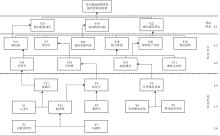
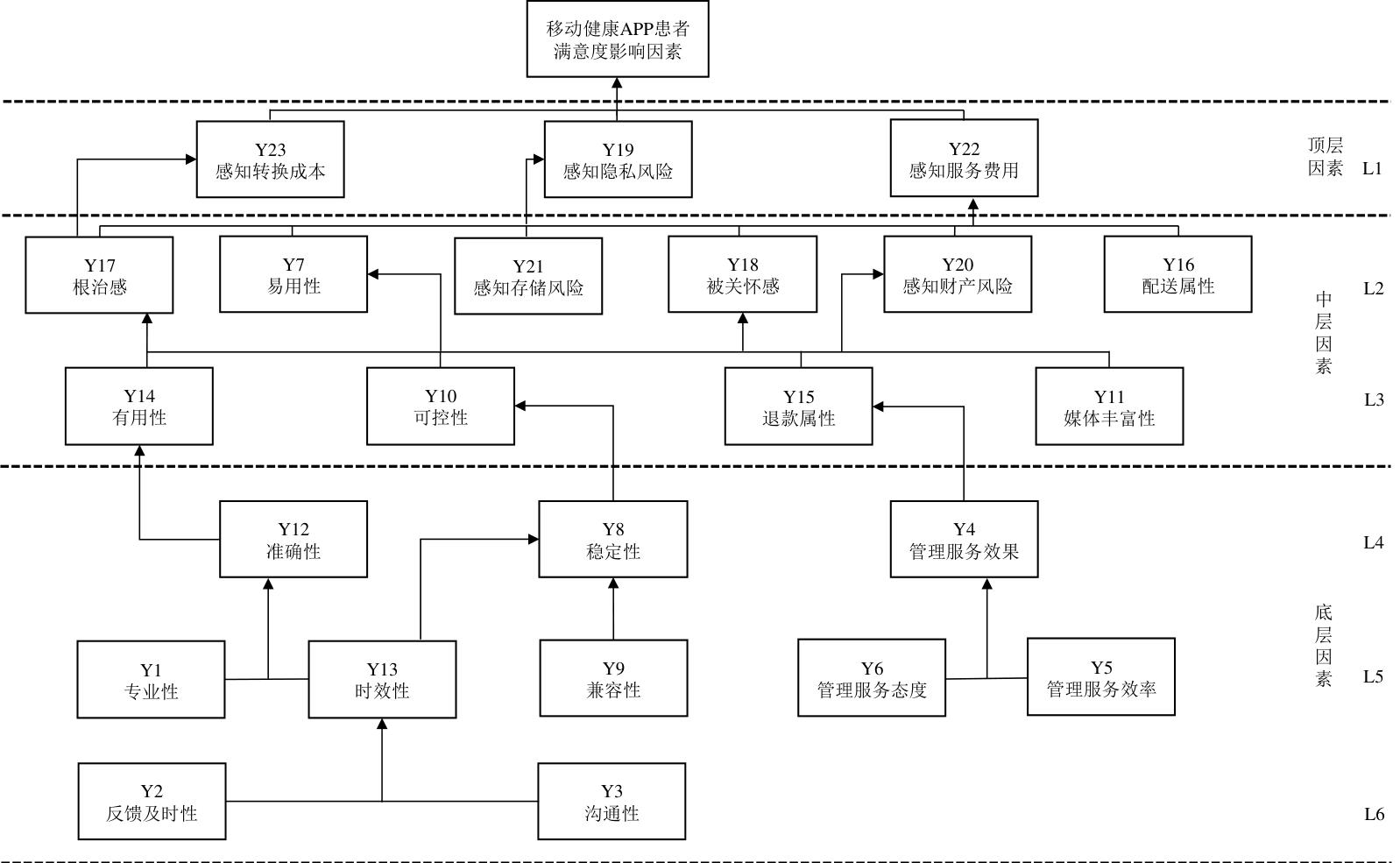
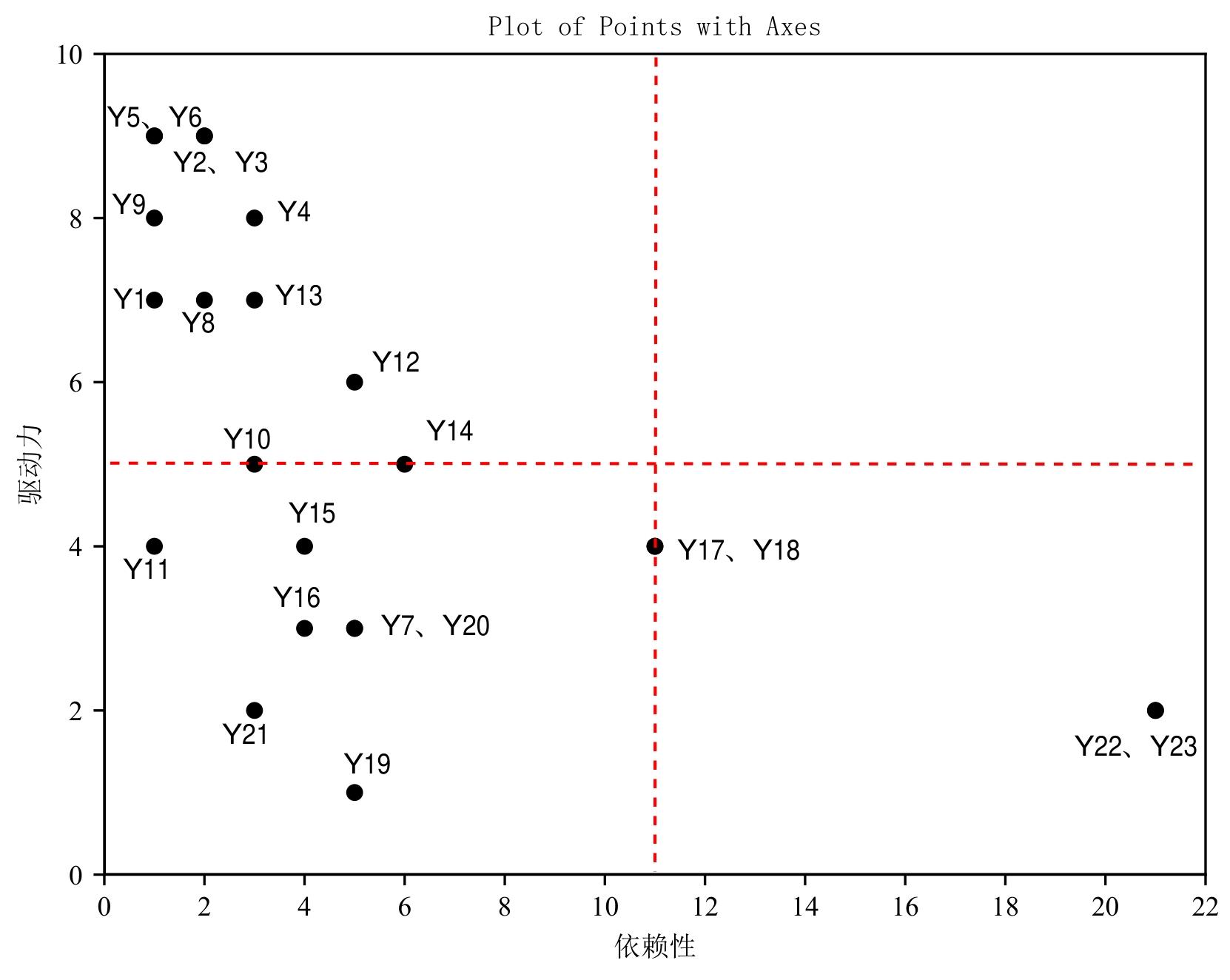
| 1 |
中国互联网络信息中心. 第53 次《中国互联网络发展状况统计报告》发布[EB/OL]. [2024⁃02⁃22]. .
|
| 2 |
YAN M, FILIERI R, RAGUSEO E, et al. Mobile apps for healthy living: Factors influencing continuance intention for health apps[J]. Technological forecasting and social change, 2021, 166: 120644.
|
| 3 |
SHEN X L, LI Y J, SUN Y Q. Wearable health information systems intermittent discontinuance[J]. Industrial management & data systems, 2018, 118(3): 506-523.
|
| 4 |
AKTER S, D'AMBRA J, RAY P, et al. Modelling the impact of mHealth service quality on satisfaction, continuance and quality of life[J]. Behaviour & information technology, 2013, 32(12): 1225-1241.
|
| 5 |
金燕, 李京珂, 耿瑞利. 隐私视角下健康类APP用户流失意愿研究[J]. 现代情报, 2021, 41(1): 67-77.
