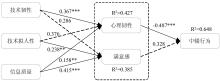
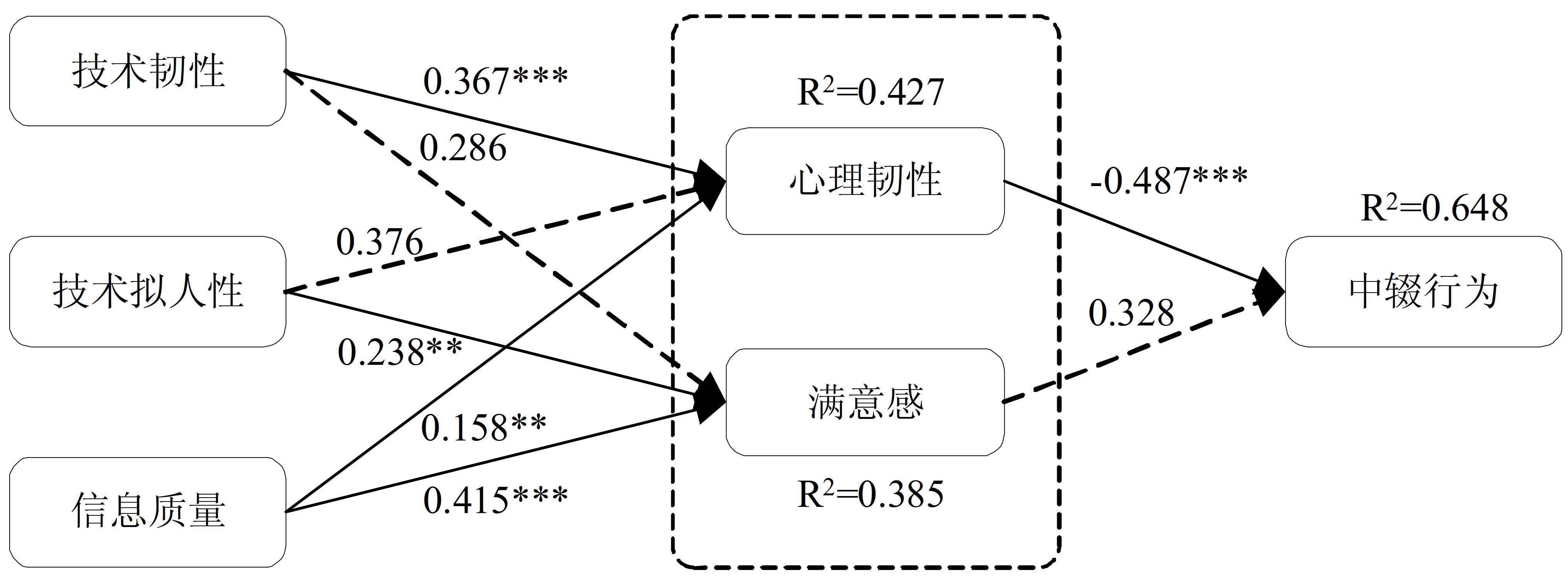
| 1 |
周渊. 我国数字经济规模超50万亿元[N]. 文汇报, 2024-01-06(1).
|
| 2 |
盛玉雷. 抢抓机遇, 加快发展数字经济[N]. 人民日报, 2024-01-18(6).
|
| 3 |
国家互联网信息办公室. 生成式人工智能服务管理暂行办法[EB/OL]. [2023-12-19].
|
| 4 |
吴清. ChatGPT热度下滑OpenAI推安卓版“续热”[N]. 中国经营报, 2023-07-31(0).
|
| 5 |
HUANG S, GRADY P. Generative AI act two[EB/OL]. [2023-10-20].
|
| 6 |
张敏, 孟蝶, 张艳. 社交网络用户间歇性中辍行为关键问题研究综述[J]. 图书情报工作, 2019, 63(21): 128-136.
