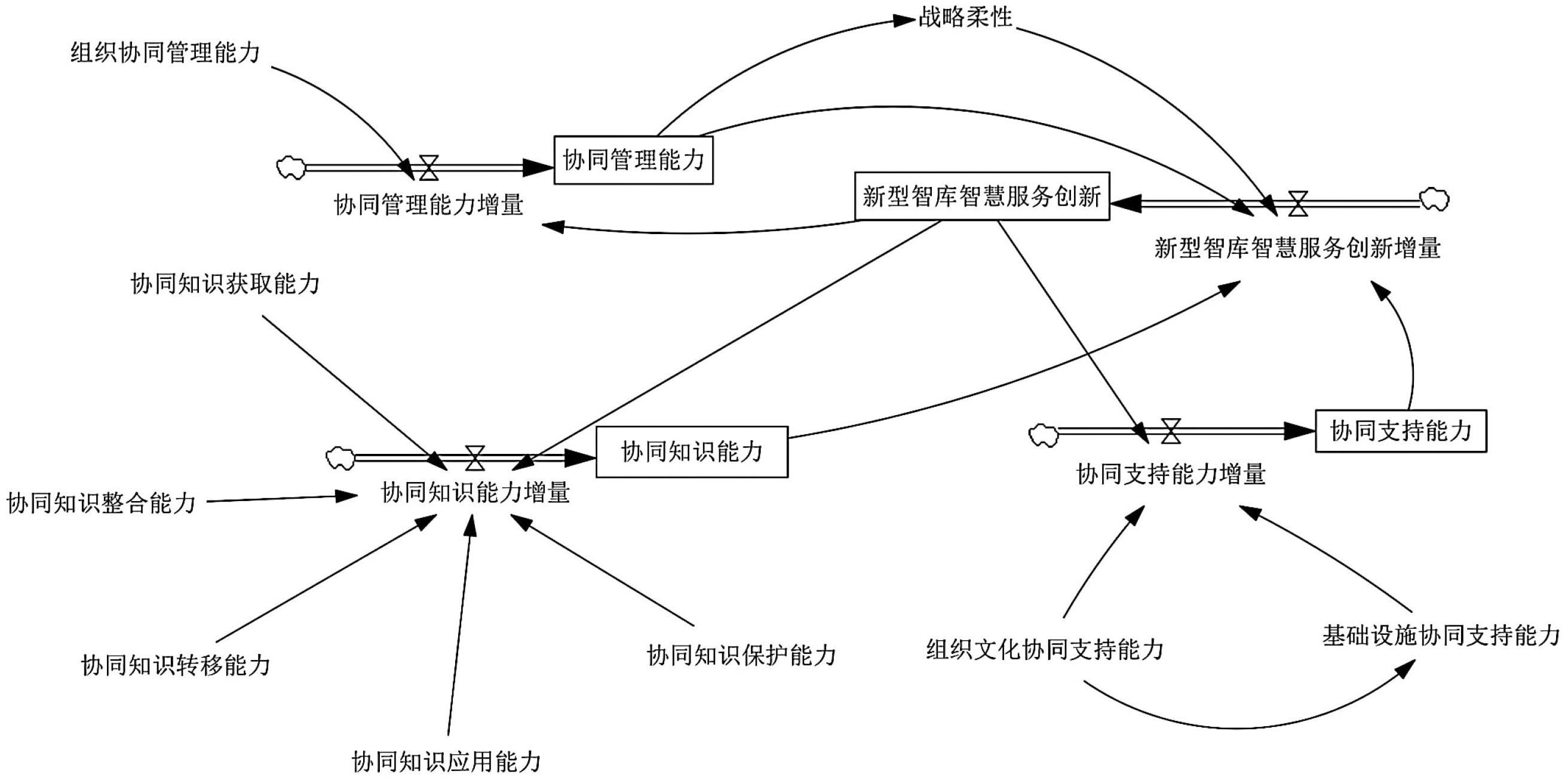
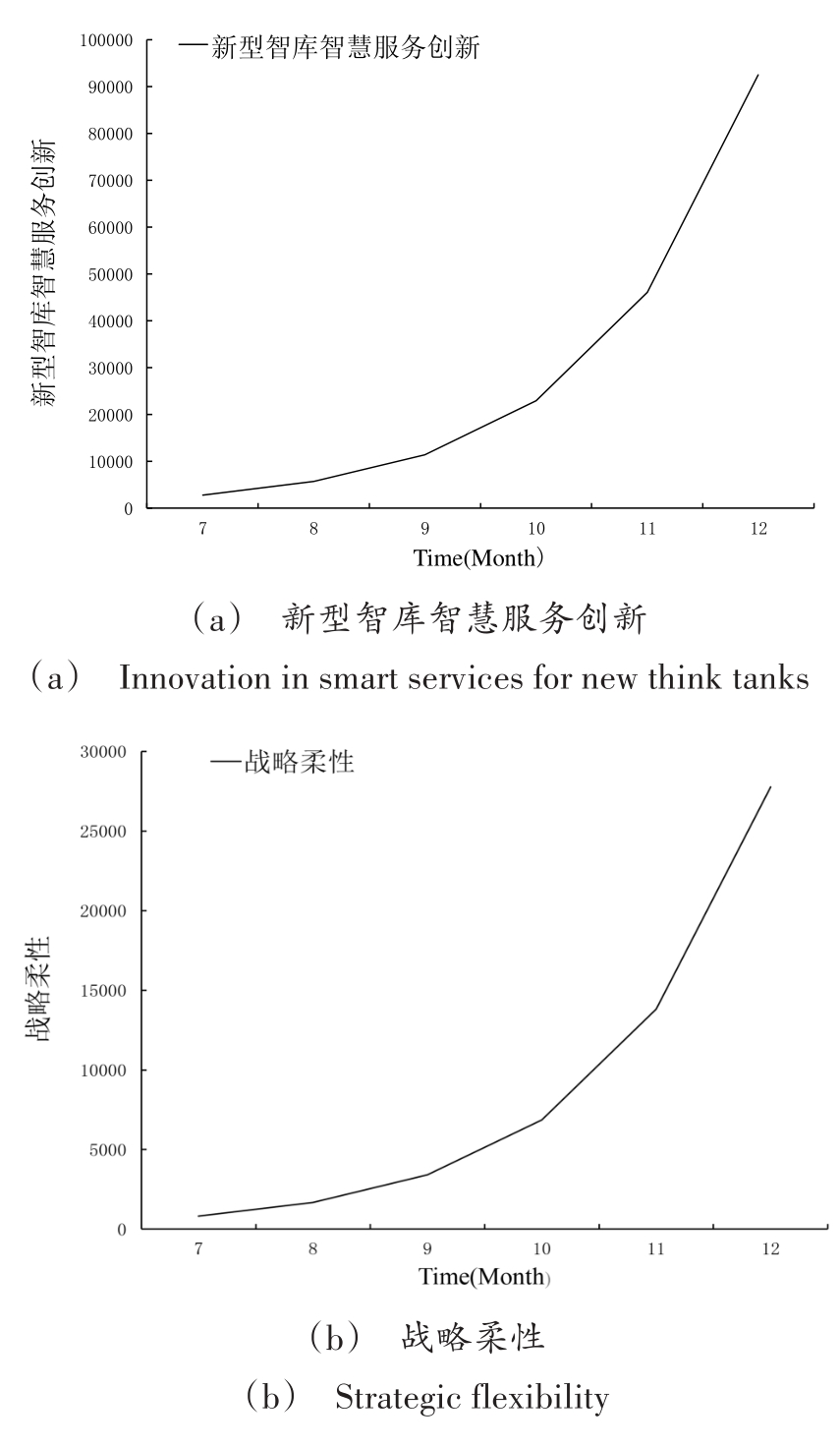
| 1 |
徐锐. 高校图书馆面向新型智库智慧服务的协同创新发展路径研究[J]. 绥化学院学报, 2021, 41(12): 134-137.
