(6): 29-37.
|
|
GONG C, WANG J. Research and analysis of AI education strategy in Japan[J]. Chinese journal of ICT in education, 2022, 28(6): 29-37.
|
| [12] |
康乐, 姚凯博. 日本人工智能教育战略行动述评[J]. 世界教育信息, 2022, 35(6): 37-44.
|
|
KANG L, YAO K B. Review of strategic actions of artificial intelligence education in Japan[J]. Journal of world education, 2022, 35(6): 37-44.
|
| [13] |
日本内阁府. 人間中心のAI社会原則[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. .
|
| [14] |
日本内阁府. AIに関する暫定的な論点整理[EB/OL]. [2025-01-17]. .
|
| [15] |
日本文部科学省. 数理・データサイエンス・AI(リテラシーレベル)モデルカリキュラム[EB/OL]. [2025-01-17]. .
|
| [16] |
LONG D R, MAGERKO B. What is AI literacy? Competencies and design considerations[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Honolulu HI USA. ACM, 2020: 1-16.
|
| [17] |
NG D T K, LEUNG J K L, CHU S K W, et al. Conceptualizing AI literacy: An exploratory review[J]. Computers and education: Artificial intelligence, 2021, 2: 100041.
|
| [18] |
CHEE H, AHN S, LEE J. A competency framework for AI literacy: Variations by different learner groups and an implied learning pathway[EB/OL]. [2025-01-31]. .
|
| [19] |
吴丹, 孙昕玦. 以人为本的人工智能素养教育探究: UNESCO教师和学生人工智能能力框架的解读与启示[J]. 农业图书情报学报, 2024, 36(8): 4-19.
|
|
WU D, SUN X J. Exploring human-centered AI literacy education: Interpretation and insights from UNESCO's AI competency framework for teachers and students[J]. Journal of library and information science in agriculture, 2024, 36(8): 4-19.
|
| [20] |
UNESCO. AI competency framework for students[EB/OL] [2025-01-22]. .
|
| [21] |
张银荣, 杨刚, 徐佳艳, 等. 人工智能素养模型构建及其实施路径[J]. 现代教育技术, 2022, 32(3): 42-50.
|
|
ZHANG Y R, YANG G, XU J Y, et al. The cultivation of AI literacy model and its implementation path[J]. Modern educational technology, 2022, 32(3): 42-50.
|
| [22] |
杨鸿武, 张笛, 郭威彤. STEM背景下人工智能素养框架的研究[J]. 电化教育研究, 2022, 43(4): 26-32.
|
|
YANG H W, ZHANG D, GUO W T. A study of literacy framework of artificial intelligence in STEM context[J]. E-education research, 2022, 43(4): 26-32.
|
| [23] |
日本文部科学省. 認定・選定校一覧[EB/OL]. [2025-01-28]. .
|
| [24] |
北陆大学. 数理・データサイエンス・AI教育プログラム取組紹介[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. .
|
| [25] |
北陆大学. AIとデータサイエンスで未来のリーダー育成[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. .
|
| [26] |
和歌山大学. 数理・データサイエンス・AI教育プログラム取組紹介[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. .
|
| [27] |
和歌山大学. 和歌山大学の数理・データサイエンス・AI教育プログラム~実践的教育を軸とした文理隔たりのない体系的な取組み~[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. .
|
| [28] |
千叶大学情报战略机构数据科学部门. リテラシーレベル数理・データサイエンス教育プログラム[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. .
|
| [29] |
千叶大学. 数理・データサイエンス・AI教育プログラム取組紹介[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. .
|
| [30] |
关西大学. 数理・データサイエンス・AI教育プログラム取組紹介[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. .
|
| [31] |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 国务院关于印发新一代人工智能发展规划的通知[EB/OL]. [2025-01-08]. .
|
| [32] |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 教育部关于印发《高等学校人工智能创新行动计划》的通知[EB/OL]. [2025-01-08]. .
|
| [33] |
浙江大学. 全文来啦!《大学生人工智能素养红皮书(2024版)》中文版全文发布[EB/OL]. [2025-01-24]. .
|
| [34] |
南京大学. 南京大学发布人工智能通识核心课方案[EB/OL]. [2025-01-08]. .
|
| [35] |
北京市教育委员会. 北京市教育委员会召开北京市属高校人工智能通识课工作部署会[EB/OL]. [2025-01-08]. .
|
| [36] |
沈阳师范大学. 审核评估进行时 | 创新“产学研融合”教育模式, 打破传统界限[EB/OL]. [2025-01-08]. .
|
| [37] |
武汉大学图书馆. 数字素养培训最新培训计划[EB/OL]. [2025-01-24]. .
|