|
|
ZHANG M, MENG D, ZHANG Y. Review of the research on the key issues of social network users' intermittently discontinuous behavior[J]. Library and information service, 2019, 63(21): 128-136.
|
| 7 |
HARRISON M. ChatGPT's explosive popularity makes it the fastest-growing app in human history[EB/OL]. [2023-02-05].
|
| 8 |
中国信息通信研究院, 京东探索研究院. 人工智能生成内容(AIGC)白皮书(2022)[EB/OL]. [2023-05-02].
|
|
China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, JD Explore Academy. Artificial intelligence generated content (AIGC) whitepaper (2022)[EB/OL]. [2023-05-02].
|
| 9 |
腾讯研究院. AIGC发展趋势报告2023:迎接人工智能的下一个时代[EB/OL]. [2023-05-02].
|
|
Tencent Research Institute. AIGC development trends report 2023: Embracing the next era of artificial intelligence[EB/OL].[2023-05-02].
|
| 10 |
Infographic: Generative AI explained by AI[EB/OL]. [2023-05-02].
|
| 11 |
BRIGHT L F, KLEISER S B, GRAU S L. Too much Facebook? An exploratory examination of social media fatigue[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2015, 44: 148-155.
|
| 12 |
张敏, 孟蝶, 张艳. 逃离还是回归? ——用户社交网络间歇性中辍行为实证研究的影响因素综述[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2019, 39(6): 43-52.
|
|
ZHANG M, MENG D, ZHANG Y. Escape or return? - A review of factors influencing users' intermittent discontinuance behavior in social networks from empirical studies[J]. Library tribune, 2019, 39(6): 43-52.
|
| 13 |
TUREL O. Untangling the complex role of guilt in rational decisions to discontinue the use of a hedonic information system[J]. European journal of information systems, 2016, 25(5): 432-447.
|
| 14 |
张玥, 李青宇, 刘雨琪, 等. 组态视角下AIGC应用平台用户中辍行为影响因素研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(3): 130-137, 148.
|
|
ZHANG Y, LI Q Y, LIU Y Q, et al. A Study on discontinuance behavior in the AIGC application platform based on the perspective of configuration[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2024, 47(3): 130-137, 148.
|
| 15 |
刘鲁川, 李旭, 张冰倩. 基于扎根理论的社交媒体用户倦怠与消极使用研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2017, 40(12): 100-106, 51.
|
|
LIU L C, LI X, ZHANG B Q. Research on social media fatigue and passive behaviors of users based on grounded theory[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2017, 40(12): 100-106, 51.
|
| 16 |
LEE A R, SON S M, KIM K K. Information and communication technology overload and social networking service fatigue: A stress perspective[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2016, 55: 51-61.
|
| 17 |
郭佳, 曹芬芳. 倦怠视角下社交媒体用户不持续使用意愿研究[J]. 情报科学, 2018, 36(9): 77-81.
|
|
GUO J, CAO F F. Research on users' discontinuous usage intention in SNS from fatigue perspective[J]. Information science, 2018, 36(9): 77-81.
|
| 18 |
张敏, 薛云霄, 罗梅芬, 等. 移动社交网络用户间歇性中辍行为形成机理的概念模型——一项基于扎根理论的探索性研究[J]. 情报资料工作, 2019, 40(4): 84-90.
|
|
ZHANG M, XUE Y X, LUO M F, et al. A conceptual model for the formation mechanism of intermittent lieutenant behavior of mobile social network users: An exploratory study based on grounded theory[J]. Information and documentation services, 2019, 40(4): 84-90.
|
| 19 |
甘春梅, 肖晨, 陈舒意, 等. 消极情感对社交网络用户间歇性中辍行为的影响机理: 基于一项混合研究[J]. 信息资源管理学报, 2023, 13(6): 125-132.
|
|
GAN C M, XIAO C, CHEN S Y, et al. Effects of negative emotions on user intermittent discontinuance behavior of social networking services: Empirical evidence from a mixed study[J]. Journal of information resources management, 2023, 13(6): 125-132.