|
|
XU R. Research on the collaborative innovation development path of university library facing the smart service of new think tank[J]. Journal of Suihua university, 2021, 41(12): 134-137.
|
| 2 |
周湘智. 中国特色新型智库:出场逻辑、运作机理与基本范式[J]. 图书情报工作, 2021, 65(15): 51-60.
|
|
ZHOU X Z. New think tanks with Chinese characteristics: Appearance logic, operation mechanism and basic paradigm[J]. Library and information service, 2021, 65(15): 51-60.
|
| 3 |
朱波, 张姝末. 基于数据驱动的高校图书馆新型智库知识服务机制研究[J]. 图书馆学刊, 2019, 41(9): 80-83, 87.
|
|
ZHU B, ZHANG S M. Research on the knowledge service mechanism of new think tank in university library based on data-driven[J]. Journal of library science, 2019, 41(9): 80-83, 87.
|
| 4 |
蔡蓉英. 新型智库服务政府决策能力的提升策略研究[J]. 智库理论与实践, 2019, 4(4): 29-37.
|
|
CAI R Y. Research on the promotion strategy of new think tank service for government decision capabilities[J]. Think tank: Theory & practice, 2019, 4(4): 29-37.
|
| 5 |
李珗, 王宏起, 李长云. 云环境下区域科技资源共享平台智慧服务研究[J]. 学习与探索, 2015(7): 112-115.
|
|
LI Y, WANG H Q, LI C Y. Research on smart service of regional science and technology resources sharing platform in cloud environment[J]. Study & exploration, 2015(7): 112-115.
|
| 6 |
李强. 面向应急管理的图书馆新型智库智慧化服务模式研究[J]. 江苏科技信息, 2022, 39(21): 28-30.
|
|
LI Q. Research on intelligent service mode of new think tank in library for emergency management[J]. Jiangsu science & technology information, 2022, 39(21): 28-30.
|
| 7 |
李永先, 杨婷婷. 大数据环境下新型智库智慧服务体系研究[J]. 经济研究导刊, 2020(26): 142-144.
|
|
LI Y X, YANG T T. Research on smart service system of new think tank in big data environment[J]. Economic research guide, 2020(26): 142-144.
|
| 8 |
白阳, 张心怡. 汇聚想法: 数据驱动下的智库协同创新服务模式研究[J]. 情报科学, 2018, 36(7): 23-29.
|
|
BAI Y, ZHANG X Y. Gather ideas: Research on collaborative innovation service model of think tank driven by data[J]. Information science, 2018, 36(7): 23-29.
|
| 9 |
张心源, 赵蓉英, 邱均平. 面向决策的美国一流智库智慧产品生产流程研究[J]. 重庆大学学报(社会科学版), 2016, 22(2): 132-138.
|
|
ZHANG X Y, ZHAO R Y, QIU J P. Research on the producing-process of decision- oriented top think tanks' intelligence products of America[J]. Journal of Chongqing university (social science edition), 2016, 22(2): 132-138.
|
| 10 |
潘苏楠, 李北伟. 基于知识管理的地方智库创新生态系统构建及运行机制研究[J]. 情报资料工作, 2020, 41(2): 106-112.
|
|
PAN S N, LI B W. Research on the construction and operation mechanism of local think tank innovation ecosystem based on knowledge management[J]. Information and documentation services, 2020, 41(2): 106-112.
|
| 11 |
胡昌平, 晏浩. 知识管理活动创新性研究之协同知识管理[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2007, 33(3): 95-97.
|
|
HU C P, YAN H. Innovative research on knowledge management based on collaborative environment[J]. Journal of library science in
|
|
China, 2007, 33(3): 95-97.