|
|
JIN Y, LI J, GENG R L. Research on the churn intention of health APP users from the perspective of privacy[J]. Journal of modern information, 2021, 41(1): 67-77.
|
| 6 |
吴大伟, 胡小飞, 赵宇翔, 等. 感知价值视角下数字健康APP用户持续采纳意愿的影响因素及路径研究: 基于fsQCA方法[J]. 图书情报工作, 2021, 65(18): 93-104.
|
|
WU D W, HU X F, ZHAO Y X, et al. Research on influencing factors and path of users' continuous adoption intention of digital health apps from the perspective of perceived value: Based on fsQCA[J]. Library and information service, 2021, 65(18): 93-104.
|
| 7 |
WANG Y W, COLLINS W B. Systematic evaluation of mobile fitness apps: Apps as the Tutor, Recorder, Game Companion, and Cheerleader[J]. Telematics and informatics, 2021, 59: 101552.
|
| 8 |
GRUNDY Q. A review of the quality and impact of mobile health apps[J]. Annual review of public health, 2022, 43: 117-134.
|
| 9 |
王萍, 陈玮, 龙秋易, 等. 基于评论和更新日志数据匹配的健康类APP与用户交互模式研究[J/OL]. 情报科学, 2024: 1-25. .
|
|
WANG P, CHEN W, LONG Q Y, et al. Research on interaction mode between health APP and users based on data matching of comments and update logs[J/OL]. Information science, 2024: 1-25. .
|
| 10 |
林伟振, 刘洪伟, 陈燕君, 等. 基于在线评论的顾客满意度研究——以健康监测穿戴产品为例[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2023, 7(5): 145-154.
|
|
LIN W Z, LIU H W, CHEN Y J, et al. Customer satisfaction modelling for healthcare wearable devices through online reviews[J]. Data analysis and knowledge discovery, 2023, 7(5): 145-154.
|
| 11 |
谢娟, 李文文, 沈鸿权, 等. 信息爆炸和信息不确定语境下的可信度判据研究: 以COVID-19疫情为例[J]. 情报学报, 2021, 40(7): 714-724.
|
|
XIE J, LI W W, SHEN H Q, et al. Study on the criteria of information credibility in the context of information explosion and uncertainty: The case of COVID-19[J]. Journal of the China society for scientific and technical information, 2021, 40(7): 714-724.
|
| 12 |
杨克虎, 李秀霞. 循证卫生决策研究方法与实践[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023.
|
|
YANG K H, LI X X. Research methods and practice of evidence-based health decision-making[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2023.
|
| 13 |
袁静, 郭玲玉. 在线健康社区用户非持续使用行为影响因素分析[J]. 现代情报, 2022, 42(2): 81-93.
|
|
YUAN J, GUO L Y. Influencing factors analysis of discontinuous use behaviors of users on online health communities[J]. Journal of modern information, 2022, 42(2): 81-93.
|
| 14 |
王辉, 王晓玉, 顾东晓, 等. 在线健康社区重大慢病患者负面评论倾向的关键影响因素分析[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42 (6): 12-20, 28.
|
|
WANG H, WANG X Y, GU D X, et al. Analysis on the key influencing factors of negative comment tendency of patients with major chronic diseases in online health community[J]. Information Science, 2024, 42 (6): 12-20, 28.
|
| 15 |
陈雨, 杨滨, 邓嵘. 感知价值视角下移动医疗问诊系统设计评价与优化[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2024, 44(5): 105-114.
|
|
CHEN Y, YANG B, DENG R. Evaluation and optimization of mobile medical consultation system design from a perceived value perspective[J]. Library tribune, 2024, 44(5): 105-114.
|
| 16 |
杨克虎, 沙勇忠, 魏志鹏. 循证社会科学总论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024.
|
|
YANG K H, SHA Y Z, WEI Z P. Overview of evidence-based social science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2024.
|
| 17 |
翟运开, 张倩, 赵栋祥. 疫情防控常态化下患者双渠道就诊满意度影响因素研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2022, 66(3): 118-129.
|
|
ZHAI Y K, ZHANG Q, ZHAO D X. Research on influencing factors of patient satisfaction with dual-channel medical treatment under the normalization of epidemic prevention[J]. Library and information service, 2022, 66(3): 118-129.
|
| 18 |
YANG H L, GUO X T, WU T S. Exploring the influence of the online physician service delivery process on patient satisfaction[J]. Decision support systems, 2015, 78: 113-121.
|