|
| 20 |
林炳炯. 以情绪为中介的社会比较与中辍行为研究[D]. 上海: 上海外国语大学, 2023.
|
|
LIN B J. Social comparison mediated by emotion and study on quitting behavior[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai International Studies University, 2023.
|
| 21 |
YUAN S B, LIU L, SU B D, et al. Determining the antecedents of mobile payment loyalty: Cognitive and affective perspectives[J]. Electronic commerce research and applications, 2020, 41: 100971.
|
| 22 |
邹纯龙, 马海群, 王今. 韧性视角下高新技术产业情报保障体系研究[J]. 现代情报, 2022, 42(12): 62-72.
|
|
ZOU C L, MA H Q, WANG J. Research on the intelligence assurance system of high-tech industry from the resilience perspective[J]. Journal of modern information, 2022, 42(12): 62-72.
|
| 23 |
KLEIN R J T, NICHOLLS R J, THOMALLA F. Resilience to natural hazards: How useful is this concept?[J]. Environmental hazards, 2003, 5(1): 35-45.
|
| 24 |
HOLLING C S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems[J]. Annual review of ecology and systematics, 1973, 4: 1-23.
|
| 25 |
袁玮玮, 张兴慧, 孟珂冰, 等. 家庭功能对大学生生活满意度的影响: 生命意义与心理韧性的链式中介效应[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2024, 32(4): 498-502.
|
|
YUAN W W, ZHANG X H, MENG K B, et al. Influence of family function on college students' life satisfaction: The chain mediating effect of meaning of life and psychological resilience[J]. China journal of health psychology, 2024, 32(4): 498-502.
|
| 26 |
安树伟, 黄艳. 突发公共卫生事件对区域经济韧性的影响机制与应对: 来自中国新冠病毒感染疫情的证据[J]. 中国软科学, 2024(1): 76-85.
|
|
AN S W, HUANG Y. Impact mechanism of public health emergencies on regional economic resilience and its response: Evidence from the COVID-19 in China[J]. China soft science, 2024(1): 76-85.
|
| 27 |
傅利平, 何兰萍. 以韧性社区建设提升基层治理现代化水平[J]. 国家治理, 2021(45): 34-37.
|
| 28 |
栾宇, 张海涛, 李依霖, 等. 基于韧性理论的突发事件情报决策体系研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(3): 95-103.
|
|
LUAN Y, ZHANG H T, LI Y L, et al. Research on emergency intelligence decision-making system based on resilience theory[J]. Information studies:Theory & application, 2024, 47(3): 95-103.
|
| 29 |
包鑫, 柯平. 图书馆赋能社区韧性: 国外经验与启示[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2023, 43(11): 120-129.
|
|
BAO X, KE P. Community resilience empowered by libraries: Foreign experience and enlightenment[J]. Library tribune, 2023, 43(11): 120-129.
|
| 30 |
BELK R W. Situational variables and consumer behavior[J]. Journal of consumer research, 1975, 2(3): 157-164.
|
| 31 |
PARK M, LENNON S J. Brand name and promotion in online shopping contexts[J]. Journal of fashion marketing and management, 2009, 13(2): 149-160.
|
| 32 |
徐孝娟, 赵宇翔, 吴曼丽, 等. S-O-R理论视角下的社交网站用户流失行为实证研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2017, 36(7): 188-194.
|
|
XU X J, ZHAO Y X, WU M L, et al. The empirical research of user exodus in social network based on the stimuli-organism-response theory[J]. Journal of intelligence, 2017, 36(7): 188-194.
|
| 33 |
张海. 基于扎根理论的网络用户信息茧房形成机制的质性研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2021, 40(3): 168-174.
|
|
ZHANG H. A qualitative study on the formation mechanism of internet users' information cocoons based on grounded theory[J]. Journal of intelligence, 2021, 40(3): 168-174.