|
| 12 |
王兴鹏, 崔明家. 面向多主体的应急知识协同管理体系构建[J]. 科技管理研究, 2020, 40(24): 192-197.
|
|
WANG X P, CUI M J. Construction of multi-agent oriented emergency knowledge collaborative management system[J]. Science and
|
|
technology management research, 2020, 40(24): 192-197.
|
| 13 |
吴金玉, 胡斌, 杨坤. 技术创新网络的一个知识协同模型: 共生理论与协同学的融合视角[J]. 科技管理研究, 2019, 39(4): 85-91.
|
|
WU J Y, HU B, YANG K. A knowledge collaboration model of technology innovation network: A perspective of integration of symbiosis theory and synergetics[J]. Science and technology management re-
|
|
search, 2019, 39(4): 85-91.
|
| 14 |
林晓欣. 信息组织4.0时代智慧化知识组织的知识协同服务[J]. 图书馆, 2021(2): 63-68.
|
|
LIN X X. Knowledge collaboration service of intelligent knowledge organization in the era of information organization 4.0[J]. Library, 2021(2): 63-68.
|
| 15 |
储节旺, 李振延. 图书馆大数据知识生态系统特征及构成研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2022, 45(2): 35-42.
|
|
CHU J W, LI Z Y. Study of the features and construction of big data knowledge ecosystem of libraries[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2022, 45(2): 35-42.
|
| 16 |
朱鹏. 协同创新中心组织管理体系构建研究——基于利益相关者视角[J]. 高教探索, 2013(3): 15-18.
|
|
ZHU P. Research on the construction of organizational management system of collaborative innovation center - Based on the perspective of stakeholders[J]. Higher education exploration, 2013(3): 15-18.
|
| 17 |
全利平, 蒋晓阳. 协同创新网络组织实现创新协同的路径选择[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2011, 28(9): 15-19.
|
|
QUAN L P, JIANG X Y. Path selection of collaborative innovation network organization to realize innovation collaboration[J]. Science & technology progress and policy, 2011, 28(9): 15-19.
|
| 18 |
宋姗姗, 季婉婧, 王金平. 智库知识协同体系构建研究[J]. 数字图书馆论坛, 2022(4): 67-72.
|
|
SONG S S, JI W J, WANG J P. Research on knowledge collaboration system construction of think tanks[J]. Digital library forum, 2022(4): 67-72.
|
| 19 |
陈静, 曾德明, 欧阳晓平. 基于探索式创新的知识整合能力对制造企业绩效的影响[J]. 系统管理学报, 2021, 30(4): 631-642.
|
|
CHEN J, ZENG D M, OUYANG X P. The impact of knowledge integration capability on the performance of manufacturing firms based on exploratory innovation[J]. Journal of systems & management, 2021, 30(4): 631-642.
|
| 20 |
何郁冰, 邹雅颖, 左霖锋. 技术多元化、组织间知识协同与企业创新持续性的关系[J]. 技术经济, 2021, 40(6): 47-58.
|
|
HE Y B, ZOU Y Y, ZUO L F. Research on the relationship between technology diversification, knowledge collaboration among organizations and the persistence of enterprise's innovation[J]. Journal of technology economics, 2021, 40(6): 47-58.
|
| 21 |
胡玮玮, 温廼. 知识转移能力体系的构建及其验证[J]. 商业经济与管理, 2018(4): 49-57.
|
|
HU W W, WEN N. Construction and verification of the knowledge transfer capability system[J]. Journal of business economics, 2018(4): 49-57.
|
| 22 |
宋伟, 张华伦, 曹镇东, 等. 知识流动视角下我国国家创新系统的演进历程[J]. 科技管理研究, 2013, 33(14): 6-9, 23.
|
|
SONG W, ZHANG H L, CAO Z D, et al. Evolution of national innovation system in China under knowledge flow perspective[J]. Science and technology management research, 2013, 33(14): 6-9, 23.