|
| 34 |
黄冬梅. 心理韧性的耗散结构系统解读[J]. 自然辩证法研究, 2019, 35(12): 117-120.
|
|
HUANG D M. The interpretation of resilience with dissipative structure system[J]. Studies in dialectics of nature, 2019, 35(12): 117-120.
|
| 35 |
张秀娥, 李梦莹. 创业韧性的驱动因素及其对创业成功的影响研究[J]. 外国经济与管理, 2020, 42(8): 96-108.
|
|
ZHANG X E, LI M Y. Research on the driving factors of entrepreneurial resilience and its influence on entrepreneurial success[J]. Foreign economics & management, 2020, 42(8): 96-108.
|
| 36 |
彭莉, 徐翠荣. 积极心理学对护士职业倦怠感影响的应用研究进展[J]. 职业与健康, 2023, 39(23): 3308-3312.
|
|
PENG L, XU C R. Research progress in the application of positive psychology on the impact of nurses' job burnout[J]. Occupation and health, 2023, 39(23): 3308-3312.
|
| 37 |
徐孝娟. 基于S-O-R理论的社交网站用户流失研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015.
|
|
XU X J. Research on user loss of social networking sites based on S-O-R theory[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015.
|
| 38 |
李娟娟. 认知视域下社会化问答社区用户知识采纳行为的影响因素研究[D]. 曲阜: 曲阜师范大学, 2022.
|
|
LI J J. A study on the influencing factors of knowledge adoption behavior of social Q&A community users from the cognitive perspective[D]. Qufu: Qufu Normal University, 2022.
|
| 39 |
唐文龙, 孙锐. 聊天机器人犯错类型与拟人化程度对用户报复性负面口碑的交互作用——愤怒情绪的中介效应[J]. 管理现代化, 2023, 43(1): 148-156.
|
|
TANG W L, SUN R. Interaction between chat bots' error types and personification degree on users' retaliatory negative word-of-mouth - Mediating effect of anger[J]. Modernization of management, 2023, 43(1): 148-156.
|
| 40 |
王晰巍, 罗然, 刘宇桐, 等. 智慧图书馆在线聊天机器人使用行为影响因素及实证研究[J]. 情报学报, 2023, 42(2): 217-230.
|
|
WANG X W, LUO R, LIU Y T, et al. Influencing factors and empirical research on the usage behavior of smart library online chatbots[J]. Journal of the China society for scientific and technical information, 2023, 42(2): 217-230.
|
| 41 |
张海, 袁顺波, 段荟. 基于S-O-R理论的移动政务APP用户使用意愿影响因素研究[J]. 情报科学, 2019, 37(6): 126-132.
|
|
ZHANG H, YUAN S B, DUAN H. Influencing factors of mobile government app users' intention based on S-O-R theory[J]. Information science, 2019, 37(6): 126-132.
|
| 42 |
张海, 刘畅, 王东波, 等. ChatGPT用户使用意愿影响因素研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2023, 46(4): 15-22.
|
|
ZHANG H, LIU C, WANG D B, et al. Research on the influencing factors of ChatGPT users' intention[J]. Information studies: Theory & application, 2023, 46(4): 15-22.
|
| 43 |
倪士光, 胡子卉, 林煜东. 科技更向善: 基于数字交互技术的青少年心理韧性培育[J]. 西北师大学报(社会科学版), 2024, 61(2): 100-114.
|
|
NI S G, HU Z H, LIN Y D. Cultivation of adolescent psychological resilience based on digital interaction technology: A literature review[J]. Journal of northwest normal university (social sciences), 2024, 61(2): 100-114.
|
| 44 |
陈智. 韧性视角下ChatGPT应用的技术特性、演化过程与治理方略[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2023, 40(23): 111-120.
|
|
CHEN Z. The technological characteristics, evolution process, and governance strategy of ChatGPT applications from the perspective of resilience[J]. Science & technology progress and policy, 2023, 40(23): 111-120.
|