|
| 23 |
廖先玲, 陈颖, 姜秀娟, 等. 企业知识创新能力模型构建及其网络结构研究——知识流动视角[J]. 科技管理研究, 2020, 40(8): 210-217.
|
|
LIAO X L, CHEN Y, JIANG X J, et al. Research on the construction of enterprise knowledge innovation ability model and its network structure: Knowledge flow perspective[J]. Science and technology management research, 2020, 40(8): 210-217.
|
| 24 |
陈帅. 隐性知识显性化的风险及规避[J]. 科技管理研究, 2005, 25(7): 136-138.
|
|
CHEN S. Risks and avoidance of explicit tacit knowledge[J]. Science and technology management research, 2005, 25(7): 136-138.
|
| 25 |
朝乐门. Web2.0在组织知识管理中的应用研究[J]. 情报资料工作, 2010(2): 49-52.
|
|
CHAO L M. On the application of web 2.0 in knowledge management of organizations[J]. Information and documentation services, 2010(2): 49-52.
|
| 26 |
李颖明, 王晓莞, 田园, 等. 基于双螺旋理论的智库项目管理研 究[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(12): 1482-1489.
|
|
LI Y M, WANG X W, TIAN Y, et al. Management of think tank research project based on double Helix structure theory[J]. Bulletin of Chinese academy of sciences, 2020, 35(12): 1482-1489.
|
| 27 |
王文华, 张卓, 蔡瑞林. 开放式创新组织间协同管理影响知识协同效应研究[J]. 研究与发展管理, 2018, 30(5): 38-48.
|
|
WANG W H, ZHANG Z, CAI R L. Knowledge synergy effect of
|
|
inter-organizational synergy management with open innovation[J]. R&D management, 2018, 30(5): 38-48.
|
| 28 |
孟添天, 柴菁敏, 郑敏钰. 知识异质性对研发团队创造力的影响——知识整合能力的中介作用和主观关系体验的调节作用[J]. 技术经济与管理研究, 2022(4): 41-45.
|
|
MENG T T, CHAI J M, ZHENG M Y. The influence of knowledge heterogeneity on team creativity: The mediating role of knowledge integration ability and the moderating role of subjective relationship experience[J]. Journal of technical economics & management, 2022(4): 41-45.
|
| 29 |
赵文丽, 叶广宇, 闫妍. 企业国际化过程中知识能力形成与提升路径研究[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2023, 40(1): 131-141.
|
|
ZHAO W L, YE G Y, YAN Y. The formation and promotion path of knowledge capability in the process of enterprise internationalization[J]. Science & technology progress and policy, 2023, 40(1): 131-141.
|
| 30 |
张振鹏. 企业管理创新影响因素与过程机制:研究综述及整合模型[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2021, 38(20): 154-160.
|
|
ZHANG Z P. Influencing factors and process mechanism of enterprise management innovation: Research review and integration model[J]. Science & technology progress and policy, 2021, 38(20): 154-160.
|
| 31 |
黄晓斌, 张明鑫. 新技术环境下的智库情报服务创新研究[J]. 图 书与情报, 2020(1): 112-119.
|
|
HUANG X B, ZHANG M X. Innovations of think tank information services in new technological environment[J]. Library & information, 2020(1): 112-119.
|
| 32 |
安萌. 知识密集型服务业合作创新的博弈分析[J]. 鲁东大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2010, 27(1): 79-82.
|
|
AN M. Game analysis of cooperative innovation in knowledge-intensive service industry[J]. Ludong university journal (philosophy and social sciences edition), 2010, 27(1): 79-82.
|
| 33 |
张志强, 苏娜. 国际智库发展趋势特点与我国新型智库建设[J]. 智库理论与实践, 2016, 1(1): 9-23.
|
|
ZHANG Z Q, SU N. Trends and characteristics of global think tanks and suggestions for Chinese think tanks construction[J]. Think tank: Theory & practice, 2016, 1(1): 9-23.
|